from sklearn import datasets
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# MICD分类器
# 只能分辨训练集中存在的类别
class MICDClassifier:
def __init__(self):
self.center_dict = {} # 分类中心点,以类别标签为键 label: center_point(list)
self.sigma = {} # 各类别样本的协方差矩阵,以类别标签为键
self.sigma_I = {} # 各类别样本协方差矩阵的逆,以类别标签为键
self.feature_number = 0 # 特征维度
self.train_state = False # 训练状态,True为训练完成,False表示还没训练过
# 特征白化,返回白化后的矩阵(numpy数组格式)
# 参数为numpy格式的数组,其格式为数学上的矩阵的转置
@staticmethod
def whitening(feature_x):
new_feature_x = np.asmatrix(feature_x).T
sigma_x = np.cov(new_feature_x)
eig_x = np.linalg.eig(sigma_x) # 计算协方差矩阵sigma_x的特征值和特征向量
diag_x = np.diag(eig_x[0])
W = np.dot(np.power(np.asmatrix(diag_x).I, 0.5), eig_x[1].T) # 记得eig_x[1]要转置!因为它是所求特征向量矩阵的转置
return np.dot(W, new_feature_x).T.A # 将矩阵转换为numpy的风格
# 根据传入的样本集(特征+标签)来训练MICD分类器,
# 其中每一个特征要求是行向量,标签也是行向量(为了与numpy array的格式对齐)
# 函数将输入的标签数组转换为字典
# 训练结果是记住样本中心点,以及根据样本计算特征的协方差矩阵
def train(self, feature_set, label_set):
new_label_set = {key: value for key, value in enumerate(label_set)} # 将标签集合转换为以下标为键的字典 index: label
self.feature_number = len(feature_set[0])
sample_num = len(label_set) # 样本个数
count = {} # 计算每个类别的样本个数 label: count(int)
# 计算每个类别的分类中心点
for index in range(sample_num):
if new_label_set[index] not in count.keys():
count[new_label_set[index]] = 0
self.sigma[new_label_set[index]] = [feature_set[index]]
else:
count[new_label_set[index]] += 1 # 计算对应标签的样本数
self.sigma[new_label_set[index]].append(feature_set[index])
if new_label_set[index] not in self.center_dict.keys():
self.center_dict[new_label_set[index]] = feature_set[index]
else:
self.center_dict[new_label_set[index]] += feature_set[index]
for _key_ in self.center_dict.keys():
for _feature_ in range(self.feature_number):
self.center_dict[_key_][_feature_] /= count[_key_]
