1.FileOutputStream文件字节输出流
作用:把内存中的数据写入到硬盘当中
构造方法
public FileOutputStream(File file) :创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件。
public FileOutputStream(String name) : 创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。
当你创建一个流对象时,必须传入一个文件路径。该路径下,如果没有这个文件,会创建该文件。如果有这个文件,会清空这个文件的数据。
写入数据的原理:(内存 - - > 硬盘)
Java程序 - - > JVM(java虚拟机)- - > OS(操作系统)- - > OS调用写数据的方法 - - > 把数据写入文件当中
public class OUTPutStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\JA\Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\a.txt"); fos.write(95); fos.close(); } }
一次写多个字节:
如果写的第一个字节是正数(0-127),那么显示的时候会查ASCII码表
如果写的第一个字节是负数,那第一个字节会和第二个字节,两个字节组成一个中文显示,查询系统默认码表(GBK)
写出指定长度字节数组: write(byte[] b, int off, int len) ,每次写出从off索引开始,len个字节
写入字符串的方法:可以使用String类中的方法把字符串,转换为字节数组
byte【】 getBytes() 将字符串转换为字节数组
public class OUTPutStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\JA\Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\a.txt"); byte[] bytes = "chris".getBytes(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes)); fos.write(bytes); fos.close(); } }
续写和换行,在构造方法中将append参数设置为true
Windows换行符号:
Linux:/n
mac:/r
public class OUTPutStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\JA\Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\a.txt",true); fos.write("你好 ".getBytes()); fos.write("咋啦 ".getBytes()); fos.close(); } }
2.FileInputStream 文件字节输入流
public class FileINputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\a.txt"); //相对路径 int len = 0; //记录读取到的字节 //循环遍历文件 while ((len = fis.read()) != -1) { System.out.print(len); } fis.close(); } }
一次读取多个字节的方法:
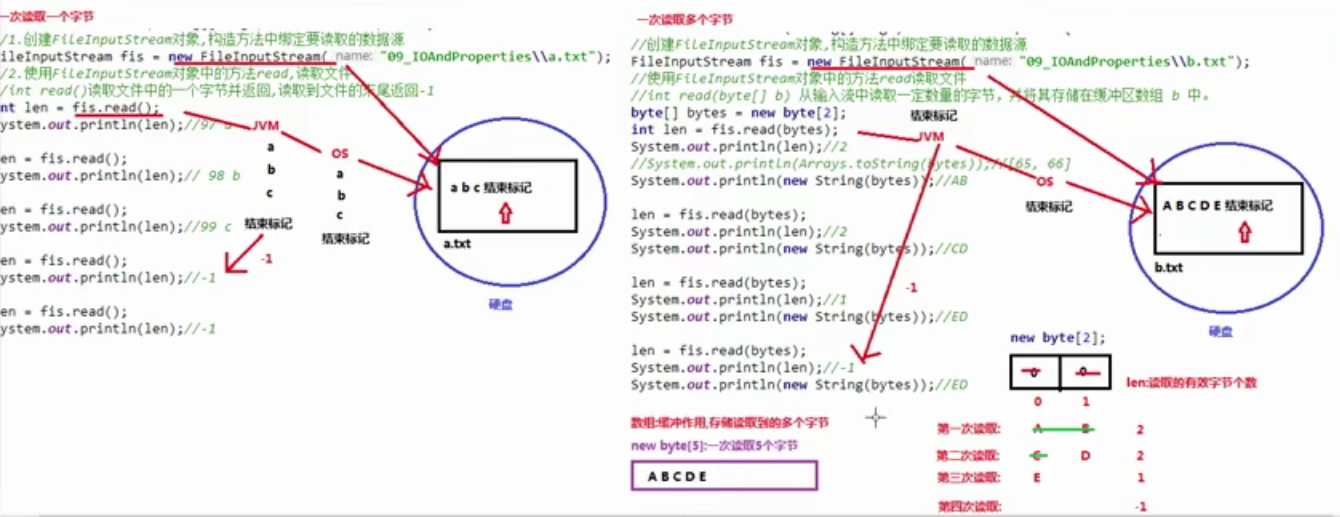
public class FileINputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\a.txt"); //相对路径 byte[] bytes = new byte[4];//建立一个能装四个字节的数组 int len = fis.read(bytes); //此时bytes里面会从文件中抓取前四个字节放入到数组中 System.out.println(len);//len表示的是读取的有效字节个数 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes)); System.out.println(new String(bytes)); } }
改进方法:
public class FileINputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\a.txt"); //相对路径 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];//建立一个能装1024个字节的数组 int len = 0; while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) { System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len)); //len为有效字节个数 } } }
文件复制:
public class FileCopy { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\Baseball\cai.jpg");//创建文件字节输入流 读取数据 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\AAD\cai.jpg");//创建文件字节输出流 写入数据 int len = 0;//记录读取的有效字节 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];//一次多读一些 while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){ fos.write(bytes,0,len);//用字节输出流把读取到的字节写入到文件中 } //释放资源,先关写的 fos.close(); fis.close(); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("复制文件的时间"+(endTime - startTime)+ "毫秒"); } }
3.文件字符输入流 FileReader
读取文件:
public class FR { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileReader fr = new FileReader("Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\a.txt"); char[] cs = new char[1024];//用来存储读取到的多个字符 int len = 0;//记录的是每次读取的有效字符个数 while ((len = fr.read(cs)) != -1) { System.out.print(new String(cs, 0, len)); } } }
4.文件字符输出流 FileWriter 写入时先写入内存缓冲区中 因为要把字符转换为字节 flush一下就行了
public class FR { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\b.txt",true); fw.write(98); char[] cs = {'a','c','e'}; fw.write(cs); fw.write("帅哥"); fw.flush(); fw.close(); } }
5.处理流中异常相关问题
变量在定义的时候可以没有值,但在使用的时候必须有值
public class FR { public static void main(String[] args) { FileWriter fw = null;//提高变量的作用域,变量的值必须先定义,不然局部无法使用 try { fw = new FileWriter("r:Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\b.txt", true); fw.write("船只"); fw.flush(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println(e); } finally { //如果创建对象失败了,那么fw的默认值为空,就会抛出空指针异常,需要进行判断 if (fw != null) { try { fw.close();//本身存在异常,需要try catch } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
JDK7的新特性 try()括号里放对象,作用域只在try里有效,而且自动释放
public class FR { public static void main(String[] args) { try (FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("r:Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\b.txt", true)) { fw.write("船只"); fw.flush(); } catch(IOException e) { System.out.println(e); } } }
6.Properties属性集 双列集合(key和value默认都是字符串) 唯一一个和IO流相结合的集合
public Object setProperty(String key, String value) : 保存一对属性。
public String getProperty(String key) :使用此属性列表中指定的键搜索属性值。
public Set<String> stringPropertyNames() :所有键的名称的集合。
public class FR { public static void main(String[] args) { Properties prop = new Properties(); //存储属性值 prop.setProperty("chris","21"); prop.setProperty("joe","20"); prop.setProperty("Lin","23"); //获取此集合中的健集 Set<String> set = prop.stringPropertyNames(); //遍历set集合,取出每一个键 for (String key : set) { //使用方法得到值 String value = prop.getProperty(key); System.out.println(key + value); } } }
(1)public void load(InputStream inStream) : 从字节输入流中读取键值对。
参数中使用了字节输入流,通过流对象,可以关联到某文件上,这样就能够加载文本中的数据了。
(2)public void store(OutputStream out,String comment)
不能写入中文!!字节输出流
(3)public void store(Writer writer,String comment)
字符输出流,可以写入中文
注释不能使用中文,一般使用空字符串
public class FR { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Properties prop = new Properties(); //存储属性值 prop.setProperty("chris","21"); prop.setProperty("joe","20"); prop.setProperty("Lin","23"); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("D:\Baseball\cai.txt"); prop.store(fw,"sava data"); fw.close(); } }
7.缓冲流
缓冲流,也叫高效流,是对4个基本的 FileXxx 流的增强,所以也是4个流,按照数据类型分类:
字节缓冲流: BufferedInputStream , BufferedOutputStream
字符缓冲流: BufferedReader(特有方法readline,无数据时返回null,末尾不含任何终止符,需自己换行) , BufferedWriter(提供了个newline方法来换行)
缓冲流的基本原理,是在创建流对象时,会创建一个内置的默认大小的缓冲区数组,通过缓冲区读写,减少系统IO次数,从而提高读写的效率。
public class Buffered { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\JA\Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\f.txt",true); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); bos.write("我是帅哥".getBytes()); bos.flush(); bos.close(); } }
复制文件的效率大大提升:
