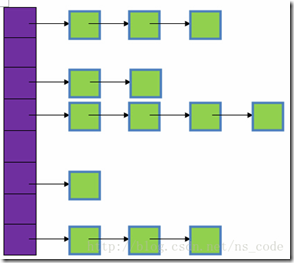
一、存储结构
在JDK1.8之前,HashMap采用桶+链表实现,本质就是采用数组+单向链表组合型的数据结构。它之所以有相当快的查询速度主要是因为它是通过计算散列码来决定存储的位置。HashMap通过key的hashCode来计算hash值,不同的hash值就存在数组中不同的位置,当多个元素的hash值相同时(所谓hash冲突),就采用链表将它们串联起来(链表解决冲突),放置在该hash值所对应的数组位置上。结构图如下:
图中,紫色部分代表哈希表,也称为哈希数组,数组中每个元素都是一个单链表的头结点,链表是用来解决冲突的,如果不同的key映射得到了数组的同一位置处,就将其放入单链表。
在JDK1.8中,HashMap的存储结构已经发生变化,它采用数组+链表+红黑树这种组合型数据结构。当hash值发生冲突时,会采用链表或者红黑树解决冲突。当同一hash值的结点数小于8时,则采用链表,否则,采用红黑树。这个重大改变,主要是提高查询速度。它的结构图如下:
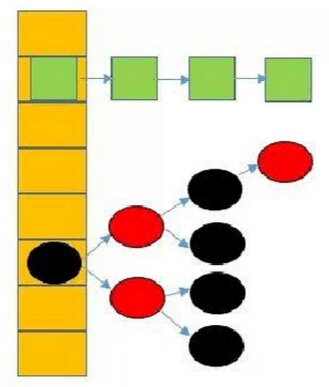
二、put方法
之所以先介绍存储结构,是为了更好的理解put方法。
public put(K key, V value)put方法调用了putVal方法,那我们再来看看它。
{
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
/*
Parameters:
hash hash for key
key the key
value the value to put
onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
Returns:
previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 如果table为空,或者还没有元素时,则扩容
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 如果首结点值为空,则创建一个新的首结点。
// 注意:(n - 1) & hash才是真正的hash值,也就是存储在table位置的index。在1.6中是封装成indexFor函数。
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else { // 到这儿了,就说明碰撞了,那么就要开始处理碰撞。
Node<K,V> e; K k;
// 如果在首结点与我们待插入的元素有相同的hash和key值,则先记录。
if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) // 如果首结点的类型是红黑树类型,则按照红黑树方法添加该元素
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else { // 到这一步,说明首结点类型为链表类型。
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
// 如果遍历到末尾时,先在尾部追加该元素结点。
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 当遍历的结点数目大于8时,则采取树化结构。
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 如果找到与我们待插入的元素具有相同的hash和key值的结点,则停止遍历。此时e已经记录了该结点
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 表明,记录到具有相同元素的结点
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e); // 这个是空函数,可以由用户根据需要覆盖
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
// 当结点数+1大于threshold时,则进行扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict); // 这个是空函数,可以由用户根据需要覆盖
return null;
}
参考: