本文体验MVC服务端和客户端验证。主要涉及:
※ 基础验证
※ 远程验证1个或多个属性及注意点
基础体验
创建MVC4的Internet项目,本身包含了基本的Model,Views,Controller.
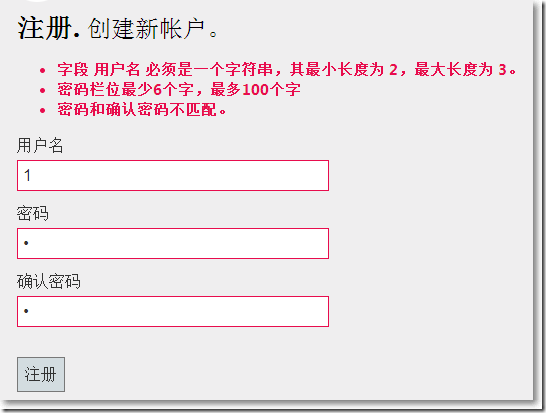
□ Model打上验证特性
public class RegisterModel { [Required] [StringLength(3, MinimumLength = 2)] //加 [Display(Name = "用户名")] public string UserName { get; set; } [Required] [StringLength(100, ErrorMessage = "{0}栏位最少{2}个字,最多{1}个字", MinimumLength = 6)] [DataType(DataType.Password)] [Display(Name = "密码")] public string Password { get; set; } [DataType(DataType.Password)] [Display(Name = "确认密码")] [Compare("Password", ErrorMessage = "密码和确认密码不匹配。")] public string ConfirmPassword { get; set; } }
□ HomeController中关于注册的部分
[AllowAnonymous] public ActionResult Register() { return View(); } // // POST: /Account/Register [HttpPost] [AllowAnonymous] [ValidateAntiForgeryToken] public ActionResult Register(RegisterModel model) { if (ModelState.IsValid) { // 尝试注册用户 try { WebSecurity.CreateUserAndAccount(model.UserName, model.Password); WebSecurity.Login(model.UserName, model.Password); return RedirectToAction("Index", "Home"); } catch (MembershipCreateUserException e) { ModelState.AddModelError("", ErrorCodeToString(e.StatusCode)); } } // 如果我们进行到这一步时某个地方出错,则重新显示表单 return View(model); }
□ /Home/Register视图
@model MvcValidation.Models.RegisterModel @{ ViewBag.Title = "注册"; } @using (Html.BeginForm()) { @Html.AntiForgeryToken() @Html.ValidationSummary() <fieldset> <legend>注册表单</legend> <ol> <li> @Html.LabelFor(m => m.UserName) @Html.TextBoxFor(m => m.UserName) </li> <li> @Html.LabelFor(m => m.Password) @Html.PasswordFor(m => m.Password) </li> <li> @Html.LabelFor(m => m.ConfirmPassword) @Html.PasswordFor(m => m.ConfirmPassword) </li> </ol> <input type="submit" value="注册" /> </fieldset> } @section Scripts { @Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jqueryval") }
□ 去除客户端验证
<appSettings>
<add key="ClientValidationEnabled" value="false" />
<add key="UnobtrusiveJavaScriptEnabled" value="false" />
</appSettings>
把与客户端验证相关的属性设置为false,发现验证慢了很多。
体验远程验证属性
有时候,比如验证用户名是否存在,我们希望可以发一个异步请求到控制器。
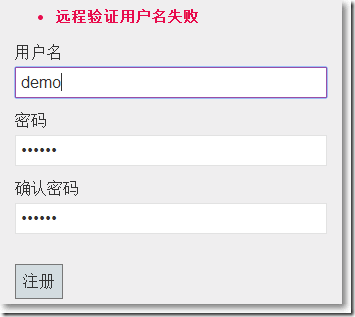
给属性打上Remote属性。
public class RegisterModel { [Required] [StringLength(6, MinimumLength = 2)] //加 [Display(Name = "用户名")] [Remote("CheckUserName","Validate", ErrorMessage = "远程验证用户名失败")] public string UserName { get; set; } [Required] [StringLength(100, ErrorMessage = "{0}栏位最少{2}个字,最多{1}个字", MinimumLength = 6)] [DataType(DataType.Password)] [Display(Name = "密码")] public string Password { get; set; } [DataType(DataType.Password)] [Display(Name = "确认密码")] [System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Compare("Password", ErrorMessage = "密码和确认密码不匹配。")] public string ConfirmPassword { get; set; } }
Validate控制器
//这里的参数userName必须和view model中的属性UserName保持一致 public JsonResult CheckUserName(string userName) { bool isValidate = false; //假设让某个username不通过 if (userName != "demo") { isValidate = true; } //Remote验证是通过get方式请求的 return Json(isValidate, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet); }
注意:
远程验证控制器方法参数必须和view model中需要远程验证的属性一致,但不区分大小写。
□ 同时远程验证多个属性
比如我们想同时远程验证UserName和Email。
我们可以在View model的其中一个属性打上Remote,其它需要Remote验证的属性放在AdditionalFields中列举。
public string UserName { get; set; }
[Remote("CheckUserName", "Validate", AdditionalFields = "UserName", ErrorMessage = "远端验证失败")]
public string Email { get; set; }
注意:
AdditionalFields列举的字段是区分大小写的。
对应控制器远程验证方法:
//这里的参数userName,email必须和view model中的属性UserName, Email保持一致,不区分大小写 public JsonResult CheckUserName(string userName, string email) { bool isValidate = false; //假设让某个username不通过 if (userName != "demo" && email != "abc@qq.com" ) { isValidate = true; } //Remote验证是通过get方式请求的 return Json(isValidate, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet); }