for _key_ in self.sigma.keys():
self.sigma[_key_] = np.cov(np.asmatrix(self.sigma[_key_]).T) # 根据样本计算特征的协方差矩阵
self.sigma_I[_key_] = np.asmatrix(self.sigma[_key_]).I.A # 计算协方差矩阵的逆,并保存为ndarray类型
self.train_state = True
# 根据输入来进行分类预测,输出以 下标—预测分类 为键值对的字典
def predict(self, feature_set):
# 先判断此分类器是否经过训练
if not self.train_state:
return {}
sample_num = len(feature_set)
distance_to = {} # 计算某个样本到各分类中心点马氏距离的平方 label: float
result = {} # 保存分类结果 index: label
for _sample_ in range(sample_num):
for _key_ in self.center_dict.keys():
delta = feature_set[_sample_] - self.center_dict[_key_]
distance_to[_key_] = np.dot(np.dot(delta.T, self.sigma_I[_key_]), delta) # 计算马氏距离的平方
result[_sample_] = min(distance_to, key=distance_to.get) # 返回最小值的键(即label)
return result
# 判断预测准确率
def accuracy(self, feature_set, label_set):
if not self.train_state:
return 0.0
correct_num = 0
total_num = len(label_set)
predict = self.predict(feature_set)
for _sample_ in range(total_num):
if predict[_sample_] == label_set[_sample_]:
correct_num += 1
return correct_num / total_num
# 根据指定的阳性类别,计算分类器的性能指标(准确率accuracy,精度precision,召回率recall,特异性specificity,F1_Score)
def performance(self, feature_set, label_set, positive):
if not self.train_state:
return {}
total_num = len(label_set)
predict = self.predict(feature_set)
true_positive, false_positive, true_negative, false_negative = 0, 0, 0, 0
for _sample_ in range(total_num):
if predict[_sample_] == label_set[_sample_]:
if label_set[_sample_] == positive:
true_positive += 1
else:
true_negative += 1
else:
if label_set[_sample_] == positive:
false_negative += 1
else:
false_positive += 1
print("true_positive: ", true_positive, "
false_positive: ", false_positive,
"
true_negative: ", true_negative, "
false_negative ", false_negative)
