1.PWA简介:
Progressive Web App 是由谷歌提出推广的,在移动端利用提供的标准化框架,在网页应用中实现和原生应用相近的用户体验。
2.PWA到底有哪些过人之处(特性)?
1、Installability(可安装性):添加到主屏
2、App Shell:第一次渲染渲个壳、等异步数据来了再填充
3、Offline Web App (离线能力)
4、Re-engageable:推送通知的能力。推送通知依赖Service Worker与HTTP Push,不过默认的支持是GCM(Google提供的云服务)
将Web和App的技术相结合:
- 不需要安装
- 快速加载
- 推送消息
- 桌面图标
- 全屏体验
3.PWA核心技术:
Web App Manifest
App shell
Service worker
push Notifion
4.manifest.json 配置文件 添加主屏配置
<link rel="manifest" href="/manifest.json">
5.Service worker 用来实现页面的缓存和离线, 后台通知等功能
Service Worker 是什么? service worker 是独立于当前页面的一段运行在浏览器后台进程里的脚本。
要求:需要HTTPS本地调试localhost 浏览器支持(目前andorid的chrome部分支持)
sw生命周期:注册完成 安装-》激活-》接管页面 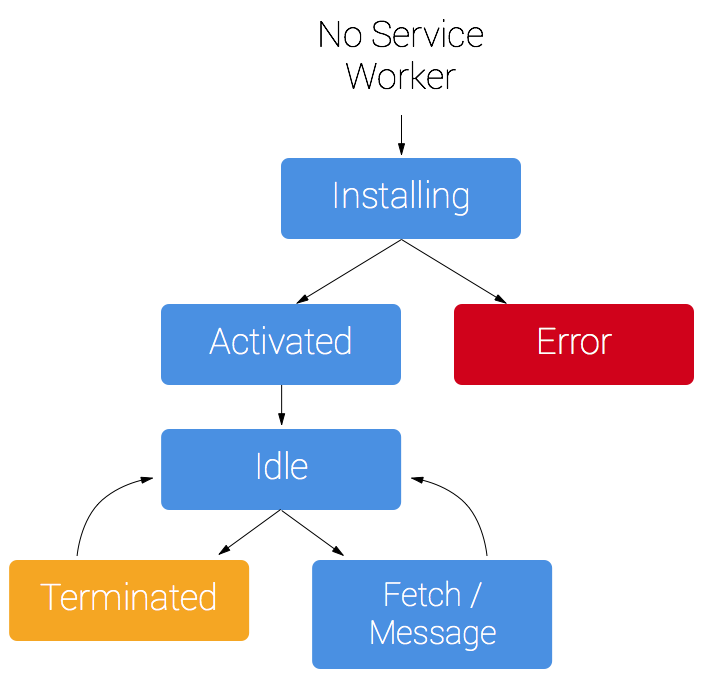
sw里面的一些简单变量说明
- self: 表示 Service Worker 作用域, 也是全局变量
- self.skipWaiting: 表示强制当前处在 waiting 状态的脚本进入 activate 状态
- self.clients.claim():获取到客户端页面的控制权
1.sw 注册:检查 Service Worker API 是否可用,如果可用,则在页面加载后注册位于 /sw.js 的服务工作线程
if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
window.addEventListener('load', function() {
navigator.serviceWorker.register('/sw.js').then(function(registration) {
// Registration was successful
console.log('ServiceWorker registration successful with scope: ', registration.scope);
}).catch(function(err) {
// registration failed
console.log('ServiceWorker registration failed: ', err);
});
});
}
2.sw安装:执行以下步骤
a.打开缓存
b.缓存文件
c.确认文件是否缓存
//SW安装
self.addEventListener('install', e=> {
console.log('[sw]ServiceWorker Install');
e.waitUntil(
caches.open(staticCache).then(function(cache) {
return cache.addAll(filesToCache)
.then(function () {
console.log('[sw]All files are cached');
return self.skipWaiting();//跳过等待直接activate
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log('[sw]Failed to cache', error);
})
})
);
});
3.sw激活: 如果你的 service worker 已经被安装,但是刷新页面时有一个新版本的可用,新版的 service worker 会在后台安装,但是还没激活。当不再有任何已加载的页面在使用旧版的 service worker 的时候,新版本才会激活。一旦再也没有更多的这样已加载的页面,新的 service worker 就会被激活。
//SW激活
self.addEventListener('activate', function(e) {
console.log('[sw]ServiceWorker Activate');
var arr = [htmlCache,staticCache];
e.waitUntil(
caches.keys().then(function(keyList) {
return Promise.all(keyList.map(function(key) {
if (arr.indexOf(key) === -1) {
console.log('[sw]ServiceWorker Removing old cache', key);
return caches.delete(key);
}
}));
})
);
return self.clients.claim(); //更新客户端取得页面控制权
});
4.sw fetch缓存和返回请求:
self.addEventListener('fetch', e=> {
// console.info('Event: Fetch');
var request = e.request;
let url = e.request.url
e.respondWith(
//If request is already in cache, return it
caches.match(request).then(function(response) {
if (response) {
console.log('[sw]Found response in cache:', url);
return response;
}
//if request is not cached, add it to cache
console.log('[sw]No response found in cache. About to fetch from network...');
return fetch(request).then(function(response) {
var responseToCache = response.clone();
//请求和响应流只能被读取一次。为了给浏览器返回响应以及把它缓存起来,我们不得不克隆一份。所以原始的会返回给浏览器,
//克隆的会发送到缓存中。它们都是读取了一次
caches.open(htmlCache).then(
function(cache) {
cache.put(request, responseToCache).catch(function(err) {
console.warn(request.url + ': ' + err.message);
});
});
console.log('[sw]Response from network is:', url);
return response;
});
})
);
});
caches.match(event.request) 允许我们对网络请求的资源和 cache 里可获取的资源进行匹配,查看是否缓存中有相应的资源
如果没有在缓存中找到匹配的资源,你可以告诉浏览器对着资源直接去fetch 默认的网络请求: fetch(event.request)
如果没有在缓存中找到匹配的资源,同时网络也不可用,你可以用 match() 把一些回退的页面作为响应来匹配这些资源,比如: caches.match('/offline.html');
6.app shell
示例链接:速卖通
7.消息推送
示例链接:https://progressive-web-application.herokuapp.com/
8.sw-toolbox
示例链接:线上环境 m.tomtop.com
api:https://googlechrome.github.io/sw-toolbox/