一、前言
目前沪深交易所都有Binary和STEP两种行情接口,本篇是我尝试对接沪市VDE的Binary接口。因为不太直观,Binary接口对于初学者来说还是有点难度的,但对于掌握了Binary通讯的大佬来说其实非常简单。网上相关的资料不能说非常少,只能说是极度少,幸运的是我找到了下面这篇博文,他讲的是对接深交所行情网关,我在他这个基础上改吧改吧居然就弄通了。
https://blog.csdn.net/s732444206/article/details/121389373
因为只是示例,所以我没有关注太多行情接口解析的内容,而主要关注Binary行情接口的原理、思路和对接。另外我是通过VDE对接的,不是行情网关,可能会有些区别但估计大差不差。
参考文档:《上海证券交易所低延时行情发布系统(LDDS)接口说明书》、《IS120_上海证券交易所行情网关BINARY数据接口规范》。
完整代码附在文末。
二、Binary接口
什么是Binary接口?我理解就是以byte来通信的接口。
常见的通信接口,比如telnet,我们建立socket连接后,读写都是通过“流”的形式,比如InputStream和OutputStream。但是我们在读到流以后直接就将流转为String来解析,发送也是直接将String通过接口发出去,这样比较简单,通信就好像两个人对话一样,我们只需要处理String即可,但问题是这样非常“浪费”。
浪费主要体现在对数字的传输,比如我们要传输一个10位的数字“1234567890”,如果是字符串格式,每一个数字占用一个char,也就是这个字符串占用char[10],一个char占用8位,那么传输这个10位数字字符串使用80个位。如果我们现在传输的不是字符串而是Int整数,我们知道一个Int32整数最大值是2147483647(有符号)和4294967295(无符号),占用32个位。如果传输Int而不是直接传输String,我们可以省下60%的流量。而行情数据中数字就是最大的传输量,通过Binary来传输行情数据可以有效的节省流量并提升传输效率。
但行情数据中又不只是数字,还有字符串的类型,这咋办呢。很简单,我们将要传输的数据以“字段”来进行定义和规范,转为byte后拼接起来即可。比如下面这个接口:
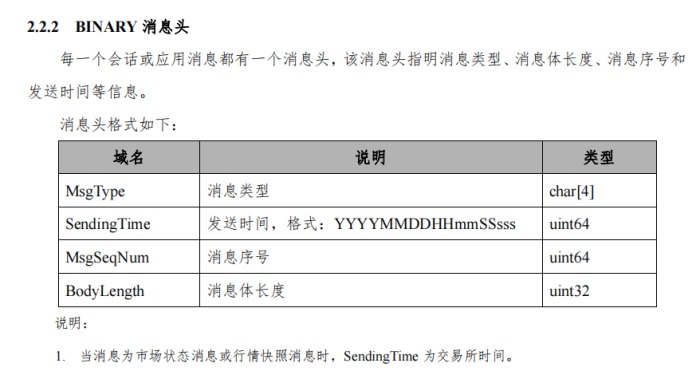
MsgType这个字段我们规定好就是char[4],那么它占用4x8=32个位。
SendingTime这个字段我们规定好是uint64,那么它占用64个位。
同理MsgSeqNum占用64个位,BodyLength占用32个位。
如果是二进制的格式就像下面这样,传输的时候只需要首位相连拼在一起,然后发出去即可。接收方则按前面约定的格式将二进制流按指定位数截断,接着再转化成需要的格式进行处理。
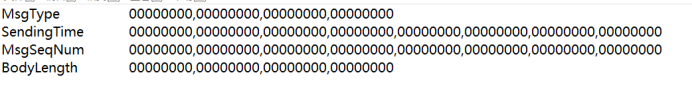
不过我们一般不会直接在二进制做处理,而使用byte(8位一组)来处理比较合适,但byte与Int、String的转换需要注意,特别是Int还分Int8、Int16、Int32、Int64。
另外浮点数怎么转换呢?通用的办法是将所有浮点数都转为整数,并约定好整数位和小数位。比如uint64,N13(5),其含义是字段占用为64位的无符号整数,传输的数值是13位的,其中最后5位是小数位,比如我们传输1234567890123,其中整数位是12345678,小数位是90123,结果是12345678.90123。
三、登录
登录消息
我们先看接口:
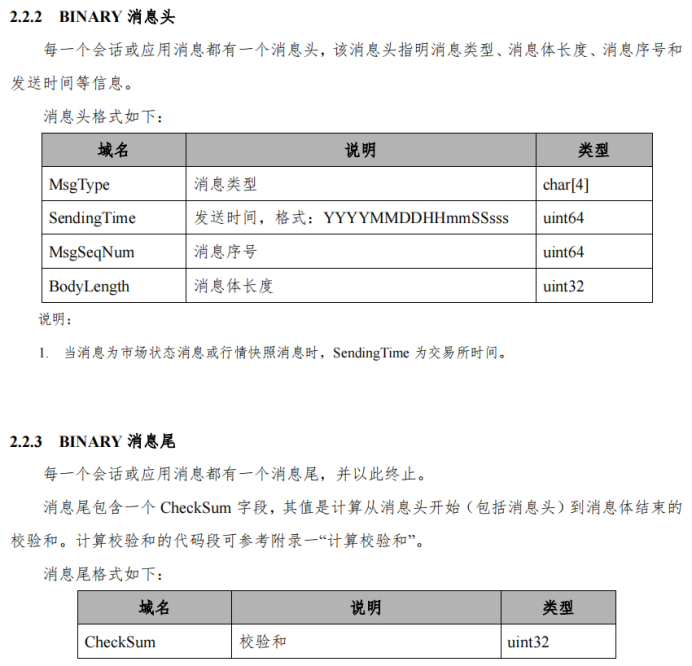
简单来说,一个登录消息包含了头、尾、体三个部分,每个部分又由若干字段组成,需要注意的是checksum是对除checksum字段外所有字段的校验和,另外关于校验和的计算也有一些要注意的后面说。

其中str2Byte、int2Byte因为涉及字段的位数,所以都是需要自己写的,byteMerger是将两个byte数组拼接在一起,最终MsgBody是包含了头、尾、体三个部分的数据,只需要发给VDE就能登录了。
Socket连接
Socket连接比较简单了,其中IP是你VDE所在服务器IP,端口是在VDE配置文件中配的。ReadThread是处理Binary行情流的。

四、行情解析
先解析head
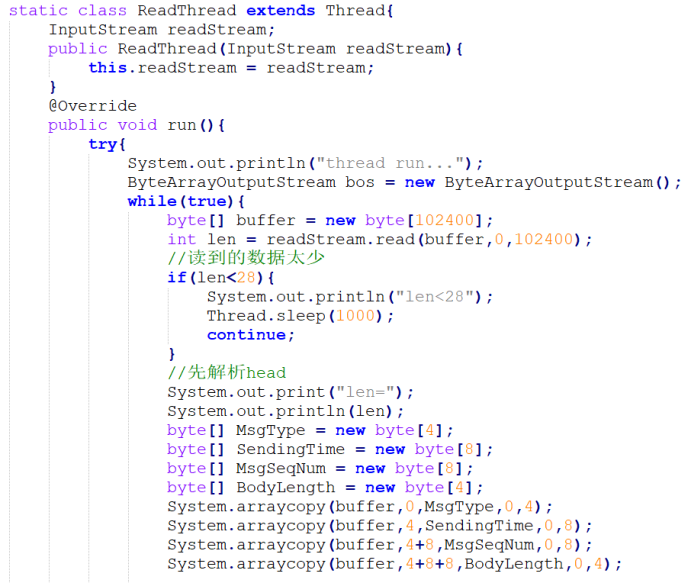
这段代码就是从socket接口中读取最大102400字节的数据,存到buffer中。这里我做了一些简化处理,后面详细说明。
根据接口,我们将buffer中指定位的内容存放到一个个特定大小的byte数组中,也就是MsgType、SendingTime、MsgSeqNum、BodyLength这些数组。

这段代码是根据接口将byte数组转化为string、int、long类型,其中int64我是用long来代替的。
校验和
