一、DHCP简单讲解
DHCP就是动态主机配置协议(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)是一种基于UDP协议且仅限用于局域网的网络协议,它的目的就是为了减轻TCP/IP网络的规划、管理和维护的负担,解决IP地址空间缺乏问题。这种网络服务有利于对网络中的客户机IP地址进行有效管理。
DHCP功能分为两个部份:一个是服务器端,而另一个是客户端(客户端不用安装) DHCP透过“租约”的概念,有效且动态的分配客户端的TCP/IP设定。
DHCP服务程序能够使局域网内的主机自动且动态的获取IP地址、子网掩码、网关地址以及DNS服务器地址等信息,且能够有效的提升地址使用率,提高配置效率,减少管理和维护成本
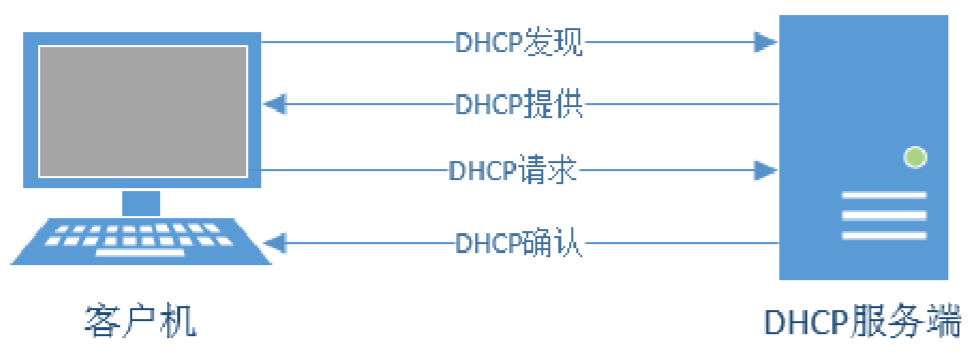
路由器DHCP服务器的三种IP分配方式:
DHCP服务器具有三种IP的分配方式,手动分配,自动分配和动态分配。其中动态分配功能最为强大,配置也最为烦琐。目前的DHCP服务器一般支持全部的几种分配方式或者是其中的两种。
手动分配:
网络管理员在DHCP服务器通过手工方法配置DHCP客户机的IP地址。当DHCP客户机要求网络服务时,DHCP服务器把手工配置的IP地址传递给DHCP客户机。
自动分配:
不需要进行任何的IP地址手工分配。当DHCP客户机第一次向DHCP服务器租用到IP地址后,这个地址就永久地分配给了该DHCP客户机,而不会再分配给其他客户机。
动态分配:
当DHCP客户机向DHCP服务器租用IP地址时,DHCP服务器只是暂时分配给客户机一个IP地址。只要租约到期,这个地址就会还给DHCP服务器,以供其他客户机使用。如果DHCP客户机仍需要一个IP地址来完成工作,则可以再要求另外一个IP地址。
动态分配方法是惟一能够自动重复使用IP地址的方法,它对于暂时连接到网上的DHCP客户机来说尤其方便,对于永久性与网络连接的新主机来说也是分配IP地址的好方法。DHCP客户机在不再需要时才放弃IP地址,如DHCP客户机要正常关闭时,它可以把IP地址释放给DHCP服务器,然后DHCP服务器就可以把该IP地址分配给申请IP地址的DHCP客户机。
使用动态分配方法可以解决IP地址不够用的困扰,例如C类网络只能支持254台主机,而网络上的主机有三百多台,但如果网上同一时间最多有200个用户,此时如果使用手工分配或自动分配将不能解决这一问题。而动态分配方式的IP地址并不固定分配给某一客户机,只要有空闲的IP地址,DHCP服务器就可以将它分配给要求地址的客户机;当客户机不再需要IP地址时,就由DHCP服务器重新收回。
浅谈DHCP IP相同的问题
DHCP IP相同,DHCP服务器优先分发尚未出租的最前IP地址,以后DHCP客户机每次重新登录网络时,就不需要再发送DHCP discover发现信息,而是直接发送包含前一次所分配的IP地址的DHCP request请求信息。当DHCP服务器收到这一信息后,它会尝试让DHCP客户机继续使用原来的IP地址,并回答一个DHCP ack确认信息。如果此IP地址已无法再分配给原来的DHCP客户机使用时,比如此IP地址已分配给其它DHCP客户机使用,则DHCP服务器给 DHCP客户机回答一个DHCP nack否认信息。当原来的DHCP客户机收到此DHCP nack否认信息后,它就必须重新发送DHCP discover发现信息来请求新的IP地址。另外,DHCP服务器向DHCP客户机出租的IP地址一般都有一个租借期限,期满后DHCP服务器便会收回出租的IP地址。如果DHCP客户机要延长其IP租约,则必须更新其IP租约。DHCP客户机启动时和IP租约期限过一半时,DHCP客户机都会自动向 DHCP服务器发送更新其IP租约的信息。
DHCP服务程序的相关术语:
作用域:
一个完整的IP地址段,DHCP服务根据作用域来管理网络的分布、分配IP地址及其他配置参数。
超级作用域:
用于支持同一个物理网络上多个逻辑IP地址子网端,包含作用域的列表,并对子作用域统一管理。
排除范围:
将某些IP地址在作用域中排除,确保这些IP地址不会被提供给DHCP客户机。
地址池:
在定义DHCP服务的作用域并应用排除范围后,剩余用来动态分配给DHCP客户机的IP地址范围。
租约:
即DHCP客户机能够使用动态分配到的IP地址的时间。
预约:
保证局域子网中特定设备总是获取到相同的IP地址。
二、搭建过程
查看一下dhcp有没有安装
# rpm -qa dhcp
[root@localhost ~]# [root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa dhcp [root@localhost ~]#
安装DHCP服务
# yum install dhcp -y
Installed: dhcp.x86_64 12:4.2.5-68.el7.centos.1 Dependency Updated: dhclient.x86_64 12:4.2.5-68.el7.centos.1 dhcp-common.x86_64 12:4.2.5-68.el7.centos.1 dhcp-libs.x86_64 12:4.2.5-68.el7.centos.1 Complete! [root@localhost ~]#
