图遍历介绍:
所谓图的遍历,即是对结点的访问。一个图有那么多个结点,如何遍历这些结点,需要特定策略,一般有两种访问策略: (1)深度优先遍历 (2)广度优先遍历
1.图的深度优先遍历介绍
1.1.深度优先遍历基本思想
图的深度优先搜索(Depth First Search)
- 深度优先遍历,从初始访问结点出发,初始访问结点可能有多个邻接结点,深度优先遍历的策略就是首先访问第一个邻接结点,然后再以这个被访问的邻接结点作为初始结点,访问它的第一个邻接结点, 可以这样理解:每次都在访问完当前结点后首先访问当前结点的第一个邻接结点。
- 我们可以看到,这样的访问策略是优先往纵向挖掘深入,而不是对一个结点的所有邻接结点进行横向访问。
- 显然,深度优先搜索是一个递归的过程
1.2.深度优先遍历算法步骤
- 访问初始结点 v,并标记结点 v 为已访问。
- 查找结点 v 的第一个邻接结点 w。
- 若 w 存在,则继续执行 4,如果 w 不存在,则回到第 1 步,将从 v 的下一个结点继续。
- 若 w 未被访问,对 w 进行深度优先遍历递归(即把 w 当做另一个 v,然后进行步骤 123)。
- 查找结点 v 的 w 邻接结点的下一个邻接结点,转到步骤 3。
- 分析图
1.3.深度优先算法的代码实现
//核心代码
//深度优先遍历算法
//i 第一次就是 0
private void dfs(boolean[] isVisited, int i) {
//首先我们访问该结点,输出
System.out.print(getValueByIndex(i) + "->");
//将结点设置为已经访问
isVisited[i] = true;
//查找结点 i 的第一个邻接结点 w
int w = getFirstNeighbor(i);
while(w != -1) {//说明有
if(!isVisited[w]) {
dfs(isVisited, w);
}
//如果 w 结点已经被访问过
w = getNextNeighbor(i, w);
}
}
//对 dfs 进行一个重载, 遍历我们所有的结点,并进行 dfs
public void dfs() {
isVisited = new boolean[vertexList.size()];
//遍历所有的结点,进行 dfs[回溯]
for(int i = 0; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) {
if(!isVisited[i]) {
dfs(isVisited, i);
}
}
}
2.图的广度优先遍历
2.1.广度优先遍历基本思想
- 图的广度优先搜索(Broad First Search)
- 类似于一个 分层搜索的过程,广度优先遍历需要使用一个队列以保持访问过的结点的顺序,以便按这个顺序来访问这些结点的邻接结点
2.2.广度优先遍历算法步骤
- 访问初始结点 v 并标记结点 v 为已访问。
- 结点 v 入队列
- 当队列非空时,继续执行,否则算法结束。
- 出队列,取得队头结点 u
- 查找结点 u 的第一个邻接结点 w
- 若结点 u 的邻接结点 w 不存在,则转到步骤 3;否则循环执行以下三个步骤:
6.1 若结点 w 尚未被访问,则访问结点 w 并标记为已访问。
6.2 结点 w 入队列
6.3 查找结点 u 的继 w 邻接结点后的下一个邻接结点 w,转到步骤 6。
2.3.广度优先算法的图示
2.4.广度优先算法的代码实现
//对一个结点进行广度优先遍历的方法
private void bfs(boolean[] isVisited, int i) {
int u ; // 表示队列的头结点对应下标
int w ; // 邻接结点 w
//队列,记录结点访问的顺序
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList();
//访问结点,输出结点信息
System.out.print(getValueByIndex(i) + "=>");
//标记为已访问
isVisited[i] = true;
//将结点加入队列
queue.addLast(i);
while( !queue.isEmpty()) {
//取出队列的头结点下标
u = (Integer)queue.removeFirst();
//得到第一个邻接结点的下标 w
w = getFirstNeighbor(u);
while(w != -1) {//找到
//是否访问过
if(!isVisited[w]) {
System.out.print(getValueByIndex(w) + "=>");
//标记已经访问
isVisited[w] = true;
//入队
queue.addLast(w);
}
//以 u 为前驱点,找 w 后面的下一个邻结点
w = getNextNeighbor(u, w); //体现出我们的广度优先
}
}
}
//遍历所有的结点,都进行广度优先搜索
public void bfs() {
isVisited = new boolean[vertexList.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) {
if(!isVisited[i]) {
bfs(isVisited, i);
}
}
}
3.图的代码汇总(韩老师)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Graph {
private ArrayList<String> vertexList; //存储顶点集合
private int[][] edges; //存储图对应的邻结矩阵
private int numOfEdges; //表示边的数目
//定义给数组 boolean[], 记录某个结点是否被访问