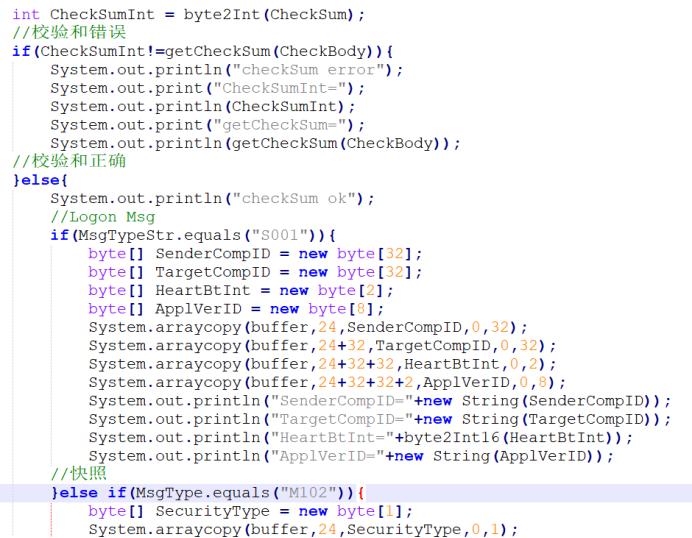
把读到的校验和与我们自己计算的校验和做个比较,必须校验通过才能进行下一步的解析。
关于校验和的计算,注意文档示例代码中是uint8,所以不是简单将byte转int就可以了,计算校验和过程中存在数值的溢出丢弃。

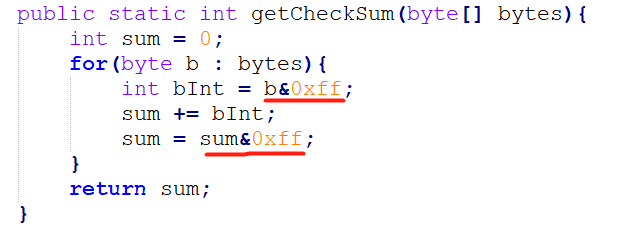
根据不同类型解析内容
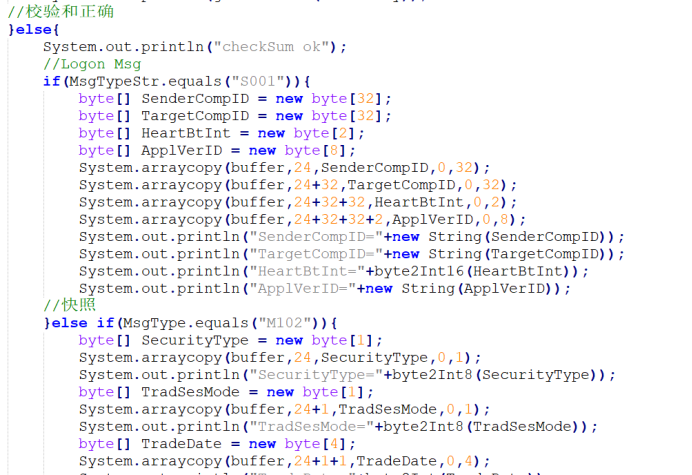
这里我只做了MsgType=S001、M102两种情况,对应logon消息和快照消息。
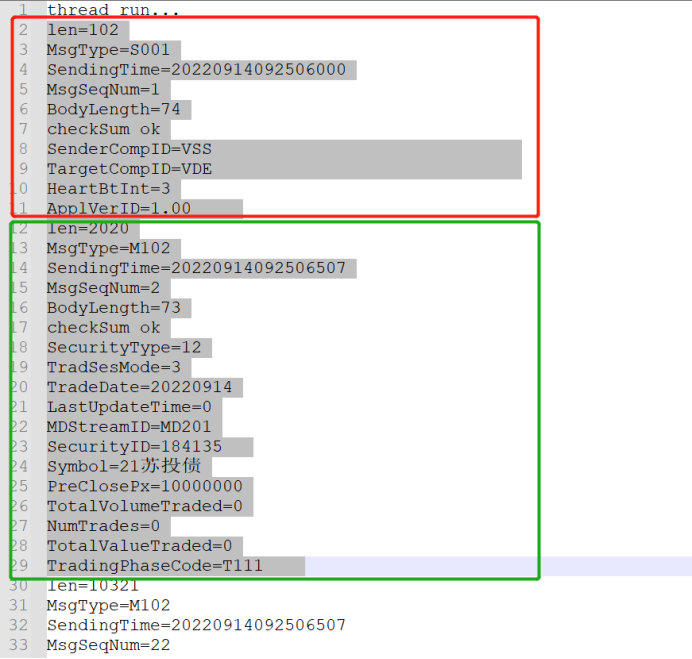
运行结果如上图,对于行情更详细的解析请参考接口文档。
流的问题

代码中,我使用了比较大的缓存来读流数据,因为处理过程中发现了一个问题:
“流行情不是逐条传输的”
也就是每次你收到的行情,不一定是完整的<head>+<body>+<checksum>这样,而可能存在下面几种情况:
1、一条完整的<head>+<body>+<checksum>
2、多条完整的<head>+<body>+<checksum>
3、一条完整的<head>+<body>+<checksum>再加上下一条行情的<head>或半个<body>
意思是流行情传输时像一条不停向你流动的河,在任意时间你从buffer中截取的数据可能有多有少,也可能只有一半,所以从socket获取到数据后,你先要把数据拼接起来,再找到有效的head和checksum,这两个之间的数据才是完整的数据。这个过程比较复杂,作为示例我就不搞了,你们加油。
五、总结
本篇我们做了个简单的上交所流行情Binary接口示例,注意只是能简单跑起来的示例,其中存在很多隐患和问题,出了毛病别找我。
完整的代码:
import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.*; import java.net.Socket; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.util.Arrays; public class connSH{ public static byte[] getNewByteArr(int n){ byte[] newByteArr = new byte[n]; for(int i=0; i<n; i++){ newByteArr[i] = 32; } return newByteArr; } public static byte[] int2Byte(int n, int size){ byte[] b = new byte[size]; int s = size; for(int i=s-1; i>=0; i-- ){ b[i] = (byte)(n>>(size-i-1)*8&0xff); } return b; } public static byte[] str2Byte(String str, int size){ byte[] strByte = str.getBytes(); byte[] strByteArr = new byte[size]; for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ strByteArr[i] = 32; } System.arraycopy(strByte, 0, strByteArr, 0, strByte.length); return strByteArr; } public static int getCheckSum(byte[] bytes){ int sum = 0; for(byte b : bytes){ int bInt = b&0xff; sum += bInt; sum = sum&0xff; } return sum; } public static byte[] byteMerger(byte[] bt1, byte[] bt2){ byte[] bt3 = new byte[bt1.length + bt2.length]; System.arraycopy(bt1, 0, bt3, 0, bt1.length); System.arraycopy(bt2, 0, bt3, bt1.length, bt2.length); return bt3; } public static long byte2Long(byte[] buffer){ long values = 0; for(int i=0;i<8;i++){ values<<=8; values|=(buffer[i]&0xff); } return values; } public static int byte2Int(byte[] buffer){ int values = 0; for(int i =0; i<4; i++){ values <<= 8; values |= (buffer[i]&0xff); } return values; } public static int byte2Int16(byte[] buffer){ int values = 0; for(int i=0; i<2; i++){ values <<= 8; values |= (buffer[i]&0xff); } return values; } public static int byte2Int8(byte[] buffer){ int values = 0; for(int i=0; i<1; i++){ values <<= 8; values |= (buffer[i]&0xff); } return values; } static class ReadThread extends Thread{ InputStream readStream; public ReadThread(InputStream readStream){ this.readStream = readStream; } @Override public void run(){ try{ System.out.println("thread run..."); ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); while(true){ //注意从socket获取的数据有多有少,不一定就是一条完整的,这里我做了简化处理 //也就是我这里只处理了一条完整的,其他的都丢弃了 byte[] buffer = new byte[102400]; int len = readStream.read(buffer,0,102400); //读到的数据太少 if(len<28){ System.out.println("len<28"); Thread.sleep(1000); continue; } //先解析head System.out.print("len="); System.out.println(len); byte[] MsgType = new byte[4]; byte[] SendingTime = new byte[8]; byte[] MsgSeqNum = new byte[8]; byte[] BodyLength = new byte[4]; System.arraycopy(buffer,0,MsgType,0,4); System.arraycopy(buffer,4,SendingTime,0,8); System.arraycopy(buffer,4+8,MsgSeqNum,0,8); System.arraycopy(buffer,4+8+8,BodyLength,0,4); String MsgTypeStr = new String(MsgType); System.out.print("MsgType="); System.out.println(MsgTypeStr); long SendingTimeInt = byte2Long(SendingTime); System.out.print("SendingTime="); System.out.println(SendingTimeInt); long MsgSeqNumInt = byte2Long(MsgSeqNum); System.out.print("MsgSeqNum="); System.out.println(MsgSeqNumInt); int BodyLengthInt = byte2Int(BodyLength); System.out.print("BodyLength="); System.out.println(BodyLengthInt); byte[] MsgBody = new byte[BodyLengthInt]; byte[] CheckSum = new byte[4]; System.arraycopy(buffer,4+8+8+4,MsgBody,0,BodyLengthInt); System.arraycopy(buffer,4+8+8+4+BodyLengthInt,CheckSum,0,4); byte[] CheckBody = new byte[4+8+8+4+BodyLengthInt]; System.arraycopy(buffer,0,CheckBody,0,CheckBody.length); int CheckSumInt = byte2Int(CheckSum); //校验和错误 if(CheckSumInt!