YOLO-V1网络结构由24个卷积层与2个全连接层构成,网络入口为448×448×3,输出维度:S×S×(B×5+C),S为划分网格数,B为每个网格负责目标个数,C为类别个数。
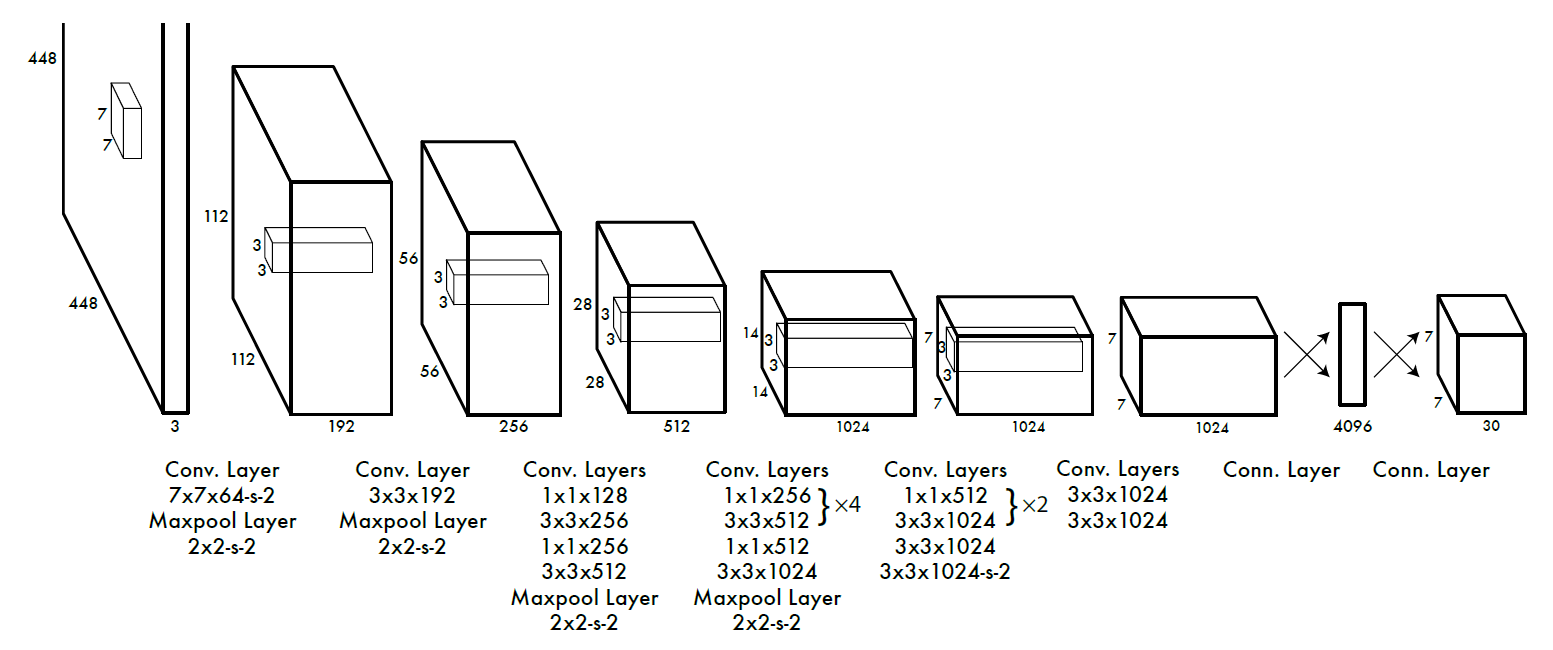

YOLO-V1是将一副图像分成S×S个网格,如果某个object的中心落在这个网格中,则这个网格就负责预测这个object,每个网格要预测B个bounding box,每个bounding box要预测一个confidence值,这个confidence代表了所预测的bounding box中含有object的置信度和这个bounding box预测的有多准这两个重要信息。
Pr(Object)∗IoUpredtruth
如果有object落在一个网格中,公式第一项取1,否则取0,第二项是bounding box和真实框的IOU的值(confidence针对每个bounding box,框中有没有网格包含object中心点。YOLO-V1中每个网格有两个bounding box,对于每个bounding box有5个预测值,x,y,w,h,confidence,每一个网格还要预测C条件类别的概率,即在一个网格包含一个object的前提下,它属于某个类别的概率。(x,y)表示bounding box相对于网格单元的边界的offset,归一化到(0,1)范围之内,而w,h表示相对于整个图片的预测宽和高,也被归一化到(0,1)范围内。c代表的是object在某个bounding box的confidence。confidence计算如下:
Pr(Classi∣Object)∗Pr(Object)∗IoUpredtruth=Pr(Classi)∗IoUpredtruth
下面说明如何将预测坐标的x,y用相对于对应网格的offset归一化到0-1和w,h是如何利用图像的宽高归一化到0-1之间。每个单元格预测的B个(x,y,w,h,confidence)向量,假设图片为S×S个网格,S=7,图片宽为wi高为hi 。
下面引用一张我看过的感觉讲解很详细的一张图片:
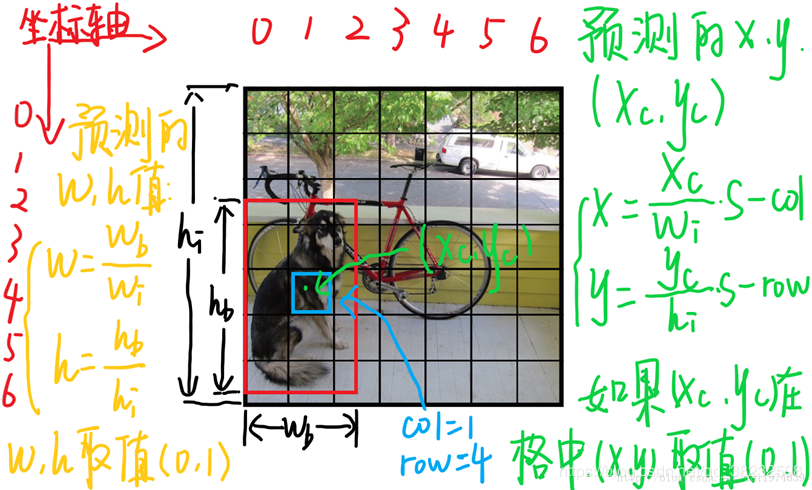
1.(x,y)是bbox的中心相对于单元格的offset对应于上图中的蓝色单元格,坐标为(xcol=1,yrow=4),加射它的预测输出是红色框bbox,设bbox的中心坐标为(xc,yc),那么最终预测出来的(x,y)是经过归一化处理的,表示的是相对于单元格的offset,公式为:x=wi / xc ∗ S−xcol,y=hi / yc ∗ S−yrow
2.(w,h)是bbox相对于整个图片的比例预测的bbox的宽高为wb,hb,(w,h)表示的是bbox相对于整张图片的占比,公式为:w=wi / wb,h=hi / hb
YOLO-V1中需要的参数
1 def __init__(self): 2 self.classes = ["aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat", "bottle", 3 "bus", "car", "cat", "chair", "cow", "diningtable", 4 "dog", "horse", "motorbike", "person", "pottedplant", 5 "sheep", "sofa", "train", "tvmonitor"] 6 #计算坐标用的 7 self.x_offset = np.transpose(np.reshape(np.array([np.arange(7)] * 7 * 2, dtype=np.float32), [2, 7, 7]), [1, 2, 0]) 8 self.y_offset = np.transpose(self.x_offset, [1, 0, 2]) 9 #输入图片大小 10 self.img_size = (448, 448) 11 #阈值 12 self.iou_threshold = 0.5 13 self.batch_size = 45 14 #计算loss需要的参数 15 self.class_scale = 2.0 16 self.object_scale = 1.0 17 self.noobject_scale = 1.0 18 self.coord_scale = 5.0