private boolean[] isVisited;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试一把图是否创建 ok
int n = 8; //结点的个数
//String Vertexs[] = {"A", "B", "C", "D", "E"};
String Vertexs[] = {"1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8"};
//创建图对象
Graph graph = new Graph(n);
//循环的添加顶点
for (String vertex : Vertexs) {
graph.insertVertex(vertex);
}
//添加边
//A-BA-C B-C B-D B-E
// graph.insertEdge(0, 1, 1); //A-B
// graph.insertEdge(0, 2, 1); //
// graph.insertEdge(1, 2, 1); //
// graph.insertEdge(1, 3, 1); //
// graph.insertEdge(1, 4, 1); //
//更新边的关系
graph.insertEdge(0, 1, 1);
graph.insertEdge(0, 2, 1);
graph.insertEdge(1, 3, 1);
graph.insertEdge(1, 4, 1);
graph.insertEdge(3, 7, 1);
graph.insertEdge(4, 7, 1);
graph.insertEdge(2, 5, 1);
graph.insertEdge(2, 6, 1);
graph.insertEdge(5, 6, 1);
//显示一把邻结矩阵
graph.showGraph();
//测试一把,我们的 dfs 遍历是否 ok
System.out.println("深度遍历");
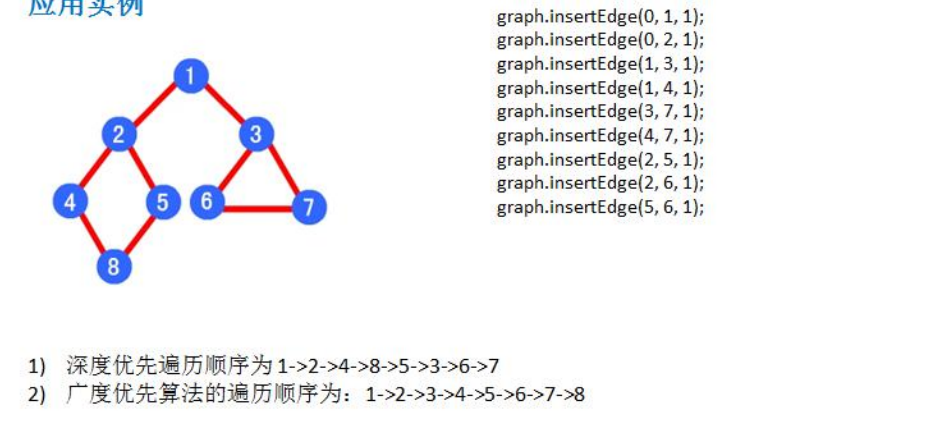
graph.dfs(); //A->B->C->D->E [1->2->4->8->5->3->6->7]
// System.out.println();
System.out.println("广度优先!");
graph.bfs(); //A->B->C->D-E [1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8]
}
//构造器
public Graph(int n) {
//初始化矩阵和 vertexList
edges = new int[n][n];
vertexList = new ArrayList<String>(n);
numOfEdges = 0;
}
//得到第一个邻接结点的下标 w
/**
* @param index
* @return 如果存在就返回对应的下标,否则返回-1
*/
public int getFirstNeighbor(int index) {
for (int j = 0; j < vertexList.size(); j++) {
if (edges[index][j] > 0) {
return j;
}
}
return -1;
}
//根据前一个邻接结点的下标来获取下一个邻接结点
public int getNextNeighbor(int v1, int v2) {
for (int j = v2 + 1; j < vertexList.size(); j++) {
if (edges[v1][j] > 0) {
return j;
}
}
return -1;
}
//深度优先遍历算法
//i 第一次就是 0
private void dfs(boolean[] isVisited, int i) {
//首先我们访问该结点,输出
System.out.print(getValueByIndex(i) + "->");
//将结点设置为已经访问
isVisited[i] = true;
//查找结点 i 的第一个邻接结点 w
int w = getFirstNeighbor(i);
while (w != -1) {//说明有
if (!isVisited[w]) {
dfs(isVisited, w);
}
//如果 w 结点已经被访问过
w = getNextNeighbor(i, w);
}
}
//对 dfs 进行一个重载, 遍历我们所有的结点,并进行 dfs
public void dfs() {
isVisited = new boolean[vertexList.size()];
//遍历所有的结点,进行 dfs[回溯]
for (int i = 0; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) {
if (!isVisited[i]) {
dfs(isVisited, i);
}
}
}
//对一个结点进行广度优先遍历的方法
private void bfs(boolean[] isVisited, int i) {
int u; // 表示队列的头结点对应下标
int w; // 邻接结点 w
//队列,记录结点访问的顺序
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList();
//访问结点,输出结点信息
System.out.print(getValueByIndex(i) + "=>");
//标记为已访问
isVisited[i] = true;
//将结点加入队列
queue.addLast(i);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//取出队列的头结点下标
u = (Integer) queue.removeFirst();
//得到第一个邻接结点的下标 w
w = getFirstNeighbor(u);