accuracy = (true_positive + true_negative) / total_num # 准确率(预测正确的样本与总样本数之比)
precision = true_positive / (true_positive + false_positive) # 精度(所有 预测 为阳性的样本中, 真值 为阳性的比例)
recall = true_positive / (true_positive + false_negative) # 召回率(所有 真值 为阳性的样本中, 预测 为阳性的比例)
specificity = true_negative / (true_negative + false_positive) # 特异性(所有 真值 为阴性的样本中, 预测 为阴性的比例)
F1_Score = (2 * precision * recall) / (precision + recall) # 精度与召回率的加权平均
return {"accuracy": accuracy, "precision": precision, "recall": recall, "specificity": specificity,
"F1_Score": F1_Score}
# 获取某一类的样本中心点
def get_center(self, key):
if key in self.center_dict.keys():
return self.center_dict[key]
else:
return []
def get_center_dict(self):
return self.center_dict
# 获取所有类别的协方差矩阵
def get_cov_dict(self):
return self.sigma
# 将字典转换为列表(只保留每个键值对的值)
def dict_values_to_list(_dict_):
if isinstance(_dict_, dict):
return list(_dict_.values())
else:
return []
# feature表示样本特征,label表示对应的标签,m行n列共计m*n个子图
def visualization_2d(feature, label, m, n):
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 20), dpi=80)
img = [[] for i in range(m * n)]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
img[i * n + j] = plt.subplot(m, n, i * n + j + 1)
plt.xlabel("x" + str(i))
plt.ylabel("x" + str(j))
# plt.xlim(-1, 9)
# plt.ylim(-1, 9)
# plt.legend() # 显示图例
plt.scatter(feature[:, i], feature[:, j], s=5, c=label, marker='.')
plt.colorbar() # 显示颜色条
plt.grid(True) # 显示网格线
plt.show()
# 展示二维平面上,二分类问题的决策线(class_1和class_2)
# feature是样本特征集合,label是对应的标签集合,对每一维特征进行两两比较,n表示特征维数
def show_decision_line(feature, label, micd_classifier, class_1=0, class_2=0, n=0):
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 12), dpi=80) # 整张画布大小与分辨率
img = [[] for i in range(n * n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