网络部分开始
1 def _build_net(self): 2 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 448, 448, 3]) 3 with tf.variable_scope('yolo'): 4 net = self.conv_layer(x, 64, 7, 2, 'conv_2') 5 net = self.max_pool_layer(net, 2, 2) 6 net = self.conv_layer(net, 192, 3, 1, 'conv_4') 7 net = self.max_pool_layer(net, 2, 2) 8 net = self.conv_layer(net, 128, 1, 1, 'conv_6') 9 net = self.conv_layer(net, 256, 3, 1, 'conv_7') 10 net = self.conv_layer(net, 256, 1, 1, 'conv_8') 11 net = self.conv_layer(net, 512, 3, 1, 'conv_9') 12 net = self.max_pool_layer(net, 2, 2) 13 net = self.conv_layer(net, 256, 1, 1, 'conv_11') 14 net = self.conv_layer(net, 512, 3, 1, 'conv_12') 15 net = self.conv_layer(net, 256, 1, 1, 'conv_13') 16 net = self.conv_layer(net, 512, 3, 1, 'conv_14') 17 net = self.conv_layer(net, 256, 1, 1, 'conv_15') 18 net = self.conv_layer(net, 512, 3, 1, 'conv_16') 19 net = self.conv_layer(net, 256, 1, 1, 'conv_17') 20 net = self.conv_layer(net, 512, 3, 1, 'conv_18') 21 net = self.conv_layer(net, 512, 1, 1, 'conv_19') 22 net = self.conv_layer(net, 1024, 3, 1, 'conv_20') 23 net = self.max_pool_layer(net, 2, 2) 24 net = self.conv_layer(net, 512, 1, 1, 'conv_22') 25 net = self.conv_layer(net, 1024, 3, 1, 'conv_23') 26 net = self.conv_layer(net, 512, 1, 1, 'conv_24') 27 net = self.conv_layer(net, 1024, 3, 1, 'conv_25') 28 net = self.conv_layer(net, 1024, 3, 1, 'conv_26') 29 net = self.conv_layer(net, 1024, 3, 2, 'conv_28') 30 net = self.conv_layer(net, 1024, 3, 1, 'conv_29') 31 net = self.conv_layer(net, 1024, 3, 1, 'conv_30') 32 net = self.flatten_layer(net) 33 net = self.dense_layer(net, 512, activation=self.Leaky_Relu, scope='fc_33') 34 net = self.dense_layer(net, 4096, activation=self.Leaky_Relu, scope='fc_34') 35 net = self.dense_layer(net, 7 * 7 * 30, scope='fc_36') 36 return net
