1.AboutException.java
import javax.swing.*;
class AboutException {
public static void main(String[] a)
{
int i=1, j=0, k;
k=i/j;
try
{
k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception
//throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!");
}
catch ( ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("被0除. "+ e.getMessage());
}
catch (Exception e)
{
if (e instanceof ArithmeticException)
System.out.println("被0除");
else
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
finally
{
JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK");
}
}
}
输出结果:
java.lang.ArithmeticException指算术上的错误,将j值改变
使用异常处理后: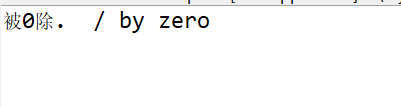
2.多层的异常捕获
public class CatchWho {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
try {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
输出结果: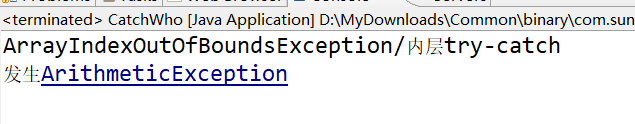
public class CatchWho2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
try {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
输出结果:

当多层嵌套时,通过catch可以捕捉相应异常,但异常不符合指定内容无法捕捉
3.多层嵌套执行
class EmbededFinally{
public static void main(String args[]) {
int result;
try {
System.out.println("in Level 1");
try {
System.out.println("in Level 2");
// result=100/0; //Level 2
try {
System.out.println("in Level 3");
result=100/0; //Level 3
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 3 finally");
}
// result=100/0; //Level 2
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 2 finally");
}
// result = 100 / 0; //level 1
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 1 finally");
}
}
}
输出结果:

当有多层嵌套的finally时,异常在不同的层次抛出 ,在不同的位置抛出,可能会导致不同的finally语句块执行顺序。
4.SystemExitAndFinally.java
public class SystemExitAndFinally {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try{
System.out.println("in main");
throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main");
//System.exit(0);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.exit(0);
}
finally
{
System.out.println("in finally");
}
}
}
输出结果:

finally语句块不一定执行。
通过System.exit(0)停止程序。
5.PrintExceptionStack.java
public class PrintExceptionStack {
public static void main( String args[] )
{
try {
method1();
}
catch ( Exception e ) {
System.err.println( e.getMessage() + "
" );
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void method1() throws Exception
{
method2();
}
public static void method2() throws Exception
{
method3();
}
public static void method3() throws Exception
{
throw new Exception( "Exception thrown in method3" );
}
}
当程序中出现异常时,JVM会依据方法调用顺序依次查找有关的错误处理程序。可使用printStackTrace 和 getMessage方法了解异常发生的情况:
printStackTrace:打印方法调用堆栈。
每个Throwable类的对象都有一个getMessage方法,它返回一个字串,这个字串是在Exception构造函数中传入的,通常让这一字串包含特定异常的相关信息
6.ThrowMultiExceptionsDemo.java
import java.io.*;
public class ThrowMultiExceptionsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
throwsTest();
}
catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println("捕捉异常");
}
}
private static void throwsTest() throws ArithmeticException,IOException {
System.out.println("这只是一个测试");
// 程序处理过程假设发生异常
throw new IOException();
//throw new ArithmeticException();
}
}
当一个方法声明出现多个异常时,在此方法调用语句处只要catch捕捉到任何一个异常,程序就可以顺利编译。
8.OverrideThrows.java
import java.io.*;
public class OverrideThrows
{
public void test()throws IOException
{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
}
}
class Sub extends OverrideThrows
{
//如果test方法声明抛出了比父类方法更大的异常,比如Exception
//则代码将无法编译……
public void test() throws FileNotFoundException
{
//...
}
}
一个子类的throws子句抛出的异常,不能是其基类同名方法抛出的异常对象的父类。