目录
一、介绍
散列表的实现被叫做散列,是一种用于常数平均时间执行插入、删除和查找的技术。通常做法是保存key-value的数据结构,理想的散列表数据结构不过是具有固定大小的数组,key 作为关键字,value 是真正存储的数据。将不同的value根据各自的key 存取在散列表中的算法叫做散列函数;
理想散列情况
我们寻找一个散列函数,该函数要在单元之间均匀的分配关键字,每个关键字 key 落在不同的位置,均匀的分布在散列数组中,互补干扰。
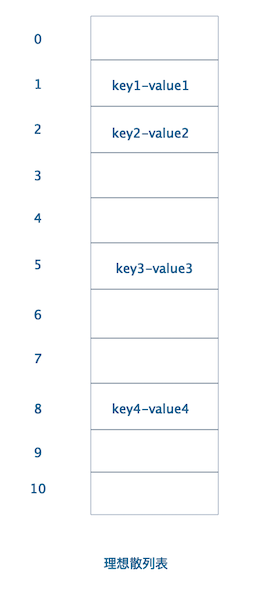
冲突
数组大小总是有限的,例如我们将12个数据插入大小为11的散列数组中,必定会有一个2个数据争抢一个位置,这种情况叫做冲突。
散列最主要的问题就是确定散列表的大小,以及解决冲突!
散列函数
将 key-value 数据存入散列表中的位置,确定该位置的算法成为散列函数。
装填因子(装载因子/加载因子)
定义装填因子 (lambda) = 表中数据个数/表大小。
二、分离链表法
将散列到同一个值的所有元素保留到一个表中。设我们散列表的数组大小为10,当我们产生冲突时,即有2个数据散列到了位置为2的地方,那我们将位置为2的位置再设定为一个散列数组。
图表说明
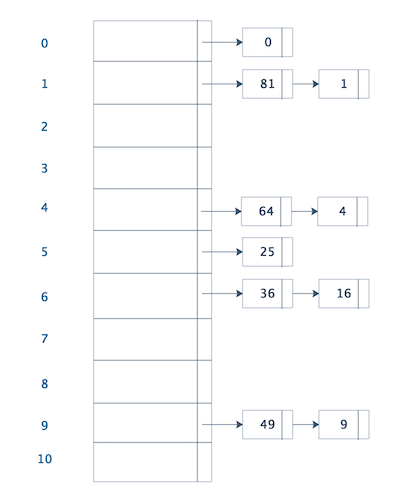
上图: 位置为1、4、6、9位置产生了冲突,每个位置被分配了2个数据,这时候,我们在冲突位置再建一个散列表,让冲突的值重新分配。
位置1:先存入数据1,再存入数据1时发生冲突,则建立新表,并将新表地址存入位置1,然后将数据1和数据81依次存入新表。我们将新元素插入到链表的前端,因为通常情况:新近插入的元素最有可能不久又被访问。
三、代码实现
Java代码说明https://github.com/dhcao/dataStructuresAndAlgorithm/blob/master/src/chapterFive/SeparateChainingHashTable.java
package chapterFive;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 散列表实现方法之一:分离链接法
* 分离链接法:在遇到冲突的时候,构建一个链表(linkedList)来存储,原位置存储链表位置。
*
* @Author: dhcao
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class SeparateChainingHashTable<T> {
/**
* desc: 构造函数
*
* @return:
* @auther: dhcao
*/
public SeparateChainingHashTable() {
this(DEFAULT_TABLE_SIZE);
}
public SeparateChainingHashTable(int size) {
theLists = new LinkedList[nextPrime(size)];
// 为表中每一个位置都创建一个表,在冲突时放入数据
for (int i = 0; i < theLists.length; i++) {
theLists[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
}
/**
* desc: 插入
*
* @auther: dhcao
*/
public void insert(T t) {
List<T> whichList = theLists[myhash(t)];
if (!whichList.contains(t)) {
whichList.add(t);
}
if (++currentSize > theLists.length) {
rehash();
}
}
/**
* desc: 删除
*
* @auther: dhcao
*/
public void remove(T t) {
List<T> whichList = theLists[myhash(t)];
if (whichList.contains(t)) {
whichList.remove(t);
currentSize--;
}
}
/**
* desc: 是否含有
*
* @auther: dhcao
*/
public boolean contains(T t) {
// 在散列表中找到散列位置都链表
List<T> whichList = theLists[myhash(t)];
return whichList.contains(t);
}
/**
* desc: 清空散列表
*
* @auther: dhcao
*/
public void makeEmpty() {
// 清空表都每个位置
for (int i = 0; i < theLists.length; i++) {
theLists[i].clear();
}
// 将当前表都大小置为0
currentSize = 0;
}
private static final int DEFAULT_TABLE_SIZE = 101;
private List<T>[] theLists;
// 当前大小
private int currentSize;
/**
* desc: 重新构造散列表(在散列表达到最大大小之后)
*
* @auther: dhcao
*/
private void rehash() {
List<T>[] oldLists = theLists;
theLists = new List[nextPrime(2 * theLists.length)];
for (int j = 0; j < theLists.length; j++) {
theLists[j] = new LinkedList<>();
}
currentSize = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < oldLists.length; i++) {
for (T item : oldLists[i]) {
insert(item);
}
}
}
/**
* desc:获取hash值
*
* @auther: dhcao
*/
private int myhash(T x) {
int hashVal = x.hashCode();
hashVal %= theLists.length;
if (hashVal < 0) {
hashVal += theLists.length;
}
return hashVal;
}
/**
* desc:下一个素数
*
* @auther: dhcao
*/
private static int nextPrime(int n) {
boolean state = isPrime(n);
while (!state) {
state = isPrime(++n);
}
return n;
}
/**
* desc:是不是素数
*
* @auther: dhcao
*/
private static boolean isPrime(int n) {
if (n == 2 || n == 3) {
return true;
}
if (n % 6 != 1 && n % 6 != 5) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 5; i * i <= n; i += 6) {
if (n % i == 0 || n % (i + 2) == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}