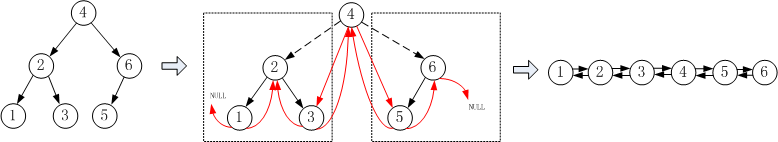
【试题描述】 将二叉搜索树转换为双向链表
对于二叉搜索树,可以将其转换为双向链表,其中,节点的左子树指针在链表中指向前一个节点,右子树指针在链表中指向后一个节点。
思路一:
采用递归思想,对于二叉搜索树,将左、右子树分别转换为双向链表,左子树转换所得链表的头结点即整个树的头结点,左子树转换所得链表的尾节点与根节点相邻;右子树转换所得链表的尾节点即整个树的尾节点,右子树转换所得链表的头结点与根节点相邻。
1 private static Node last; 2 public static Node treeToList(Node tree) 3 { 4 Node head; 5 // 若树为空,返回空 6 if (tree == null) 7 return null; 8 9 // 若无左子树,则该根节点为链表的头结点 10 if (tree.left == null) 11 head = tree; 12 // 若有左子树,递归调用转换函数将左子树转换为双向链表 13 // 左子树转换所得链表的头结点是整个树的头结点 14 // 左子树链表的尾结点与根节点相邻 15 else 16 { 17 head = treeToList(tree.left); 18 tree.left = last; 19 last.right = tree; 20 } 21 //若无右子树,则该根节点为链表的尾结点 22 if (tree.right == null) 23 last = tree; 24 //若有右子树,递归调用转换函数将右子树转换为双向链表 25 //右子树转换所得链表的尾结点是整个树的尾结点 26 //右子树链表的头结点与根节点相邻 27 else 28 { 29 tree.right = treeToList(tree.right); 30 tree.right.left = tree; 31 } 32 return head; 33 34 }
思路二:
我们可以中序遍历整棵树。按照这个方式遍历树,比较小的结点先访问。如果我们每访问一个结点,假设之前访问过的结点已经调整成一个排序双向链表,我们再把调整当前结点的指针将其链接到链表的末尾。当所有结点都访问过之后,整棵树也就转换成一个排序双向链表了。
1 // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 2 // Covert a sub binary-search-tree into a sorted double-linked list 3 // Input: pNode - the head of the sub tree 4 // pLast - the tail of the double-linked list 5 // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 6 private static Node pLast; 7 8 public static void treeToList(Node pNode) 9 { 10 if (pNode == null) 11 return; 12 Node pCurrent = pNode; 13 14 // Convert the left sub-tree 15 if (pCurrent.left != null) 16 treeToList(pCurrent.left); 17 18 // Put the current node into the double-linked list 19 pCurrent.left = pLast; 20 21 if (pLast != null) 22 pLast.right = pCurrent; 23 24 pLast = pCurrent; 25 // Convert the right sub-tree 26 if (pCurrent.right != null) 27 treeToList(pCurrent.right); 28 } 29 30 // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 31 // Covert a binary search tree into a sorted double-linked list 32 // Input: pHead - the head of tree 33 // Output: the head of sorted double-linked list 34 // ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 35 public static Node convertTree(Node root) 36 { 37 treeToList(root); 38 39 // Get the head of the double-linked list 40 Node pHead = pLast; 41 while (pHead != null && pHead.left != null) 42 pHead = pHead.left; 43 44 return pHead; 45 46 }