查看dhcp的版本号
# rpm -qa dhcp
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa dhcp dhcp-4.2.5-68.el7.centos.1.x86_64
查看一下dhcp.conf配置文件
# cat /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf # # DHCP Server Configuration file. # see /usr/share/doc/dhcp*/dhcpd.conf.example # see dhcpd.conf(5) man page # [root@localhost ~]#
DHCP执行程序
[root@localhost ~]# ls /usr/sbin/dhcrelay /usr/sbin/dhcrelay [root@localhost ~]# [root@localhost ~]# ls /usr/sbin/dhcpd /usr/sbin/dhcpd [root@localhost ~]#
查看DHCP配置文件模板
# cat /usr/share/doc/dhcp-4.2.5/dhcpd.conf.example
# # DHCP Server Configuration file. # see /usr/share/doc/dhcp*/dhcpd.conf.example # see dhcpd.conf(5) man page # # dhcpd.conf # # Sample configuration file for ISC dhcpd # # option definitions common to all supported networks... option domain-name "example.org"; option domain-name-servers ns1.example.org, ns2.example.org; default-lease-time 600; #默认租约时间单位秒 max-lease-time 7200; #最大租约时间单位秒 # Use this to enble / disable dynamic dns updates globally. #ddns-update-style none; # If this DHCP server is the official DHCP server for the local # network, the authoritative directive should be uncommented. #authoritative; # Use this to send dhcp log messages to a different log file (you also # have to hack syslog.conf to complete the redirection). log-facility local7; # No service will be given on this subnet, but declaring it helps the # DHCP server to understand the network topology. subnet 10.152.187.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { #定义子网 } # This is a very basic subnet declaration. subnet 10.254.239.0 netmask 255.255.255.224 { range 10.254.239.10 10.254.239.20; #IP地址池 option routers rtr-239-0-1.example.org, rtr-239-0-2.example.org; } # This declaration allows BOOTP clients to get dynamic addresses, # which we don't really recommend. subnet 10.254.239.32 netmask 255.255.255.224 { range dynamic-bootp 10.254.239.40 10.254.239.60; option broadcast-address 10.254.239.31; option routers rtr-239-32-1.example.org; } # A slightly different configuration for an internal subnet. subnet 10.5.5.0 netmask 255.255.255.224 { range 10.5.5.26 10.5.5.30; option domain-name-servers ns1.internal.example.org; #DNS服务器 option domain-name "internal.example.org"; #可选 设置默认搜索域 option routers 10.5.5.1; #网关 option broadcast-address 10.5.5.31; #可选 备选广播地址 default-lease-time 600; max-lease-time 7200; } # Hosts which require special configuration options can be listed in # host statements. If no address is specified, the address will be # allocated dynamically (if possible), but the host-specific information # will still come from the host declaration. host passacaglia { hardware ethernet 0:0:c0:5d:bd:95; filename "vmunix.passacaglia"; server-name "toccata.fugue.com"; } # Fixed IP addresses can also be specified for hosts. These addresses # should not also be listed as being available for dynamic assignment. # Hosts for which fixed IP addresses have been specified can boot using # BOOTP or DHCP. Hosts for which no fixed address is specified can only # be booted with DHCP, unless there is an address range on the subnet # to which a BOOTP client is connected which has the dynamic-bootp flag # set. host fantasia { #主机 hardware ethernet 08:00:07:26:c0:a5; #指定文件服务器MAC地址 fixed-address fantasia.fugue.com; #指定IP地址 } # You can declare a class of clients and then do address allocation # based on that. The example below shows a case where all clients # in a certain class get addresses on the 10.17.224/24 subnet, and all # other clients get addresses on the 10.0.29/24 subnet. class "foo" { match if substring (option vendor-class-identifier, 0, 4) = "SUNW"; } shared-network 224-29 { subnet 10.17.224.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { option routers rtr-224.example.org; } subnet 10.0.29.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { option routers rtr-29.example.org; } pool { allow members of "foo"; range 10.17.224.10 10.17.224.250; } pool { deny members of "foo"; range 10.0.29.10 10.0.29.230; } }
在配置文件中通常包括三部分,分别是声明(declarations)、参数(parameters)、选项(option)。
a、声明是用来描述dhcpd服务器中对网络布局的划分,是网络设置的逻辑范围。
B、参数用来表明如何执行任务,是否要执行任务或将哪些网络配置选项发送给客户。
c、选项是用来配置dhcp的可选参数,全部用option关键字作为开始。
一个标准的DHCP配置文件应该包括全局配置参数、子网网段声明、地址配置选项以及地址配置参数:

全局配置参数用于定义整个配置文件的全局参数,而子网网段声明用于配置整个子网段的地址属性
三、配置实例
假设有一个公司的局域网,在该网络中用linux搭建dhcp服务器,网络中的ip地址网段为192.168.1.0,子网掩码为255.255.255.0,动态分配的ip地址区间为192.168.0.3~192.168.0.254,dns服务器地址为114.114.114.114,网关为192.168.1.1,公司总经理计算机的ip地址有特殊要求,设置ip地址为192.168.1.88。改如何进行配置?