while (w != -1) {//找到
//是否访问过
if (!isVisited[w]) {
System.out.print(getValueByIndex(w) + "=>");
//标记已经访问
isVisited[w] = true;
//入队
queue.addLast(w);
}
//以 u 为前驱点,找 w 后面的下一个邻结点
w = getNextNeighbor(u, w); //体现出我们的广度优先
}
}
}
//遍历所有的结点,都进行广度优先搜索
public void bfs() {
isVisited = new boolean[vertexList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) {
if (!isVisited[i]) {
bfs(isVisited, i);
}
}
}
//图中常用的方法
//返回结点的个数
public int getNumOfVertex() {
return vertexList.size();
}
//显示图对应的矩阵
public void showGraph() {
for (int[] link : edges) {
System.err.println(Arrays.toString(link));
}
}
//得到边的数目
public int getNumOfEdges() {
return numOfEdges;
}
//返回结点 i(下标)对应的数据 0->"A" 1->"B" 2->"C"
public String getValueByIndex(int i) {
return vertexList.get(i);
}
//返回 v1 和 v2 的权值
public int getWeight(int v1, int v2) {
return edges[v1][v2];
}
//插入结点
public void insertVertex(String vertex) {
vertexList.add(vertex);
}
//添加边
/**
* @param v1 表示点的下标即使第几个顶点 "A"-"B" "A"->0 "B"->1
* @param v2 第二个顶点对应的下标
* @param weight 表示
*/
public void insertEdge(int v1, int v2, int weight) {
edges[v1][v2] = weight;
edges[v2][v1] = weight;
numOfEdges++;
}
}
4.图的代码汇总(自己)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class Graph {
//存储顶点集合
private List<String> vertexList;
//存储图对应的邻结矩阵
private int[][] edges;
//表示边的数目
private int numOfEdges;
//定义数据boolean[],记录某个结点是否被访问
private boolean[] isVisited;
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1();
//test2();
}
public static void test1() {
Graph graph = new Graph(5);
graph.insertVertex("A");
graph.insertVertex("B");
graph.insertVertex("C");
graph.insertVertex("D");
graph.insertVertex("E");
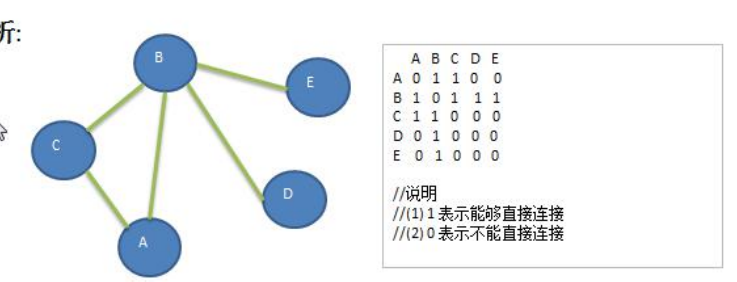
graph.insertEdge(0, 1, 1);//A-B
graph.insertEdge(0, 2, 1);//A-C
graph.insertEdge(1, 2, 1);//B-C
graph.insertEdge(1, 3, 1);//B-D
graph.insertEdge(1, 4, 1);//B-E
graph.showGraph();
System.out.println("深度优先遍历");
graph.dfs();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("广度优先遍历");
graph.bfs();
}
public static void test2() {
Graph graph = new Graph(8);
graph.insertVertex("1");
graph.insertVertex("2");
graph.insertVertex("3");
graph.insertVertex("4");
graph.insertVertex("5");
graph.insertVertex("6");
graph.insertVertex("7");
graph.insertVertex("8");
graph.insertEdge(0, 1, 1);
graph.insertEdge(0, 2, 1);
graph.insertEdge(1, 3, 1);
graph.insertEdge(1, 4, 1);
graph.insertEdge(3, 7, 1);
graph.insertEdge(4, 7, 1);
graph.insertEdge(2, 5, 1);
graph.insertEdge(2, 6, 1);
graph.insertEdge(5, 6, 1);
graph.showGraph();
System.out.println("深度优先遍历");
graph.dfs();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("广度优先遍历");