需要的一些层
1 # 激活函数使用Leaky 2 def Leaky_Relu(self, x): 3 return tf.maximum(x * 0.1, x) 4 # 卷积层 5 def conv_layer(self, x, filter, kernel_size, stride, scope): 6 channel = x.get_shape().as_list()[-1] 7 weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[kernel_size, kernel_size, channel, filter], stddev=0.1), 8 name="weights") 9 bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([filter, ]), name="biases") 10 pad_size = kernel_size // 2 11 x = tf.pad(x, paddings=[[0, 0], [pad_size, pad_size], [pad_size, pad_size], [0, 0]]) 12 13 conv = tf.nn.conv2d(x, weight, strides=[1, stride, stride, 1], padding="VALID", name=scope) 14 output = self.Leaky_Relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv, bias)) 15 return output 16 # 最大池化层 17 def max_pool_layer(self, x, pool_size, stride): 18 return tf.nn.max_pool(x, [1, pool_size, pool_size, 1], strides=[1, stride, stride, 1], padding="SAME") 19 # 全连接层 20 def dense_layer(self, x, filter, activation=None, scope=None): 21 channel = x.get_shape().as_list()[-1] 22 weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[channel, filter], stddev=0.1), name="weights") 23 bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([filter, ]), name="biases") 24 output = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(x, weight, bias, name=scope) 25 if activation: 26 output = activation(output) 27 return output 28 # flatten层 29 def flatten_layer(self, x): 30 x = tf.transpose(x, [0, 3, 1, 2]) 31 shape = x.get_shape().as_list()[1:] 32 nums = np.product(shape) 33 return tf.reshape(x, [-1, nums])
网络部分结束