问题描述:
图着色问题(Graph Coloring Problem, GCP) 又称着色问题,是最著名的NP-完全问题之一。
数学定义:给定一个无向图G=(V, E),其中V为顶点集合,E为边集合,图着色问题即为将V分为K个颜色组,每个组形成一个独立集,即其中没有相邻的顶点。其优化版本是希望获得最小的K值。
图的m-着色判定问题——给定无向连通图G和m种不同的颜色。用这些颜色为图G的各顶点着色,每个顶点着一种颜色,是否有一种着色法使G中任意相邻的2个顶点着不同颜色?
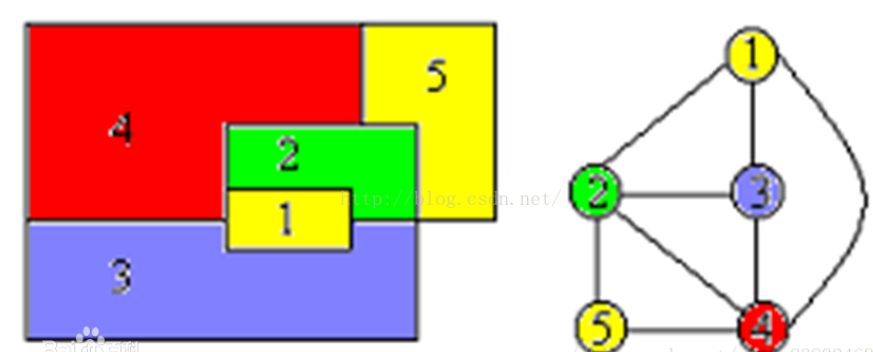
抽象为图结构
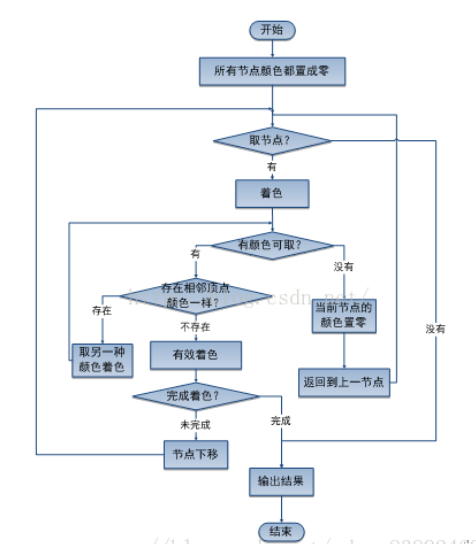
算法流程
问题简单分析:
这个问题和八皇后还有求子集和等问题都具有类似之处,其核心在通过遍历找到所有的问题子集 ,但是在递归遍历的时候,都在加一个判断,将那些明显不满足条件的情况给直接排出,减少问题的规模,其实这类问题,在递归遍历的时候都是类似与对一颗树的便利每个节点相当走到此时的状态,然后再判断此时的状态是否能继续走下去,如果不能就将其回溯到上一个节点,避免浪费时间。
下面以一个简单例子作分析: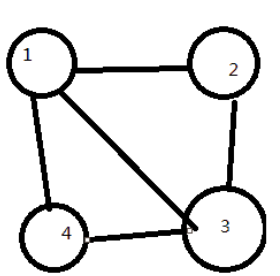
分析如下: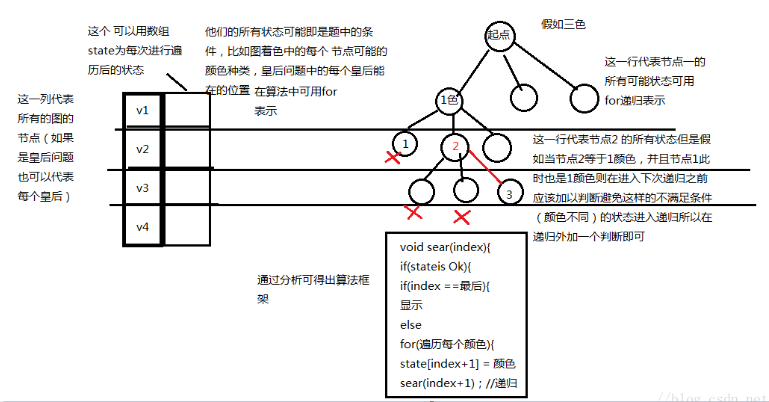
时间复杂度分析:
代码实现如下:

import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { static int[][] e = new int[5][5]; //存储各个边的情况连同为1 不连为0 static int[] state = new int[e.length]; //表示当前染色情况 static int Colornum = 3;//共有几种颜色 static void sear(int index) {//递归函数 if (isOk(index)) {//判断当前状态能否满足条件 if (index == e.length - 1) {//base case 若已经染到最后一个节点则输出情况 Show(index); } else { for (int i = 1; i <= Colornum; i++) {//将所有 的颜色情况给遍历 state[index + 1] = i;//假如下一个染色, sear(index + 1);//进入下次递归并且在递归的入口判断是否满足条件 } } } } //打印当前状态 private static void Show(int index) { for (int i = 1; i <= index; i++) { System.out.println(i + "is " + "Color " + state[i]); } System.out.println(); } //判断是否能染色 private static boolean isOk(int index) { for (int i = 1; i < index; i++) { if (e[index][i] == 1 && state[i] == state[index])//当两个节点是连同并且颜色一样则不满足返回false return false; } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int n = in.nextInt(); //输入边的情况 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { int a = in.nextInt(); int b = in.nextInt(); e[a][b] = 1; e[b][a] = 1; } //从0开始递归,但0不是一个节点 sear(0); } }
实现结果如下: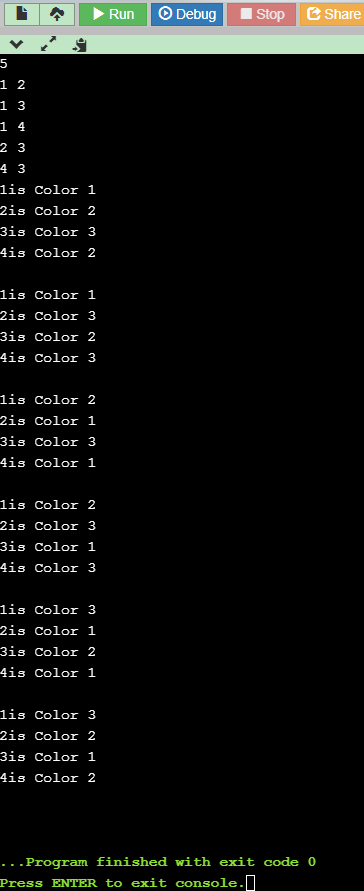