img[i * n + j] = plt.subplot(n, n, i * n + j + 1)
center_1 = micd_classifier.get_center(class_1)
center_2 = micd_classifier.get_center(class_2)
c_1 = [center_1[i], center_1[j]] # class_1类中心点的i, j两维的分量
c_2 = [center_2[i], center_2[j]] # class_2类中心点的i, j两维的分量
center_3 = [(c_1[0] + c_2[0]) / 2, (c_1[1] + c_2[1]) / 2] # 两点连线的中点
k2, b2 = calculate_vertical_line(c_1, c_2) # 两点中垂线的斜率和截距
plt.scatter(feature[:, i], feature[:, j], c=label, s=20, marker='.') # 整个样本集在特征0和2上的散点图
plt.scatter(c_1[0], c_1[1], c='b', marker='x') # 显示micd分类器计算的样本中心点
plt.scatter(c_2[0], c_2[1], c='b', marker='x')
plt.colorbar() # 显示散点图的颜色条
plt.grid(True) # 显示网格线
plt.axis('equal') # 横纵坐标间隔大小相同
plt.axline(c_1, c_2, color='c', linestyle="--", label="connected line")
plt.axline(center_3, slope=k2, color='r', label="decision line")
if i == j:
plt.legend() # 对角线上的子图显示出图例
plt.xlabel("feature " + str(i))
plt.ylabel("feature " + str(j))
plt.tight_layout() # 自动调整子图大小,减少相互遮挡的问题
plt.show()
# 计算两点连线,返回斜率和纵截距(假设是二维平面上的点,并且用列表表示)
def calculate_connected_line(point_1, point_2):
if len(point_1) != 2 or len(point_2) != 2:
return None
k = (point_1[1] - point_2[1]) / (point_1[0] - point_2[0])
b = (point_1[0] * point_2[1] - point_2[0] * point_1[1]) / (point_1[0] - point_2[0])
return k, b
# 计算两点中垂线,返回斜率和纵截距(假设是二维平面上的点,并且用列表表示)
def calculate_vertical_line(point_1, point_2):
if len(point_1) != 2 or len(point_2) != 2:
return None
k = -(point_1[0] - point_2[0]) / (point_1[1] - point_2[1])
b = (point_1[1] + point_2[1] + (point_1[0] + point_2[0]) * (point_1[0] - point_2[0]) / (
point_1[1] - point_2[1])) / 2
return k, b
# 去除某个类别的样本,返回两个numpy数组
def remove_from_sample(feature, label, _class_):
new_feature = []
new_label = []
for index in range(len(label)):
if label[index] != _class_:
