转载请注明出处 http://www.cnblogs.com/cnwutianhao/p/6746981.html
前几天客户提需求,对App增加一个功能,这个功能目前市面上已经很常见,那就是应用内切换语言。啥意思,就是 英、中、法、德、日。。。语言随意切换。
(本案例采用Data-Bingding模式,麻麻再也不用担心我findViewBy不到Id了哈哈,开个玩笑)
先上示例图:
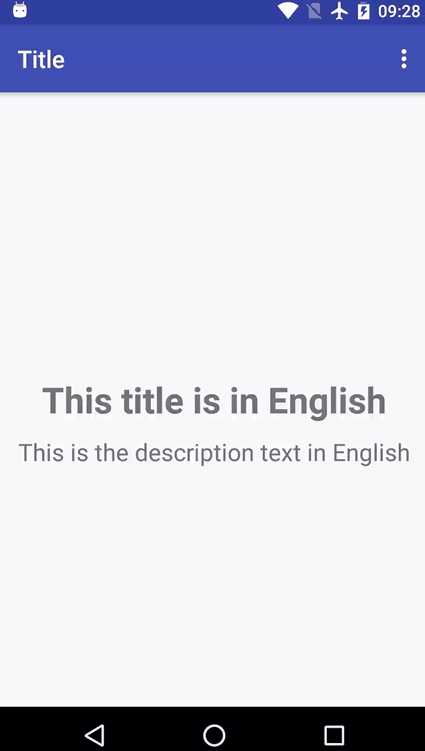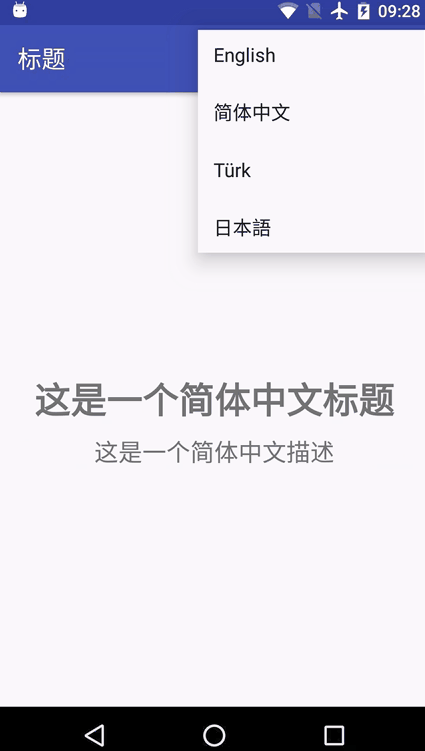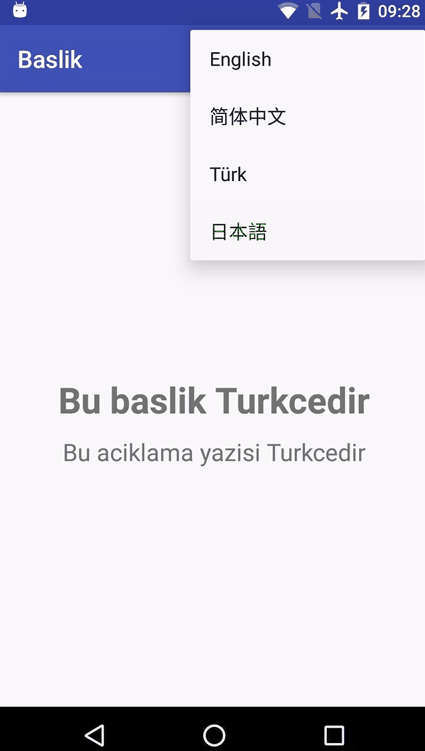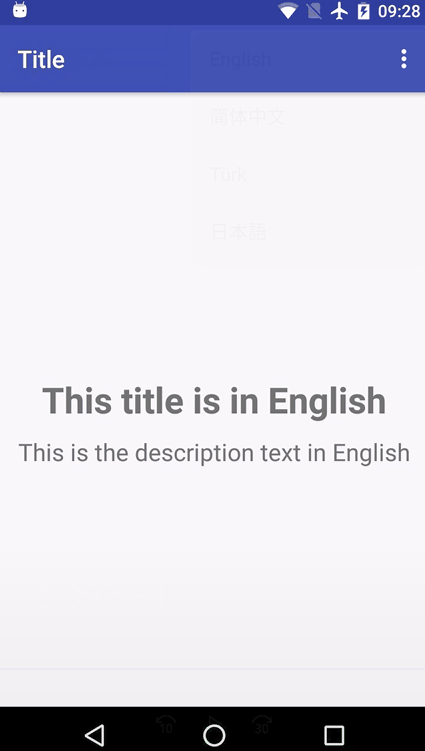
代码实现:
布局文件(Data-Binding模式),很简单就是两行文字
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <RelativeLayout xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.tnnowu.android.switchlanguage.MainActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/titleTextView" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:text="@string/title" android:textSize="30sp" android:textStyle="bold" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/descTextView" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/titleTextView" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" android:text="@string/desc" android:textSize="20sp" /> </RelativeLayout> </layout>
从实例中我们可以看到右上角是有Menu
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <item android:id="@+id/language_english" android:orderInCategory="100" android:title="@string/menu_english" /> <item android:id="@+id/language_simplified_chinese" android:orderInCategory="100" android:title="@string/menu_simplified_chinese" /> <item android:id="@+id/language_turkish" android:orderInCategory="100" android:title="@string/menu_turkish" /> <item android:id="@+id/language_japanese" android:orderInCategory="100" android:title="@string/menu_japanese" /> </menu>
(既然是多语言,所以就要有N个strings)
 ,本案例我创建了4种语言。
,本案例我创建了4种语言。
好的,Menu的布局写完了,接下来就是实现Menu功能,记住实现Menu就两套代码,一个 onCreateOptionsMenu , 另一个是 onOptionsItemSelected 。
@Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu, menu); return true; }
@Override public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { int id = item.getItemId(); if (id == R.id.language_english) { updateViews("en"); } else if (id == R.id.language_simplified_chinese) { updateViews("zh"); } else if (id == R.id.language_turkish) { updateViews("tr"); } else if (id == R.id.language_japanese) { updateViews("ja"); } return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); }
在这里,可以看到,我们自定义一个 updateViews() 方法,用来实现切换预言时界面的改变
private void updateViews(String languageCode) { Context context = LocaleHelper.setLocale(this, languageCode); Resources resources = context.getResources(); mBinding.titleTextView.setText(resources.getString(R.string.title)); mBinding.descTextView.setText(resources.getString(R.string.desc)); setTitle(resources.getString(R.string.toolbar_title)); }