我们只要把配置文件修改一下即可,如下:
# cat /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf # # DHCP Server Configuration file. # see /usr/share/doc/dhcp*/dhcpd.conf.example # see dhcpd.conf(5) man page # ddns-update-style none; #定义DNS服务动态更新的类型,类型包括:none不支持动态更新、interim互动更新模式、ad-hoc特殊更新模式
ignore client-updates; #忽略、(allow/允许)客户机更新DNS记录 subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 { #意思是我所分配的ip地址所在的网段为192.168.1.0 子网掩码为255.255.255.0 range 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.254; #租用IP地址的范围
default-lease-time 86400; #默认租约时间 max-lease-time 518400; #最大租约时间 option routers 192.168.1.1; #路由器网关地址,这里是当前 dhcp 机器的网关地址 option domain-name-servers 114.114.114.114,8.8.8.8; #设置DNS域名服务器 host fantasia { #设置主机声明 hardware ethernet 00:0c:29:eb:31:23; #指定dhcp客户的mac地址 fixed-address 192.168.1.88; #给指定的mac地址分配ip }
} [root@localhost ~]#
重启DHCP服务器
# systemctl restart dhcpd
注意:重启DHCP服务器时,确保设置的物理地址网卡没有IP地址,处于关机状态为最佳,否则重启时报错
设置开机自启动
# chkconfig dhcpd on
或者
# systemctl enable dhcpd
模拟总经理计算机
查看总经理计算机物理地址(MAC)
# cat /sys/class/net/eno16777736/address
[root@localhost ~]# cat /sys/class/net/eno16777736/address 00:0c:29:eb:31:23 [root@localhost ~]#
确认一下IP
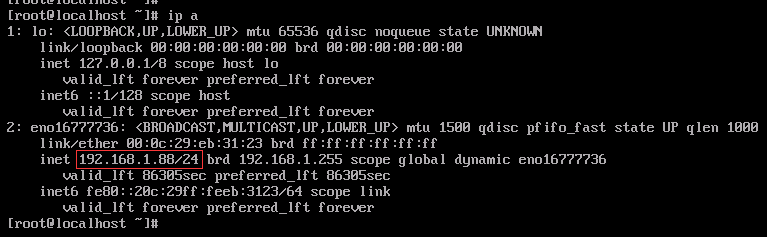
四、DHCP相关的使用信息
/var/lib/dhcpd/dhcpd.leases 这个文件专门记录了DHCP的分配情况
[root@localhost dhcpd]# pwd /var/lib/dhcpd [root@localhost dhcpd]# [root@localhost dhcpd]# ls dhcpd6.leases dhcpd.leases dhcpd.leases~ [root@localhost dhcpd]# [root@localhost dhcpd]# cat dhcpd.leases # The format of this file is documented in the dhcpd.leases(5) manual page. # This lease file was written by isc-dhcp-4.2.5 lease 192.168.1.3 { starts 5 2019/02/15 15:05:37; ends 6 2019/02/16 15:05:37; tstp 6 2019/02/16 15:05:37; cltt 5 2019/02/15 15:05:37; binding state free; hardware ethernet 00:0c:29:eb:31:23; } lease 192.168.1.4 { starts 0 2019/02/17 15:08:35; ends 1 2019/02/18 15:08:35; cltt 0 2019/02/17 15:08:35; binding state active; next binding state free; rewind binding state free; hardware ethernet c8:d3:ff:de:22:83; uid "�01310323377336"203"; client-hostname "LAPTOP-6T0LVEVT"; } server-duid "�00�01�00�01#371|300�00�14)207$273"; [root@localhost dhcpd]#
参考博客:
centos7.0中搭建dhcp服务器
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_18831583/article/details/79001796
centos6.5上DHCP安装与配置
https://blog.csdn.net/kongxx/article/details/43523225
centos7配置DHCP服务
http://www.bubuko.com/infodetail-1804738.html
详述DHCP服务器的三种IP分配方式
https://www.cnblogs.com/sunflower627/p/3627654.html
linux下dhcp服务器分配出去的IP地址及剩余IP地址
https://blog.csdn.net/zhang_danf/article/details/24321855
end