1 前备知识
归一化:把数据变成(0,1)或者(1,1)之间的小数,主要是为了方便数据处理。归一化是一种简化计算的方式,即将有量纲的表达式,经过变换,化为无量纲的表达式,成为纯量。有以下几种方式:
(1)x' = (x-x_min)/(x_max-x_min)
其中,x是归一化前的值,x'是归一化后的值,x_max、x_min分别是样本的最大最小值;
(2)平均归一化:x' = (x-u)/(x_max-x_min)
其中,x是归一化前的值,x'是归一化后的值,u是样本的均值,x_max、x_min分别是样本的最大最小值;
*注:(1)和(2)有一个缺陷就是当有新数据加入时,可能导致max和min的变化,需要重新定义。
(3)非线性归一化
1)对数函数转换:y = log10(x)
2)反余切函数转换:y = atan(x) * 2 / π
3)经常用在数据分化比较大的场景,有些数值很大,有些很小。通过一些数学函数,将原始值进行映射。该方法包括 log、指数,正切等。需要根据数据分布的情况,决定非线性函数的曲线,比如log(V, 2)还是log(V, 10)等。
/** @brief Normalizes the norm or value range of an array.
The function cv::normalize normalizes scale and shift the input array elements so that
f[| exttt{dst} | _{L_p}= exttt{alpha}f]
(where p=Inf, 1 or 2) when normType=NORM_INF, NORM_L1, or NORM_L2, respectively; or so that
f[min _I exttt{dst} (I)= exttt{alpha} , \, \, max _I exttt{dst} (I)= exttt{beta}f]
when normType=NORM_MINMAX (for dense arrays only). The optional mask specifies a sub-array to be
normalized. This means that the norm or min-n-max are calculated over the sub-array, and then this
sub-array is modified to be normalized. If you want to only use the mask to calculate the norm or
min-max but modify the whole array, you can use norm and Mat::convertTo.
In case of sparse matrices, only the non-zero values are analyzed and transformed. Because of this,
the range transformation for sparse matrices is not allowed since it can shift the zero level.
Possible usage with some positive example data:
@code{.cpp}
vector<double> positiveData = { 2.0, 8.0, 10.0 };
vector<double> normalizedData_l1, normalizedData_l2, normalizedData_inf, normalizedData_minmax;
// Norm to probability (total count)
// sum(numbers) = 20.0
// 2.0 0.1 (2.0/20.0)
// 8.0 0.4 (8.0/20.0)
// 10.0 0.5 (10.0/20.0)
normalize(positiveData, normalizedData_l1, 1.0, 0.0, NORM_L1);
// Norm to unit vector: ||positiveData|| = 1.0
// 2.0 0.15
// 8.0 0.62
// 10.0 0.77
normalize(positiveData, normalizedData_l2, 1.0, 0.0, NORM_L2);
// Norm to max element
// 2.0 0.2 (2.0/10.0)
// 8.0 0.8 (8.0/10.0)
// 10.0 1.0 (10.0/10.0)
normalize(positiveData, normalizedData_inf, 1.0, 0.0, NORM_INF);
// Norm to range [0.0;1.0]
// 2.0 0.0 (shift to left border)
// 8.0 0.75 (6.0/8.0)
// 10.0 1.0 (shift to right border)
normalize(positiveData, normalizedData_minmax, 1.0, 0.0, NORM_MINMAX);
@endcode
@param src input array.
@param dst output array of the same size as src .
@param alpha norm value to normalize to or the lower range boundary in case of the range
normalization.
@param beta upper range boundary in case of the range normalization; it is not used for the norm
normalization.
@param norm_type normalization type (see cv::NormTypes).
@param dtype when negative, the output array has the same type as src; otherwise, it has the same
number of channels as src and the depth =CV_MAT_DEPTH(dtype).
@param mask optional operation mask.
@sa norm, Mat::convertTo, SparseMat::convertTo
*/
CV_EXPORTS_W void normalize( InputArray src, InputOutputArray dst, double alpha = 1, double beta = 0, int norm_type = NORM_L2, int dtype = -1, InputArray mask = noArray());
/** @overload
@param src input array.
@param dst output array of the same size as src .
@param alpha norm value to normalize to or the lower range boundary in case of the range
normalization.
@param normType normalization type (see cv::NormTypes).
*/
CV_EXPORTS void normalize( const SparseMat& src, SparseMat& dst, double alpha, int normType );
//程序DEMO流程: //读取图片--》判断并显示图片--》转换为灰度图--》转换为浮点数类型数组--》四种归一化方式 //1)scale and shift by NORM_MINMAX //2)scale and shift by NORM_INF //3)scale and shift by NORM_L1 //4)scale and shift by NORM_L2 //--》归一化的范围设置为1.0 - 0 //--》不同的归一化方式结果出来要乘以对应的数值 //--》将结果转换为CV_8UC1 //--》显示图片 #include"opencv2opencv.hpp" #include"iostream" using namespace std; using namespace cv; int main(int argc, char** argv) { Mat src = imread("G:\CVworkstudy\program_wwx\研习社140课时\ZhaiZhigang140\colormap.png"); if (src.empty()) { printf("Could not load image... "); return -1; } imshow("srcImg", src); Mat src_gray, src_gray_f; cvtColor(src, src_gray, CV_RGB2GRAY);//转换为灰度图 src_gray.convertTo(src_gray_f, CV_32F);//转换为浮点数类型数组 //scale and shift by NORM_MINMAX Mat dst = Mat::zeros(src_gray.size(), CV_32FC1); normalize(src_gray_f, dst, 1.0, 0, NORM_MINMAX); Mat result = dst * 255; result.convertTo(dst, CV_8UC1); imshow("NORM_MINMAX", dst); //scale and shift by NORM_INF normalize(src_gray_f, dst, 1.0, 0, NORM_INF); result = dst * 255; result.convertTo(dst, CV_8UC1); imshow("NORM_INF", dst); //scale and shift by NORM_L1 normalize(src_gray_f, dst,1.0, 0, NORM_L1); result = dst * 100000000; result.convertTo(dst, CV_8UC1); imshow("NORM_L1", dst); //scale and shift by NORM_L2 normalize(src_gray_f, dst, 1.0, 0, NORM_L2); result = dst * 10000; result.convertTo(dst, CV_8UC1); imshow("NORM_L2", dst); waitKey(0); return 0; }
4 运行结果
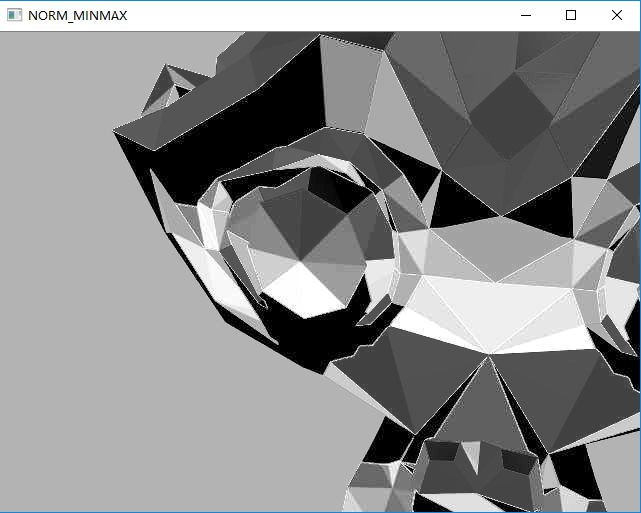


5 扩展及注意事项
null