集合
1.1集合介绍:
集合是Java中提供的一种容器,可以用来存储多个数据。它与数组的不同之处在于,数组的长度是固定的,集合的长度是可变的。集合中存储的元素必须是引用数据类型。
1.2集合的继承实现关系
查看API可以知道,ArrayList类继承了抽象类AbstractList,同时实现接口List,List接口又继承了Collection接口。
Collection接口常用的子接口有:List接口、Set接口。
List接口常用的子类有:ArrayList类、LinkedList类。
Set接口常用的子类有:HashSet类、LinkedHashSet类

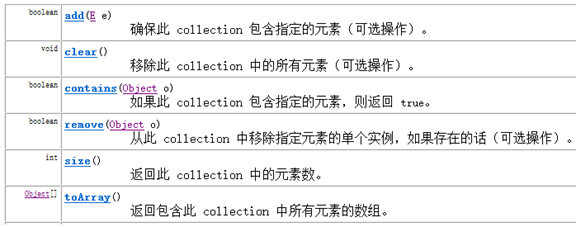
1.3Collection接口的基本方法
迭代器
2.1 Iterator接口常用方法
迭代器可以用来遍历集合,下面用代码演示用迭代器遍历一个集合
package com.oracle.demo01; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Iterator; public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub /*Collection<String> coll=new ArrayList(); coll.add("吴二狗"); coll.add("吴三桂"); coll.add("吴四娘"); coll.add("吴五六"); coll.add("吴六一");*/ /*//1.获得Iterator对象 Iterator<String> it=coll.iterator(); //判断集合是否下一个有元素 while(it.hasNext()) { String str=it.next(); System.out.println(str); }*/ //for循环的形式 /*for(Iterator<String> it=coll.iterator();it.hasNext();) { System.out.println(it.next()); }*/ Collection<Person> c=new ArrayList(); Person p1=new Person("吴二狗",18,"女"); Person p2=new Person("吴三贵",20,"女"); Person p3=new Person("吴四娘",22,"女"); c.add(p1); c.add(p2); c.add(p3); Iterator<Person> it=c.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } for(Iterator<Person> it2=c.iterator();it2.hasNext();) { System.out.println(it2.next()); } } }
2.2集合元素的向下转型
通过前面的学习,我们知道集合中可以存储任何对象。那么存进去的数据还是原来的类型吗?不是了,而是提升成了Object。取出时要使用元素的特有内容,必须要将元素向下转型。
Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add("abc"); coll.add("aabbcc"); coll.add(1); Iterator it = coll.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { //由于元素被存放进集合后全部被提升为Object类型 //当需要使用子类对象特有方法时,需要向下转型 String str = (String) it.next(); System.out.println(str.length()); }
2.3泛型边界
使用泛型的好处:
将运行时期的ClassCastException,转移到了编译时期变成了编译失败。
避免了类型强转的麻烦。
import java.util.ArrayList; public class Test3 { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Chef> cf = new ArrayList<Chef>(); ArrayList<? extends Emp> list = cf;//? extends Emp 表示这是一个Emp泛型的子类泛型 Chef c = new Chef("1号",40); cf.add(c); Emp e = new Emp("a",30); //list.add(c);//但是,不能往里面对象 因为list的泛型 有可能是Emp类的其他子类 ArrayList<? super Emp>liste = new ArrayList<Object>(); //? super Emp 表示 liste的泛型是Emp或者其父类泛型 liste.add(c);//也可以放子类 liste.add(e);//可以放Emp类 //但这样取出时有风险,如果集合内有Emp的其他子类,那例如Chef c = (Chef)liste.get(index);有可能报错 } }
2.4泛型通配符
使用泛型通配符,可以向集合中存入任何类型的元素
package com.oracle.demo02; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Iterator; import com.oracle.demo01.Person; public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Collection<String> arr=new ArrayList<String>(); arr.add("123"); arr.add("abc"); arr.add("456"); // String[] str=new String[arr.size()]; // String[] str1=arr.toArray(str); // for(String s:str1) { // System.out.println(s); // } get(arr); Collection<Person> arr2=new ArrayList<Person>(); arr2.add(new Person("张三",18,"男")); get(arr2); } public static void get(Collection<?> coll) { Iterator<?> it=coll.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } } }
2.5增强for循环
package com.oracle.demo02; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Iterator; public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Collection<String> coll=new ArrayList<String>(); coll.add("1"); coll.add("Leeboring"); coll.add("1.5"); Iterator<String> it=coll.iterator(); // while(it.hasNext()) { // System.out.println(it.next().length()); // } /* * for(数据类型 变量:目标容器){} * 数据类型:目标容器里边存的什么类型数据 * * */ int arr[]= {12,6,9,8,7}; for(int i:arr) { System.out.println(i); } for(String str:coll) { System.out.println(str); } } }