解题代码部分来自网友,如果有不对的地方,欢迎各位大佬评论
题目1、胡同门牌号小明家住在一条胡同里。胡同里的门牌号都是连续的正整数,由于历史原因,最小的号码并不是从1开始排的。
有一天小明突然发现了有趣的事情:
如果除去小明家不算,胡同里的其它门牌号加起来,刚好是100!
并且,小明家的门牌号刚好等于胡同里其它住户的个数!
请你根据这些信息,推算小明家的门牌号是多少?
请提交该整数,不要填写任何多余的内容或说明性文字。
运行结果有两个:8和10,但是针对此题,答案到底是8还是10还是8和10,不好判定。以下代码仅供参考。
(1)8
(2)10
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 2;i < 200;i++) {
int sum = 0;
int count = 0;
for(int j = i;j < 200;j++) {
count++;
sum = sum + j;
if(sum - count + 1 == 100 && count - 1 >= i)
System.out.println("i = "+i+", j = "+j+", count = "+(count-1));
}
}
}
}
把1~16的数字填入4x4的方格中,使得行、列以
及两个对角线的和都相等,满足这样的特征时称
为:四阶幻方。
四阶幻方可能有很多方案。如果固定左上角为1
,请计算一共有多少种方案。
比如:
1 2 15 16
12 14 3 5
13 7 10 4
8 11 6 9
以及:
1 12 13 8
2 14 7 11
15 3 10 6
16 5 4 9
就可以算为两种不同的方案。
请提交左上角固定为1时的所有方案数字,不要
填写任何多余内容或说明文字。
答案:416
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static boolean[] used = new boolean[17];
public static ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
public static int count = 0;
public boolean check(int[] A, int step) {
if(step >= 4)
if(A[0] + A[1] + A[2] + A[3] != 34)
return false;
if(step >= 8)
if(A[4] + A[5] + A[6] + A[7] != 34)
return false;
if(step >= 12)
if(A[8] + A[9] + A[10] + A[11] != 34)
return false;
if(step >= 13)
if(A[0] + A[4] + A[8] + A[12] != 34 || A[3] + A[6] + A[9] + A[12] != 34)
return false;
if(step >= 14)
if(A[1] + A[5] + A[9] + A[13] != 34)
return false;
if(step >= 15)
if(A[2] + A[6] + A[10] + A[14] != 34)
return false;
if(step >= 16)
if(A[3] + A[7] + A[11] + A[15] != 34 || A[0] + A[5] + A[10] + A[15] != 34)
return false;
return true;
}
public void dfs(int[] A, int step) {
if(check(A, step) == false)
return;
if(step == 16) {
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer("");
for(int i = 0;i < A.length;i++)
s.append(A[i]);
if(!list.contains(s.toString())) {
list.add(s.toString());
count++;
}
return;
}
for(int i = 2;i <= 16;i++) {
if(used[i] == false) {
used[i] = true;
A[step] = i;
dfs(A, step + 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main test = new Main();
int[] A = new int[16];
A[0] = 1;
used[1] = true;
test.dfs(A, 1);
System.out.println(count);
}
}
标题:显示二叉树
排序二叉树的特征是:
某个节点的左子树的所有节点值都不大于本节点
值。
某个节点的右子树的所有节点值都不小于本节点
值。
为了能形象地观察二叉树的建立过程,小明写了
一段程序来显示出二叉树的结构来。
class BiTree
{
private int v;
private BiTree l;
private BiTree r;
public BiTree(int v){
this.v = v;
}
public void add(BiTree the){
if(the.v < v){
if(l==null) l
= the;
else l.add
(the);
}
else{
if(r==null) r
= the;
else r.add
(the);
}
}
public int getHeight(){
int h = 2;
int hl = l==null? 0 :
l.getHeight();
int hr = r==null? 0 :
r.getHeight();
return h + Math.max
(hl,hr);
}
public int getWidth(){
int w = (""+v).length();
if(l!=null) w +=
l.getWidth();
if(r!=null) w +=
r.getWidth();
return w;
}
public void show(){
char[][] buf = new char
[getHeight()][getWidth()];
printInBuf(buf, 0, 0);
showBuf(buf);
}
private void showBuf(char[][] x){
for(int i=0; i<x.length;
i++){
for(int j=0;
j<x[i].length; j++)
System.out.print(x[i][j]==0? ' ':x[i][j]);
System.out.println();
}
}
private void printInBuf(char[][]
buf, int x, int y){
String sv = "" + v;
int p1 = l==null? x :
l.getRootPos(x);
int p2 = getRootPos(x);
int p3 = r==null? p2 :
r.getRootPos(p2+sv.length());
buf[y][p2] = '|';
for(int i=p1; i<=p3; i+
+) buf[y+1][i]='-';