着色问题的应用:
问题描述:
n个人参加某项特殊考试。 为了公平,要求任何两个认识的人不能分在同一个考场。求是少需要分几个考场才能满足条件。
输入格式
第一行,一个整数n(1 < n < 100),表示参加考试的人数。
第二行,一个整数m,表示接下来有m行数据
以下m行每行的格式为:两个整数a,b,用空格分开 (1<=a,b<=n) 表示第a个人与第b个人认识。 输出格式
一行一个整数,表示最少分几个考场。
代码实现:

import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> list = null; static HashSet<Integer>[] map; public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int n = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); map = new HashSet[n + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int key = input.nextInt(); int value = input.nextInt(); if (map[key] == null) { map[key] = new HashSet<Integer>(); } if (map[value] == null) { map[value] = new HashSet<Integer>(); } map[key].add(value); map[value].add(key); } list = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (list.size() == 0) { ArrayList<Integer> child = new ArrayList<Integer>(); child.add(i); list.add(child); } else { boolean zhaodaomei = false; for (int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++) { if (isBo(j, i)) { list.get(j).add(i); zhaodaomei = true; break; } } if (zhaodaomei == false) {// 没找到哦 ArrayList<Integer> child = new ArrayList<Integer>(); child.add(i); list.add(child); } } } System.out.println(list.size()); } public static boolean isBo(int school, int num) { ArrayList<Integer> child = list.get(school); HashSet<Integer> set = map[num]; if (set == null) return true; for (int i = 0; i < child.size(); i++) { Integer stu = child.get(i); if (set.contains(stu)) { return false; } } return true; } }
实现结果:
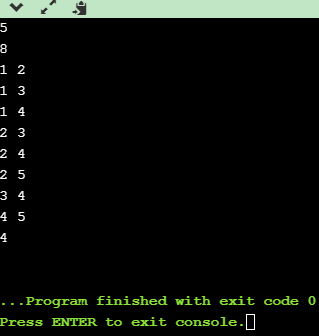
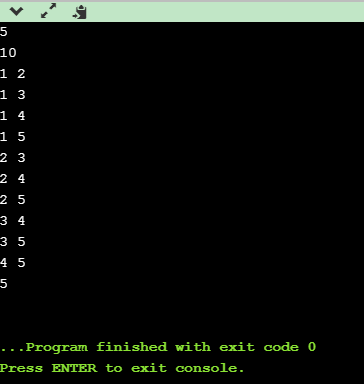
参考文献:北大《算法设计与分析》公开课
CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/wdays83892469/article/details/79648258
