【重要】代码有误,我已经更新了
可能有时候会有这样的需求,我们的应用程序需要弹出一个窗口,或者是包含多个窗口。同时呢,又不想真正的用Window,尤其是当我们写XBAP应用的时候。恰巧WPF里面又没有MDI……
当然,我们有几种解决办法。
一种比较简单的办法是,用UserControl仿造一个窗口放在应用程序里面,然后将Visibility设置为隐藏。接着,在我们需要的时候,让它显示。但是,这种方式,一个两个还好说,如果稍微一多,那管理起来就比较麻烦了。
另外我们还可以启动一个真实的窗口,然后通过调用API,来SetParent,把子窗口放在父窗口中。但是如果是Xbap,可能这些操作都要受到限制。而且这样的窗口要改改样式很困难。
有没有别的方法来在应用程序内部仿造窗口呢?
在这篇文章里面,我们就来试试怎么用CustomControl来打造模拟的窗口。
上图先:
首先是一般的情况:

然后是最大化的情况:

XBAP程序(需要改改安全策略)
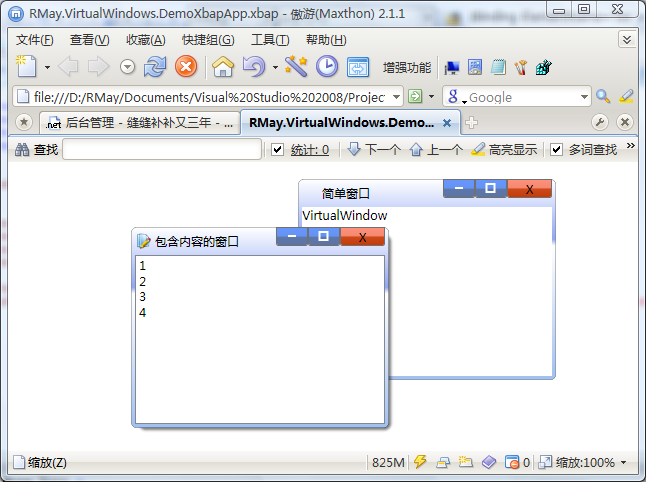
最小化没做,因为现在还没想清楚最小化后怎么放这些窗口。
当然,这些“窗口”都是可以拖来拖去的,而且可以任意改变大小。
【分析】
其实要模拟一个窗口的外观并不困难。难点在于对窗口的操作上,最主要的包括移动,修改大小,最大最小化,关闭。
对于最大最小化这样的操作,我们可以用Command来完成。但是鼠标拖拽移动、改变大小,是跟UI关系很紧密的操作,而CustomControl最主要的特点是UI和逻辑的解耦。WPF中提供Thumb来做拖拽的工作,那么算一下总共有多少这东西吧:移动一个,四周的Resize和四角的Resize,总共9个。我可不想我的做的这个控件上标记着一堆TemplatePart。
所以,我决定从Thumb继承,写两个东西,一个叫Repostioner,用来改变位置;一个叫Resizer,用来改变大小。而是使用它们的时候,我们只需要把这两个控件放到某个控件中,指定一下要操作的对象,然后这个控件就能拖拖拽拽了。
【控件的实现】
Repositioner
在WPF里面,切记没有横坐标、纵坐标这种东西(即使是Canvas,那也是个附加属性),如果我们想改变某个元素的位置,最好的方法是用TranslateTransform。
所以,在指定了Repositioner要操作的对象之后,我们需要给它添加一个TranslateTransform

 Code
Code
protected virtual void OnTargetElementChanged(FrameworkElement oldValue, FrameworkElement newValue)
{
if (newValue != null)
{
//newValue.HorizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center;
//newValue.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Center;
if (newValue.RenderTransform == null)
{
newValue.RenderTransform = PositionTransform;
}
else if (newValue.RenderTransform is TransformGroup)
{
TransformGroup group = newValue.RenderTransform as TransformGroup;
group.Children.Add(PositionTransform);
}
else
{
TransformGroup group = new TransformGroup();
group.Children.Add(newValue.RenderTransform);
group.Children.Add(PositionTransform);
newValue.RenderTransform = group;
}
}
}那么,在我们拖拽Repostioner的时候,就可以通过这个Transform来改变控件的位置了。

 Code
Code
public Repositioner()
{
PositionTransform = new TranslateTransform();
this.DragStarted += new DragStartedEventHandler(OnDragStarted);
this.DragCompleted += new DragCompletedEventHandler(OnDragCompleted);
this.DragDelta += new DragDeltaEventHandler(OnDragDelta);
}
#endregion
#region Handle Drag Events
private void OnDragCompleted(object sender, DragCompletedEventArgs e)
{
if (CanDrag)
{
OnDragCompleted(e);
}
}
private void OnDragStarted(object sender, DragStartedEventArgs e)
{
if (CanDrag)
{
OnDragStarted(e);
}
}
private void OnDragDelta(object sender, DragDeltaEventArgs e)
{
if (CanDrag)
{
OnDragDelta(e);
}
}
protected virtual void OnDragCompleted(DragCompletedEventArgs e)
{
//
}
protected virtual void OnDragStarted(DragStartedEventArgs e)
{
//
}
protected virtual void OnDragDelta(DragDeltaEventArgs e)
{
if (TargetElement != null)
{
PositionTransform.X += e.HorizontalChange;
PositionTransform.Y += e.VerticalChange;
}
}
注意,Thumb里面没有OnDragXXX的方法来重载,所以我只能做事件响应,并且以虚方法的方式提供,供子类重载。这会在后面的Resizer中看到。
除此之外,我还让Repostioner实现了ICommandSource接口,这是一个伏笔,因为我们会需要一个“双击最大化/恢复”窗口大小的操作,而这个操作通过Command来触发。

 Code
Code
#region ICommandSource Members
public ICommand Command
{
get { return (ICommand)GetValue(CommandProperty); }
set { SetValue(CommandProperty, value); }
}
// Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for Command. This enables animation, styling, binding, etc
public static readonly DependencyProperty CommandProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("Command", typeof(ICommand), typeof(Repositioner), new UIPropertyMetadata(null));
public object CommandParameter
{
get { return (object)GetValue(CommandParameterProperty); }
set { SetValue(CommandParameterProperty, value); }
}
// Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for CommandParameter. This enables animation, styling, binding, etc
public static readonly DependencyProperty CommandParameterProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("CommandParameter", typeof(object), typeof(Repositioner), new UIPropertyMetadata(null));
public IInputElement CommandTarget
{
get { return (IInputElement)GetValue(CommandTargetProperty); }
set { SetValue(CommandTargetProperty, value); }
}
// Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for CommandTarget. This enables animation, styling, binding, etc
public static readonly DependencyProperty CommandTargetProperty =
DependencyProperty.Register("CommandTarget", typeof(IInputElement), typeof(Repositioner), new UIPropertyMetadata(null));
protected override void OnPreviewMouseDoubleClick(MouseButtonEventArgs e)
{
base.OnPreviewMouseDoubleClick(e);
CommandHelper.ExecuteCommandSource(this);
}
#endregion 在上面的代码中,我让Repostioner双击的时候触发Command,而Command的执行是通过CommandHelper来调用的。
CommandHelper

 Code
Code
public static class CommandHelper
{
public static void ExecuteCommandSource(ICommandSource commandSource)
{
ICommand command = commandSource.Command;
if (command != null)
{
object commandParameter = commandSource.CommandParameter;
IInputElement commandTarget = commandSource.CommandTarget;
RoutedCommand routedCommand = command as RoutedCommand;
if (routedCommand != null)
{
if (commandTarget == null)
{
commandTarget = commandSource as IInputElement;
}
if (routedCommand.CanExecute(commandParameter, commandTarget))
{
routedCommand.Execute(commandParameter, commandTarget);
}
}
else if (command.CanExecute(commandParameter))
{
command.Execute(commandParameter);
}
}
}
}Resizer
Resizer直接从Repostioner继承。这是因为,在改变大小的时候,可能需要改变位置。
比如,向左拖拽着改变大小的时候,我们需要把控件的位置相应地往左移动,才能保证右边沿不动。

 Code
Code
// 确保高宽是有效值
protected override void OnDragStarted(DragStartedEventArgs e)
{
if (TargetElement != null)
{
if (double.IsNaN(TargetElement.Width))
{
TargetElement.Width = TargetElement.ActualWidth;
}
if (double.IsNaN(TargetElement.Height))
{
TargetElement.Height = TargetElement.ActualHeight;
}
}
}
protected override void OnDragDelta(DragDeltaEventArgs e)
{
if (TargetElement != null)
{
double deltaX = 0.0;
double deltaY = 0.0;
double finalWidth = this.TargetElement.Width;
double finalHeight = this.TargetElement.Height;
double minWidth = double.IsNaN(this.TargetElement.MinWidth) ? 0.0 : this.TargetElement.MinWidth;
double minHeight = double.IsNaN(this.TargetElement.MinHeight) ? 0.0 : this.TargetElement.MinHeight;
// 考虑到四个角的方向其实就是上下左右四个方向的组合
// 因此使用标志位作判断,分别处理即可
int direction = (int)this.Direction;
// Left
if ((direction & 0x1000) != 0)
{
finalWidth -= e.HorizontalChange;
deltaX = e.HorizontalChange;
}
// Top
if ((direction & 0x0100) != 0)
{
finalHeight -= e.VerticalChange;
deltaY = e.VerticalChange;
}
// Right
if ((direction & 0x0010) != 0)
{
finalWidth += e.HorizontalChange;
}
// Bottom
if ((direction & 0x0001) != 0)
{
finalHeight += e.VerticalChange;
}
// 判断是否有效
if (finalWidth < minWidth)
{
finalWidth = minWidth;
deltaX = 0.0;
}
if (finalHeight < minHeight)
{
finalHeight = minHeight;
deltaY = 0.0;
}
this.TargetElement.Width = finalWidth;
this.TargetElement.Height = finalHeight;
this.PositionTransform.X += deltaX;
this.PositionTransform.Y += deltaY;
} 需要注意的是,虽然总共有8个Resize的方向,但是只有上下左右四个方向是最基本的,而左上,右上,左下,右下是这个四个基本方向的组合。所以,我们只需要处理四个方向的逻辑即可。但是在Xaml里面,我们没法写诸如"Top | Left"这样的“或”操作的表达式,因此,ResizerDirection这个枚举类型还是要8个值的。为了简化处理,我将这个枚举类型标记为[Flags],并且附上了初值,组合值恰好等于基本值取或。这样,在处理代码中,我们把Direction的值分别同四个基本方向的值按位求与,只要不等于0,那就表示在这个方向上发生了变化。(一般情况下,Left和Right是不会同时变化,当然,如果使用Surface这种可以多点触发的触摸屏技术,你就可以用手拉着窗口的左右两边拖放了,嘿嘿)
Resizer的鼠标是在Style中定义,一共写个8个Trigger,虽然用代码会简单一些,但是我认为这是属于UI层的东西,还是放到Style去描述比较好,因为使用者可能想换成别的鼠标样式。
测试Repostioner和Resizer
好,现在我们来试试写好的这两个东东能不能用吧。我们放个Border,在放个Grid来装Repostioner和Resizer。

 Code
Code
<Border x:Name="TestBorder" Background="Blue" Height="200" Width="250" MinWidth="30" MinHeight="20" Canvas.Top="231" Canvas.Left="41">
<Grid >
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="4"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="4"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="4"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="4"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<lib:Resizer Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" Background="Red" Direction="TopLeft" TargetElement="{Binding ElementName=TestBorder}"/>
<lib:Resizer Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="1" Background="Black" Direction="Top" TargetElement="{Binding ElementName=TestBorder}"/>
<lib:Resizer Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="2" Background="Red" Direction="TopRight" TargetElement="{Binding ElementName=TestBorder}"/>
<lib:Resizer Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" Background="Black" Direction="Left" TargetElement="{Binding ElementName=TestBorder}"/>
<lib:Resizer Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="2" Background="Black" Direction="Right" TargetElement="{Binding ElementName=TestBorder}"/>
<lib:Resizer Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="0" Background="Red" Direction="BottomLeft" TargetElement="{Binding ElementName=TestBorder}"/>
<lib:Resizer Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="1" Background="Black" Direction="Bottom" TargetElement="{Binding ElementName=TestBorder}"/>
<lib:Resizer Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="2" Background="Red" Direction="BottomRight" TargetElement="{Binding ElementName=TestBorder}"/>
<DockPanel Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1">
<lib:Repositioner DockPanel.Dock="Top" Background="Gray" Height="20" TargetElement="{Binding ElementName=TestBorder}"/>
<Border/>
</DockPanel>
</Grid>
</Border>神奇的事情发生了!在应用的时候,我们没写一句代码,只是简单地将Repostioner和Resizer放到Grid里面,指定他们的目标元素是TestBorder,这个Border就能拖来拖去,并且任意改变大小了!
图中,灰色部分是Repostioner,红色的是四个边角Resizer,黑色的是边线Resizer,蓝色的是Border。怎么样?已经有点Window的样子了吧?
注意,Repostioner和Resizer不一定非得放到目标元素中去,你甚至可以放到外面,只需要指定目标即可。(你可以画一个模拟的笔记本触摸板了,呵呵)

VirtualWindow
现在我们着手做模拟的窗口。
首先,我们添加一个自定义控件,添加一些跟Window相关的DependencyProperty,这个过程是很机械化,代码就不粘贴。
比较重要的地方是在VirtualWindow中定义的Command和它状态改变的逻辑。

 Code
Code
/// <summary>
/// Gets 操作窗口命令
/// </summary>
public ICommand OperationCommand { get; private set; }
// 改变窗口状态的命令
private class WindowOperationCommand : ICommand
{
private VirtualWindow _window = null;
public WindowOperationCommand(VirtualWindow window)
{
_window = window;
}
#region ICommand Members
public bool CanExecute(object parameter)
{
return true;
}
// 从不使用,故保留空
public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged
{
add { }
remove { }
}
public void Execute(object parameter)
{
string value = parameter.ToString();
switch (value)
{
case "Close":
_window.Close();
break;
case "Max":
_window.WindowState = WindowState.Maximized;
break;
case "Reset":
_window.WindowState = WindowState.Normal;
break;
case "Min":
_window.WindowState = WindowState.Minimized;
break;
}
}
#endregion
}我在VirtualWindow的内部定义了一个WindowOperationCommand类,实现了ICommand接口,而不是使用RoutedCommand。它通过一个OperationCommand属性暴露给外面。一般轻量的Command这样写也就足够了,我也就懒得再去注册RoutedCommand,然后再注册CommandBinding了。
这个命令是通过传入不同的参数来执行相应的操作的。
最大化,和恢复状态还是比较好做的。有一点麻烦的是怎么对齐。研究了半天发现用VisualTreeHelper.GetOffset能拿到相对位移,我们再给他一个TranslateTranform让它反向移动相应的距离即可。

 Code
Code
// 最大化
private void Maximize()
{
StoreNormalState();
Panel ownerPanel = this.OwnerPanel;
if (ownerPanel != null)
{
this.HasShadow = false;
this.CanMove = false;
this.CanResize = false;
// 将VirtualWindow大小绑定到父Panel的大小
Binding binding = new Binding("ActualWidth");
binding.Source = this.OwnerPanel;
this.SetBinding(VirtualWindow.WidthProperty, binding);
binding = new Binding("ActualHeight");
binding.Source = this.OwnerPanel;
this.SetBinding(VirtualWindow.HeightProperty, binding);
// 对齐位置
// 通过VisualTreeHelper.GetOffset来拿到相对于父Panel的位移
Vector vector = VisualTreeHelper.GetOffset(this);
this.RenderTransform = new TranslateTransform(-vector.X, -vector.Y);
}
}
// 恢复正常状态
private void RestoreNormalState()
{
this.RenderTransform = this._normalTransform;
BindingOperations.ClearBinding(this, WidthProperty);
BindingOperations.ClearBinding(this, HeightProperty);
this.Width = _normalSize.Width;
this.Height = _normalSize.Height;
this.CanResize = this._normalCanResize;
this.CanMove = this._normalCanMove;
}
// 保存正常状态下的参数
private void StoreNormalState()
{
// 注意,在最大化的时候我们需要去掉现有的Transform,所以在这儿要保存。
this._normalTransform = this.RenderTransform;
this._normalSize.Width = this.ActualWidth;
this._normalSize.Height = this.ActualHeight;
this._normalCanMove = this.CanMove;
this._normalCanResize = this.CanResize;
}但是,需要特别注意的是,这个代码的结果跟具体的Panel有关系,因为不同的Panel会有不同的Arrange方式来布局Child,可能最后布局的结果跟我们的期望的相去甚远。
同样,父Panel的布局方式还会影像到Resizer。比如说,我们放到Grid中,当我们向右拖动右边沿的Resizer的时候,我们期望的结果是控件不动,宽度向右变宽。然后,由于Grid对于Alignment设置为Stretch的Child,会按照位移加上Margin的最终值来重新布局,因此我们会看到,该控件同时会往左发生移动。同时,由于Panel的Messure方法会影响到Child的RenderSize,所以最后可能会看到VirtualWindow被截掉一部分。所以,虽然理论上VirtualWindow了可以放到任何Panel(甚至任何控件)中,但我还是建议使用的时候大家放到Canvas里面,因为Canvas的定位是绝对定位的。目前就我测试的情况来看,当VirtualWindow的Alignment分别设置为Top和Left之后,可以在StackPanel中和不设置Row和Column的Grid中正常使用。另外,我重载了Alignment的初始值,分别设为了Left和Top。
VirtualWindow的模板比较复杂,我就不贴上来了,下载代码后可以自己看。因为是自定义控件,所以它的模板可以随便改,这样,修改样式的工作会很简单。
【写在最后】
VirtualWindow的最小化功能我还没做,因为没想好应该是个什么效果。我在考虑要不要搞个VirtualDesktop来管理这些窗口,这样还可以提供最小化的支持。当然,这些Window都是跑在一个线程中的,如果一个Window死掉,别的Window也挂了。为此,必须让非UI代码跑在不同的线程中,所以VirtualDesktop会是个相当艰巨的任务。
可能实际项目中这些东东都用不到,不过做这些东西乐趣多多,呵呵。
代码下载https://files.cnblogs.com/RMay/RMay.VirtualWindows.rar