public class Buffered { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { long s = System.currentTimeMillis(); BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\JA\Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\f.txt")); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\JA\Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\g.txt",true); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; while ((len = bis.read(bytes))!= -1){ bos.write(bytes,0,len); } bis.close(); bos.close(); long e = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("共耗时" + (e-s) + "毫秒"); } }
文本排序练习!!!重点
public class TextSort { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.先创建hashmap集合对读取的数据进行存储 HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); //2.创建两个流对象 BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\f.txt")); BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\new.txt")); //3.使用readline方法来逐行读取文本 String line; //用来记录文本 while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) { //4.对读取的文本进行切割 String[] arr = line.split("\."); //序号和文本以.来分割 //5.把切割好的键和值写入到hashmap中 map.put(arr[0], arr[1]); //每次读取时arr【0】为序号 arr【1】为文本 } //6.遍历hashmap集合 for (String key : map.keySet()){ String value = map.get(key); // 通过key获取value line = key + "." + value; //这就是完整的一条内容 //7.将数据写回去 writer.write(line); writer.newLine();//换行 } reader.close(); writer.close(); } }
8.转换流
转换流 java.io.InputStreamReader ,是Reader的子类,是从字节流到字符流的桥梁。它读取字节,并使用指定的字符集将其解码为字符。它的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以接受平台的默认字符集。
构造方法
InputStreamReader(InputStream in) : 创建一个使用默认字符集的字符流。
InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName) : 创建一个指定字符集的字符流。
转换流 java.io.OutputStreamWriter ,是Writer的子类,是从字符流到字节流的桥梁。使用指定的字符集将字符编码为字节。它的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以接受平台的默认字符集。
构造方法
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream in) : 创建一个使用默认字符集的字符流。
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream in, String charsetName) : 创建一个指定字符集的字符流。
public class FileINputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\f.txt"),"gbk"); osw.write("你好"); osw.flush(); osw.close(); } }
9.序列化和反序列化流
序列化操作
1. 一个对象要想序列化,必须满足两个条件:
该类必须实现 java.io.Serializable 接口, Serializable 是一个标记接口,不实现此接口的类将不会使任何状态序列化或反序列化,会抛出 NotSerializableException 。
该类的所有属性必须是可序列化的。如果有一个属性不需要可序列化的,则该属性必须注明是瞬态的,使用transient 关键字修饰。
Static关键字修饰的变量是不能被序列化的,序列化的都是对象,因为static优先于对象进入到内存中
public class FileINputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("Part1-basic\src\basicpart\day01\StreamM\f.txt")); oos.writeObject(new Person("chris",20)); //该类必须是标记接口的可序列化对象 oos.close(); } }
另外,当JVM反序列化对象时,能找到class文件,但是class文件在序列化对象之后发生了修改,那么反序列化操作也会失败,抛出一个 InvalidClassException 异常。发生这个异常的原因如下:
该类的序列版本号与从流中读取的类描述符的版本号不匹配
该类包含未知数据类型
该类没有可访问的无参数构造方法
Serializable 接口给需要序列化的类,提供了一个序列版本号。 serialVersionUID 该版本号的目的在于验证序列化的对象和对应类是否版本匹配。
解决方法:在类中加入
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
10.打印流 PrintStream
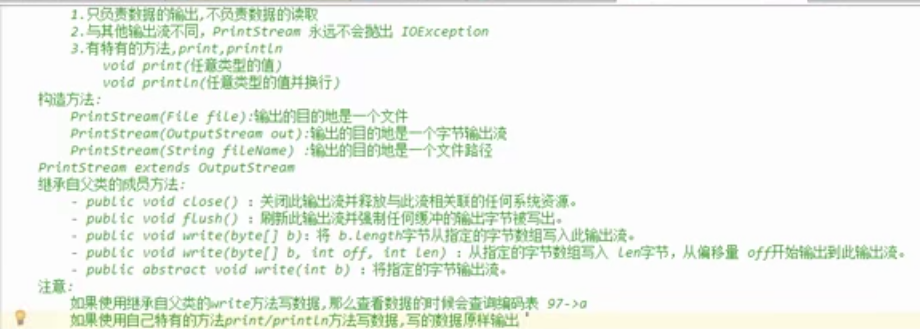
可以改变打印流向