graph.bfs();
}
//得到第一个邻接结点的下标 w
public int getFirstNeighbor(int index) {
for (int j = 0; j < vertexList.size(); j++) {
if (edges[index][j] > 0) {
return j;
}
}
return -1;
}
//根据前一个邻接结点的下标来获取下一个邻接结点
public int getNextNeighbor(int v1, int v2) {
for (int j = v2 + 1; j < vertexList.size(); j++) {
if (edges[v1][j] > 0) {
return j;
}
}
return -1;
}
//深度优先遍历算法
public void dfs() {
isVisited = new boolean[vertexList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < vertexList.size(); i++) {
if (!isVisited[i]) {
dfs(isVisited, i);
}
}
}
//深度优先遍历算法
//i 第一次就是 0
private void dfs(boolean[] isVisited, int i) {
//首先我们访问该结点,输出
System.out.print(getValueByIndex(i) + "->");
//将结点设置为已经访问
isVisited[i] = true;
//查找结点 i 的第一个邻接结点 w
int w = getFirstNeighbor(i);
while (w != -1) {//说明有
if (!isVisited[w]) {
dfs(isVisited, w);
}
//如果 w 结点已经被访问过
w = getNextNeighbor(i, w);
}
}
//广度优先遍历算法
public void bfs() {
isVisited = new boolean[vertexList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < vertexList.size(); i++) {
if (!isVisited[i]) {
bfs(isVisited, i);
}
}
}
//广度优先遍历算法
private void bfs(boolean[] isVisited, int i) {
//首先我们访问该结点,输出
System.out.print(getValueByIndex(i) + "->");
//将结点设置为已经访问
isVisited[i] = true;
//定义队列,用于存放已经访问的结点索引
LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.addLast(i);
//遍历队列
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int u = queue.removeFirst();//从队列头部获取元素并从队列中删除
int w = getFirstNeighbor(u);//索引为u的邻结点
while (w != -1) {
//若结点还未被访问
if (!isVisited[w]) {
//输出结点
System.out.print(getValueByIndex(w) + "->");
//将结点设置为已经访问
isVisited[w] = true;
//将以访问的结点加入队列
queue.addLast(w);
}
//获取u结点的邻结点的w的下一个结点
w = getNextNeighbor(u, w);
}
}
}
public Graph(int size) {
vertexList = new ArrayList<>(size);
edges = new int[size][size];
numOfEdges = 0;
isVisited = new boolean[size];
}
//图中常用的方法
//返回结点的个数
public int getNumOfVertex() {
return vertexList.size();
}
//显示图对应的矩阵
public void showGraph() {
for (int[] link : edges) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(link));
}
}
//得到边的数目
public int getNumOfEdges() {
return numOfEdges;
}
//返回结点 i(下标)对应的数据 0->"A" 1->"B" 2->"C"
public String getValueByIndex(int i) {
return vertexList.get(i);
}
//返回 v1 和 v2 的权值
public int getWeight(int v1, int v2) {
return edges[v1][v2];
}
//插入结点
public void insertVertex(String vertex) {
vertexList.add(vertex);
}
//添加边
/**
* @param v1 表示点的下标即使第几个顶点 "A"-"B" "A"->0 "B"->1
* @param v2 第二个顶点对应的下标
* @param weight 表示
*/
public void insertEdge(int v1, int v2, int weight) {
edges[v1][v2] = weight;
edges[v2][v1] = weight;
numOfEdges++;
}
}
5.图的深度优先 VS 广度优先