公布一个 语言判断的类 LocaleHelper
public class LocaleHelper { private static final String SELECTED_LANGUAGE = "Locale.Helper.Selected.Language"; public static Context onAttach(Context context) { String lang = getPersistedData(context, Locale.getDefault().getLanguage()); return setLocale(context, lang); } public static Context onAttach(Context context, String defaultLanguage) { String lang = getPersistedData(context, defaultLanguage); return setLocale(context, lang); } public static String getLanguage(Context context) { return getPersistedData(context, Locale.getDefault().getLanguage()); } public static Context setLocale(Context context, String language) { persist(context, language); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N) { return updateResources(context, language); } return updateResourcesLegacy(context, language); } private static String getPersistedData(Context context, String defaultLanguage) { SharedPreferences preferences = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(context); return preferences.getString(SELECTED_LANGUAGE, defaultLanguage); } private static void persist(Context context, String language) { SharedPreferences preferences = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(context); SharedPreferences.Editor editor = preferences.edit(); editor.putString(SELECTED_LANGUAGE, language); editor.apply(); } @TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.N) private static Context updateResources(Context context, String language) { Locale locale = new Locale(language); Locale.setDefault(locale); Configuration configuration = context.getResources().getConfiguration(); configuration.setLocale(locale); return context.createConfigurationContext(configuration); } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") private static Context updateResourcesLegacy(Context context, String language) { Locale locale = new Locale(language); Locale.setDefault(locale); Resources resources = context.getResources(); Configuration configuration = resources.getConfiguration(); configuration.locale = locale; resources.updateConfiguration(configuration, resources.getDisplayMetrics()); return context; } }
最后还要做的操作就是,自定义一个Application类,用来设定App的默认语言(当然了,要将这个Application应用到Manifest中)
public class BaseApplication extends Application { @Override protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) { super.attachBaseContext(LocaleHelper.onAttach(base, "en")); } }
本案例实现App内语言切换代码量不大,通俗易懂,无垃圾代码。
示例代码下载地址:App内切换语言
关注我的新浪微博,请认准黄V认证,获取最新安卓开发资讯。
关注科技评论家,领略科技、创新、教育以及最大化人类智慧与想象力!