new_feature.append(feature[index])
new_label.append(label[index])
return np.asarray(new_feature), np.asarray(new_label)
if __name__ == '__main__':
iris = datasets.load_iris()
iris_x = iris.data
iris_y = iris.target
micd = MICDClassifier() # 创建MICD分类器
print(np.cov(micd.whitening(iris_x).T)) # 显示白化后的样本协方差矩阵
# 显示白化前后的散点图
# visualization_2d(iris_x, iris_y, 4, 4)
# visualization_2d(np.asarray(iris_x_whitening).T, iris_y, 4, 4)
# 去除线性可分的类(0类)
iris_x_nonlinear, iris_y_nonlinear = remove_from_sample(iris_x, iris_y, 0)
# 去除线性不可分类(1类)
iris_x_linear, iris_y_linear = remove_from_sample(iris_x, iris_y, 1)
# visualization_2d(iris_x_nonlinear, iris_y_nonlinear, 4, 4) # 显示4个特征两两对比的散点图(包括自己比自己)
# x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris_x_linear, iris_y_linear, test_size=0.3) # 使用线性可分的两类
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris_x_nonlinear, iris_y_nonlinear, test_size=0.3) # 使用线性不可分的两类
micd.train(x_train, y_train) # 训练
print("========== center points of this two classes =========
", micd.get_center_dict()
, "
======================================================")
print("========== covariance matrix of this two classes =========
", micd.get_cov_dict()
, "
======================================================")
# print(np.asarray(dict_values_to_list(micd.predict(x_test)))) # 用numpy数组格式显示预测结果
# print(y_test)
performance = micd.performance(x_test, y_test, 1) # 当以1类为阳性时,计算micd分类器的性能指标
print(performance)
# 展示每个特征两两对比图,显示决策线
show_decision_line(x_test, y_test, micd, class_1=1, class_2=2, n=4)
- 在鸢尾花数据集上
-
去除线性可分的类(1类),结果如下:
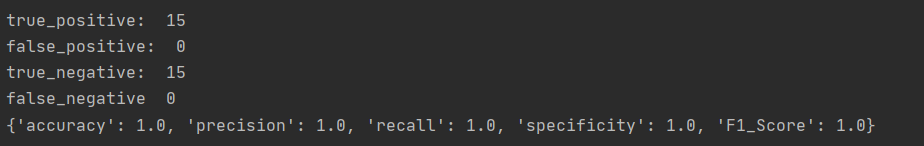
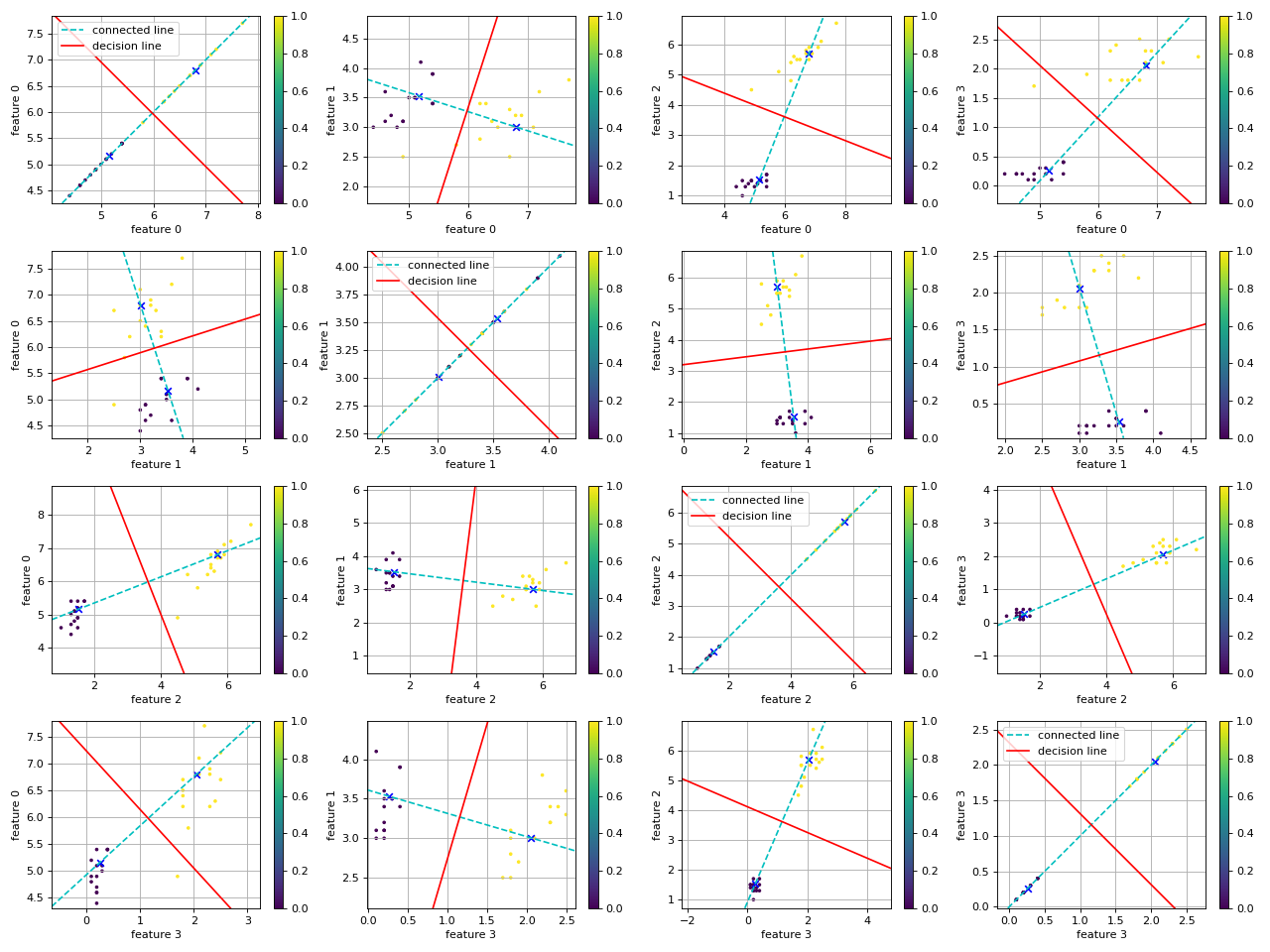
-
去除线性不可分的类(0类),结果如下:
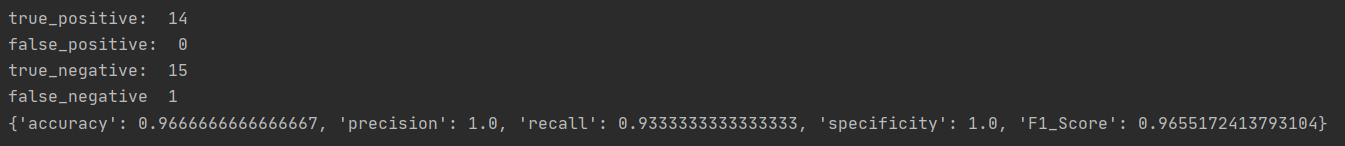
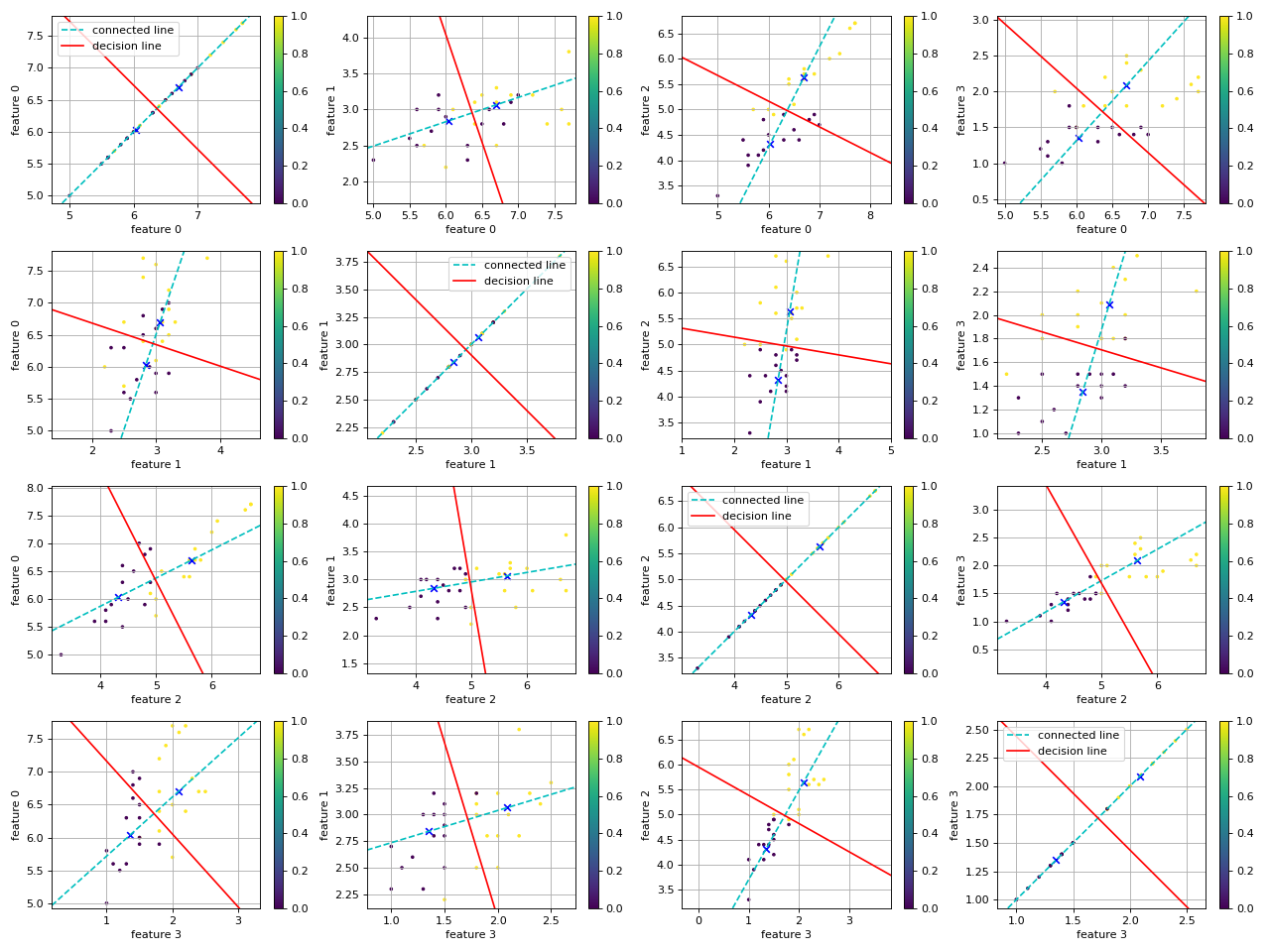
-