for(int i=0; i<sv.length
(); i++) ________________________________; //填空
位置
if(p1<p2) buf[y+1][p1]
= '/';
if(p3>p2) buf[y+1][p3]
= '\';
if(l!=null) l.printInBuf
(buf,x,y+2);
if(r!=null) r.printInBuf
(buf,p2+sv.length(),y+2);
}
private int getRootPos(int x){
return l==null? x : x +
l.getWidth();
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[]
args)
{
BiTree tree = new
BiTree(500);
tree.add(new BiTree
(200));
tree.add(new BiTree
(509));
tree.add(new BiTree
(100));
tree.add(new BiTree
(250));
tree.add(new BiTree
(507));
tree.add(new BiTree
(600));
tree.add(new BiTree
(650));
tree.add(new BiTree
(450));
tree.add(new BiTree
(510));
tree.add(new BiTree
(440));
tree.add(new BiTree
(220));
tree.show();
}
}
对于上边的测试数据,应该显示出:
|
/--------------500---
| |
/--200--- /--509---
| | | |
/--250--- 507 /--600
| | | |
/--450 510 650
|
(如有对齐问题,请参考【图1.png】)
请分析程序逻辑,填写划线部分缺失的代码。
注意,只填写缺少的部分,不要填写已有的代码
或符号,也不要加任何说明文字。
答案:buf[y+1][p2+i] = sv.charAt(i)
X星的坦克战车很奇怪,它必须交替地穿越正能量辐射区和负能量辐射区才能保持正常运转,否则将报废。
某坦克需要从A区到B区去(A,B区本身是安全区,没有正能量或负能量特征),怎样走才能路径最短?
已知的地图是一个方阵,上面用字母标出了A,B区,其它区都标了正号或负号分别表示正负能量辐射区。
例如:
A + - + -
- + - - +
- + + + -
+ - + - +
B + - + -
坦克车只能水平或垂直方向上移动到相邻的区。
数据格式要求:
输入第一行是一个整数n,表示方阵的大小, 4<=n<100
接下来是n行,每行有n个数据,可能是A,B,+,-中的某一个,中间用空格分开。
A,B都只出现一次。
要求输出一个整数,表示坦克从A区到B区的最少移动步数。
如果没有方案,则输出-1
例如:
用户输入:
5
A + - + -
- + - - +
- + + + -
+ - + - +
B + - + -
则程序应该输出:
10
资源约定:
峰值内存消耗(含虚拟机) < 512M
CPU消耗 < 2000ms
请严格按要求输出,不要画蛇添足地打印类似:“请您输入...” 的多余内容。
所有代码放在同一个源文件中,调试通过后,拷贝提交该源码。
注意:不要使用package语句。不要使用jdk1.7及以上版本的特性。
注意:主类的名字必须是:Main,否则按无效代码处理。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static int min = 1000 * 1000;
public static int n;
public static String[][] map;
public static int[][] move = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; //表示分别向上、下、左、右移动一步
public void dfs(boolean[][] visited, int x, int y, int count) {
if(map[x][y].equals("B")) {
min = Math.min(min, count);
return;
}
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i++) {
int tempX = x + move[i][0];
int tempY = y + move[i][1];
if(tempX >= 0 && tempX < n && tempY >= 0 && tempY < n) {
if(!map[x][y].equals(map[tempX][tempY]) && !visited[tempX][tempY]) {
visited[tempX][tempY] = true;
dfs(visited, tempX, tempY, count + 1);
visited[tempX][tempY] = false;
}
}
}
}
public void getResult() {
int startX = 0, startY = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++)
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++)
if(map[i][j] == "A") {
startX = i;
startY = j;
}
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][n];
visited[startX][startY] = true;
dfs(visited, startX, startY, 0);
if(min == 1000 * 1000)
System.out.println("-1");
else
System.out.println(min);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main test = new Main();
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
in.nextLine();
String[] T = new String[n];
map = new String[n][n];
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
T[i] = in.nextLine();
map[i] = T[i].split(" ");
}
test.getResult();
}
}
Pear有一个字符串,不过他希望把它切成两段。
这是一个长度为N(<=10^5)的字符串。
Pear希望选择一个位置,把字符串不重复不遗漏地切成两段,长度分别是t和N-t(这两段都必须非空)。
Pear用如下方式评估切割的方案:
定义“正回文子串”为:长度为奇数的回文子串。
设切成的两段字符串中,前一段中有A个不相同的正回文子串,后一段中有B个不相同的非正回文子串,则该方案的得分为A*B。
注意,后一段中的B表示的是:“…非正回文…”,而不是: “…正回文…”。
那么所有的切割方案中,A*B的最大值是多少呢?
【输入数据】
输入第一行一个正整数N(<=10^5)
接下来一行一个字符串,长度为N。该字符串仅包含小写英文字母。
【输出数据】
一行一个正整数,表示所求的A*B的最大值。
【样例输入】
10
bbaaabcaba
【样例输出】
38
【数据范围】
对于20%的数据,N<=100
对于40%的数据,N<=1000
对于100%的数据,N<=10^5
资源约定:
峰值内存消耗(含虚拟机) < 512M
CPU消耗 < 2000ms
请严格按要求输出,不要画蛇添足地打印类似:“请您输入…” 的多余内容。
所有代码放在同一个源文件中,调试通过后,拷贝提交该源码。
注意:不要使用package语句。不要使用jdk1.7及以上版本的特性。
注意:主类的名字必须是:Main,否则按无效代码处理。
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static String A, S;
public int Manacher(String M, String N) {
int count = 0; //统计字符串M中不同正回文串个数
int[] P = new int[M.length()];
int mx = 0, id = 0;
for(int i = 1;i < M.length();i++) {
if(mx > i)
P[i] = Math.min(P[2 * id - i], mx - i);
else
P[i] = 1;
while(i+P[i] < M.length() && i-P[i] >= 0 &&
M.charAt(i+P[i]) == M.charAt(i-P[i]))
P[i]++;
if(P[i] + i > mx) {
mx = i + P[i];
id = i;
}
}
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<String>();
for(int i = 2;i < P.length;i = i + 2) {
int len = P[i] - 1;
int j = i / 2 - 1; //回文串中心字符在字符串N中的位置
if(len == 0) {
String s = N.substring(j, j + 1);
if(!set.contains(s)) {
set.add(s);
count++;
}
} else if(len % 2 == 1){
for(int k = 0;k <= len / 2;k++) {
String s = N.substring(j - k, j + k + 1);
if(!set.contains(s)) {
set.add(s);
count++;
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
public int getAllChildern(String M) {
int count = 0; //统计字符串M所有不同子串个数
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<String>();
for(int i = 0, len = 1;i < M.length();i++, len++) {
for(int j = 0;j <= M.length() - len;j++) {
String s = M.substring(j, j + len);
if(!set.contains(s)) {
set.add(s);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
public void getResult() {
int max = -1;
for(int i = 1;i < A.length() - 1;i++) {
String s1 = S.substring(0, i * 2 + 1);
String s2 = "$" + S.substring(i * 2 + 1);
String s3 = A.substring(0, i);
String s4 = A.substring(i);
int a = Manacher(s1, s3);
int b = getAllChildern(s4) - Manacher(s2, s4);
max = Math.max(max, a * b);
}
System.out.println(max);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main test = new Main();
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
A = in.next();
StringBuilder s1 = new StringBuilder("$#");
for(int i = 0;i < A.length();i++) {
s1.append(A.charAt(i));
s1.append("#");
}
S = s1.toString();
test.getResult();
}
}
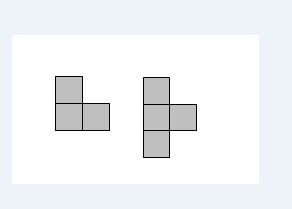
为了让蓝桥杯竞赛更顺利的进行,主办方决定给竞赛的机房重新铺放瓷砖。机房可以看成一个n*m的矩形,而这次使用的瓷砖比较特别,有两种形状,如【图1.png】所示。在铺放瓷砖时,可以旋转。
主办方想知道,如果使用这两种瓷砖把机房铺满,有多少种方案。
【输入格式】
输入的第一行包含两个整数,分别表示机房两个方向的长度。
【输出格式】
输出一个整数,表示可行的方案数。这个数可能很大,请输出这个数除以65521的余数。
【样例输入1】
4 4
【样例输出1】
2
【样例说明1】
这两种方案如下【图2.png】所示:
【样例输入2】
2 6
【样例输出2】
4
【数据规模与约定】
对于20%的数据,1<=n, m<=5。
对于50%的数据,1<=n<=100,1<=m<=5。
对于100%的数据,1<=n<=10^15,1<=m<=6。
资源约定:
峰值内存消耗(含虚拟机) < 512M
CPU消耗 < 8000ms
请严格按要求输出,不要画蛇添足地打印类似:“请您输入…” 的多余内容。
所有代码放在同一个源文件中,调试通过后,拷贝提交该源码。
注意:不要使用package语句。不要使用jdk1.7及以上版本的特性。
注意:主类的名字必须是:Main,否则按无效代码处理。