=getCheckSum(CheckBody)){ System.out.println("checkSum error"); System.out.print("CheckSumInt="); System.out.println(CheckSumInt); System.out.print("getCheckSum="); System.out.println(getCheckSum(CheckBody)); //校验和正确 }else{ System.out.println("checkSum ok"); //Logon Msg if(MsgTypeStr.equals("S001")){ byte[] SenderCompID = new byte[32]; byte[] TargetCompID = new byte[32]; byte[] HeartBtInt = new byte[2]; byte[] ApplVerID = new byte[8]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24,SenderCompID,0,32); System.arraycopy(buffer,24+32,TargetCompID,0,32); System.arraycopy(buffer,24+32+32,HeartBtInt,0,2); System.arraycopy(buffer,24+32+32+2,ApplVerID,0,8); System.out.println("SenderCompID="+new String(SenderCompID)); System.out.println("TargetCompID="+new String(TargetCompID)); System.out.println("HeartBtInt="+byte2Int16(HeartBtInt)); System.out.println("ApplVerID="+new String(ApplVerID)); //快照 }else if(MsgTypeStr.equals("M102")){ byte[] SecurityType = new byte[1]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24,SecurityType,0,1); System.out.println("SecurityType="+byte2Int8(SecurityType)); byte[] TradSesMode = new byte[1]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24+1,TradSesMode,0,1); System.out.println("TradSesMode="+byte2Int8(TradSesMode)); byte[] TradeDate = new byte[4]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24+1+1,TradeDate,0,4); System.out.println("TradeDate="+byte2Int(TradeDate)); byte[] LastUpdateTime = new byte[4]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24+1+1+4,LastUpdateTime,0,4); System.out.println("LastUpdateTime="+byte2Int(LastUpdateTime)); byte[] MDStreamID = new byte[5]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24+1+1+4+4,MDStreamID,0,5); System.out.println("MDStreamID="+new String(MDStreamID)); byte[] SecurityID = new byte[8]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24+1+1+4+4+5,SecurityID,0,8); System.out.println("SecurityID="+new String(SecurityID)); byte[] Symbol = new byte[8]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24+1+1+4+4+5+8,Symbol,0,8); System.out.println("Symbol="+new String(Symbol,"GBK")); byte[] PreClosePx = new byte[8]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24+1+1+4+4+5+8+8,PreClosePx,0,8); System.out.println("PreClosePx="+byte2Long(PreClosePx)); byte[] TotalVolumeTraded = new byte[8]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24+1+1+4+4+5+8+8+8,TotalVolumeTraded,0,8); System.out.println("TotalVolumeTraded="+byte2Long(TotalVolumeTraded)); byte[] NumTrades = new byte[8]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24+1+1+4+4+5+8+8+8+8,NumTrades,0,8); System.out.println("NumTrades="+byte2Long(NumTrades)); byte[] TotalValueTraded = new byte[8]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24+1+1+4+4+5+8+8+8+8+8,TotalValueTraded,0,8); System.out.println("TotalValueTraded="+byte2Long(TotalValueTraded)); byte[] TradingPhaseCode = new byte[8]; System.arraycopy(buffer,24+1+1+4+4+5+8+8+8+8+8+8,TradingPhaseCode,0,8); System.out.println("TradingPhaseCode="+new String(TradingPhaseCode)); } } } }catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } } public static void main(String[] args){ try{ //head byte[] MsgType = str2Byte("S001", 4); byte[] SendingTime = int2Byte(0,8); byte[] MsgSeqNum = int2Byte(0,8); byte[] BodyLength = int2Byte(32+32+2+8,4); //logon body byte[] SenderCompID = str2Byte("VSS",32); byte[] TargetCompID = str2Byte("VDE",32); byte[] HeartBtInt = int2Byte(0,2); byte[] AppVerID = str2Byte("1.00",8); byte[] MsgBody = byteMerger(MsgType, SendingTime); MsgBody = byteMerger(MsgBody, MsgSeqNum); MsgBody = byteMerger(MsgBody, BodyLength); MsgBody = byteMerger(MsgBody, SenderCompID); MsgBody = byteMerger(MsgBody, TargetCompID); MsgBody = byteMerger(MsgBody, HeartBtInt); MsgBody = byteMerger(MsgBody, AppVerID); //checksum byte[] CheckSum = int2Byte(getCheckSum(MsgBody),4); MsgBody = byteMerger(MsgBody, CheckSum); //connect Socket socket = new Socket("xxx你的IP",9126); OutputStream outStream = socket.getOutputStream(); outStream.write(MsgBody); outStream.flush(); //listion thread ReadThread readThread = new ReadThread(socket.getInputStream()); readThread.start(); while(true){ Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("every 3000..."); } }catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } }