前几天说的FileReader、InputStreamReader、StreamDecoder,是将字节通根据对应字符集转换成字符的流,这样在输出时,由于一次调用只返回一个字符,需要使用循环来输出多个字符,而且还要通过返回值来判断是否读取完毕结束循环,不够灵活。采用BufferedReader来包装这些流,就能使其更加便捷,提高效率。
先来看一个例子,对于之前的FileReader举例,我们使用do while循环来输出4个字符,但如果用BufferedReader来包装再输出,就会是这样:
public static void main(String args[]){ try { BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\img\test.txt")); try { System.out.println(reader.readLine()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
这就变得非常的简单,不用循环,且可以一行一行得输出。
那么接下来我们来看BufferedReader的源码:
一、属性域:
//被包装的字符流(一般为Reader的实例类) private Reader in; //字符缓冲区 private char cb[]; //读取完一次字符(执行一次fill())后,字符填充进字符缓冲区cb[]中,这时可从cb[]中读取字符, // 此时nextChar为下一个要读取的字符的下标,nChars是缓冲区字符总个数 private int nChars, nextChar; //定义两个常量,第一个表示无效,第二个表示未标记,标记定从0开始,故-1表示未标记 private static final int INVALIDATED = -2; private static final int UNMARKED = -1; private int markedChar = UNMARKED; //不是很懂这个变量的用处,但原版注解说明在markedChar > 0时才有效 private int readAheadLimit = 0; /* Valid only when markedChar > 0 */ //如果下个字符是换行符,则跳过--专用于readLine()方法里面控制 /** If the next character is a line feed, skip it */ private boolean skipLF = false; //设置标志时的markedSkipLF--用于mark()方法的变量 /** The skipLF flag when the mark was set */ private boolean markedSkipLF = false; //默认字符缓冲区大小 private static int defaultCharBufferSize = 8192; //用于readLine()方法时初始化StringBuffer的初始容量 private static int defaultExpectedLineLength = 80;
二、构造函数:
public BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz) { super(in); if (sz <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0"); this.in = in; cb = new char[sz]; nextChar = nChars = 0; }
public BufferedReader(Reader in) { this(in, defaultCharBufferSize); }
下面这个构造函数,本质是调用前一个,size设置为默认字符缓冲区大小(8192)。
三、重要方法
1)fill():
此方法主要是用来从底层字节流取出字节并根据字符集转码成字符(参照之前的博文)填充至他自己的字符缓冲区中。
private void fill() throws IOException { int dst; if (markedChar <= UNMARKED) { /* No mark */ dst = 0; } else { /* Marked */ int delta = nextChar - markedChar; if (delta >= readAheadLimit) { /* Gone past read-ahead limit: Invalidate mark */ markedChar = INVALIDATED; readAheadLimit = 0; dst = 0; } else { if (readAheadLimit <= cb.length) { /* Shuffle in the current buffer */ System.arraycopy(cb, markedChar, cb, 0, delta); markedChar = 0; dst = delta; } else { /* Reallocate buffer to accommodate read-ahead limit */ char ncb[] = new char[readAheadLimit]; System.arraycopy(cb, markedChar, ncb, 0, delta); cb = ncb; markedChar = 0; dst = delta; } nextChar = nChars = delta; } } int n; do { n = in.read(cb, dst, cb.length - dst); } while (n == 0); if (n > 0) { nChars = dst + n; nextChar = dst; } }
方法大致分两种情况:
第一种是没有标记的情况(no mark),此时直接设det为0,然后从下标0开始填充整个字符缓冲区,直到填满,再将nextChar设为0,nChar设为cb.length(dst+n,n为成功读取的字符数,一般情况下就等于cb.length)。
第二种情况是有标记的情况(markedChar>UNMARKED),此时字符缓冲区中有标记,进行的操作如下:
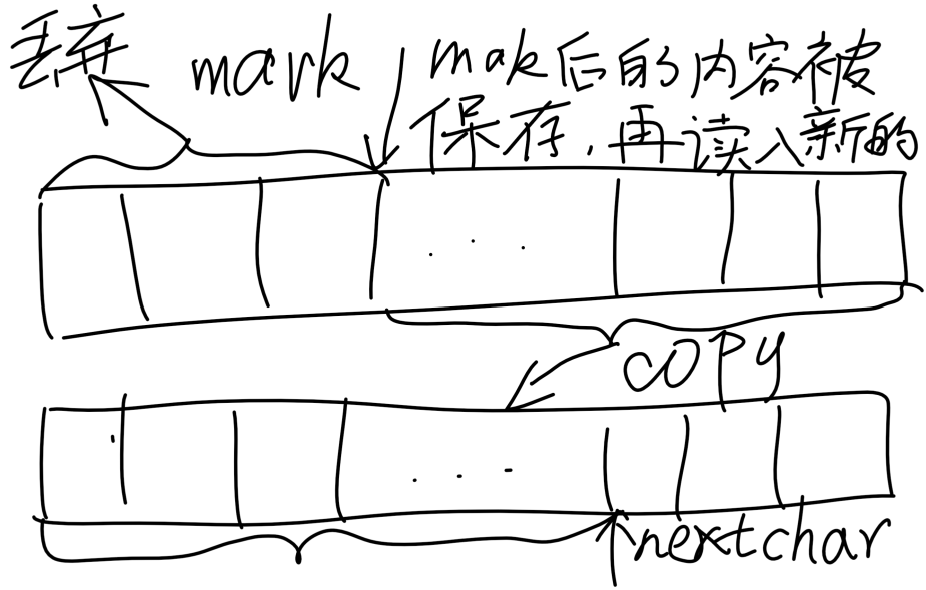
然后这段mark后到nextChar之间的内容的长度需要跟readAheadLimit比较(如果太长会导致爆内存,所以要设定一个限制),如果小于readAheadLimit则被认为是合法标记,再判断readAheadLimit与cb.length之间的大小,如果更大,则需要重新创建长度为readAheadLimit的字符缓冲区,再把mark后的内容复制进去,如果较小,则直接复制mark后的内容。(因为readAheadLimit更大的话,mark后到nextChar之间的内容长度可能会大于原字符缓冲区的长度导致溢出,所以要加入这个判断)。
拷贝工作完成后,再将字符缓冲区中余下的空位填满,之后返回nextChar就是图上的位置,nChar就是缓冲区总字符数。
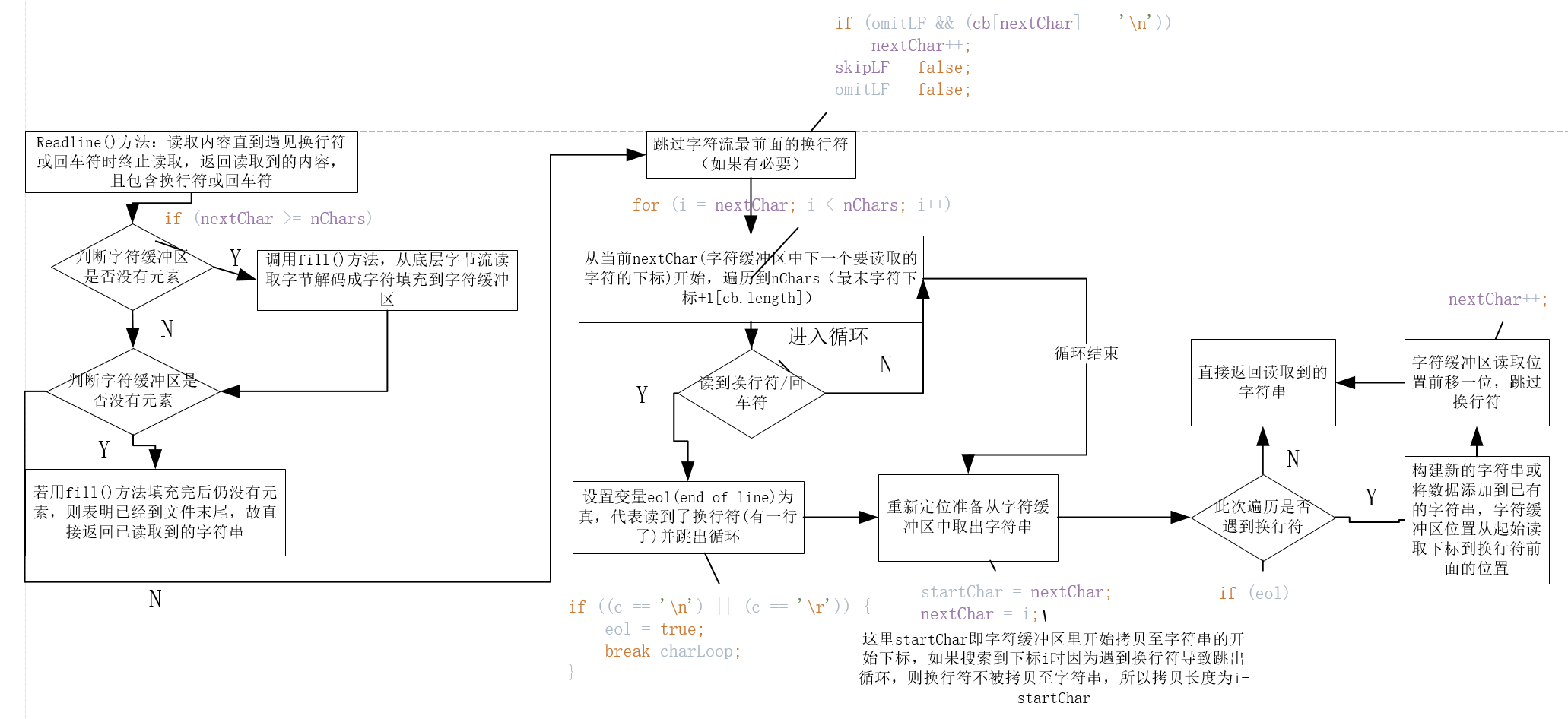
2)readline():
此方法直接通过源码和流程图展示:
String readLine(boolean ignoreLF) throws IOException { StringBuffer s = null; int startChar; synchronized (lock) { ensureOpen(); boolean omitLF = ignoreLF || skipLF; bufferLoop: for (;;) { if (nextChar >= nChars) fill(); if (nextChar >= nChars) { /* EOF */ if (s != null && s.length() > 0) return s.toString(); else return null; } boolean eol = false; char c = 0; int i; /* Skip a leftover ' ', if necessary */ if (omitLF && (cb[nextChar] == ' ')) nextChar++; skipLF = false; omitLF = false; charLoop: for (i = nextChar; i < nChars; i++) { c = cb[i]; if ((c == ' ') || (c == ' ')) { eol = true; break charLoop; } } startChar = nextChar; nextChar = i; if (eol) { String str; if (s == null) { str = new String(cb, startChar, i - startChar); } else { s.append(cb, startChar, i - startChar); str = s.toString(); } nextChar++; if (c == ' ') { skipLF = true; } return str; } if (s == null) s = new StringBuffer(defaultExpectedLineLength); s.append(cb, startChar, i - startChar); } } }
之后的其他方法将会在后面进行补遗