简单数据交换格式
CSV:
一般用 open() 函数和字符串拆分 split() 方法,但python有内置的csv模块
读:


import csv with open(r"C:UserJeryDesktop测试.csv", 'r', encoding='utf-8')as rf: r = csv.reader(rf, dialect=csv.excel) for row in r: print("|".join(row))
写:
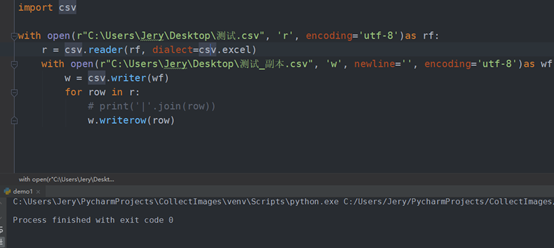
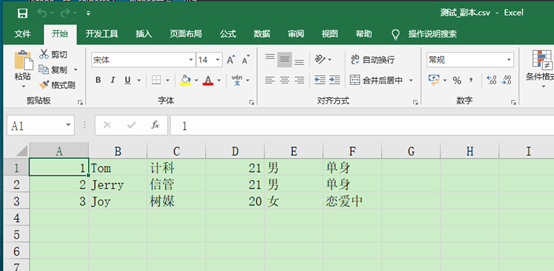
import csv with open(r"C:UserJeryDesktop测试.csv", 'r', encoding='utf-8')as rf: r = csv.reader(rf, dialect=csv.excel) with open(r"C:UserJeryDesktop测试_副本.csv", 'w', encoding='utf-8')as wf: w = csv.writer(wf) for row in r: # print("|".join(row)) w.writerow(row)
参数newline设置为空字符,就是在写入一行数据时不再加换行符,默认writer写入数据是会加换行符。
XML
XML主要由标签构成,主要分为:
声明:如:<?xml version=”1.0” encoding=”UTF-8”?>
根元素:根元素只有一个
子元素:若为空,写法可以为<node/>
属性:<node id=”1”>
命名空间:<node xmlns:***=”***”>
限定名:特定元素或属性,如<node:body>
解析:SAX解析和DOM解析:
SAX基于事件驱动,遇到文档标签就会触发相应事件,只能读文档,解析速度快。
DOM基于文档对象,将文档作为树状结构分析,会获取节点内容及属性,一次性将文档读入内存,能够修改文档。
eg:

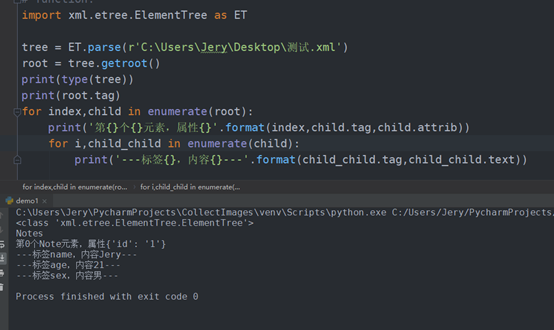
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET tree = ET.parse(r'C:UsersJeryDesktop测试.xml') root = tree.getroot() print(type(tree)) print(root.tag) for index,child in enumerate(root): print('第{}个{}元素,属性{}'.format(index,child.tag,child.attrib)) for i,child_child in enumerate(child): print('---标签{},内容{}---'.format(child_child.tag,child_child))
XPath:
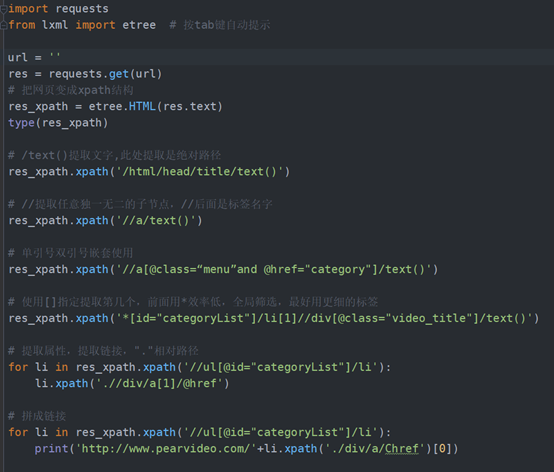
import requests from lxml import etree # 按tab键自动提示 url = '' res = requests.get(url) # 把网页变成xpath结构 res_xpath = etree.HTML(res.text) type(res_xpath) # /text()提取文字,此处提取是绝对路径 res_xpath.xpath('/html/head/title/text()') # //提取任意独一无二的子节点,//后面是标签名字 res_xpath.xpath('//a/text()') # 单引号双引号嵌套使用 res_xpath.xpath('//a[@class=“menu”and @href="category"]/text()') # 使用[]指定提取第几个,前面用*效率低,全局筛选,最好用更细的标签 res_xpath.xpath('*[id="categoryList"]/li[1]//div[@class="video_title"]/text()') # 提取属性,提取链接,"."相对路径 for li in res_xpath.xpath('//ul[@id="categoryList"]/li'): li.xpath('.//div/a[1]/@href') # 拼成链接 for li in res_xpath.xpath('//ul[@id="categoryList"]/li'): print('http://www.pearvideo.com/'+li.xpath('./div/a/Chref')[0])
JSON:
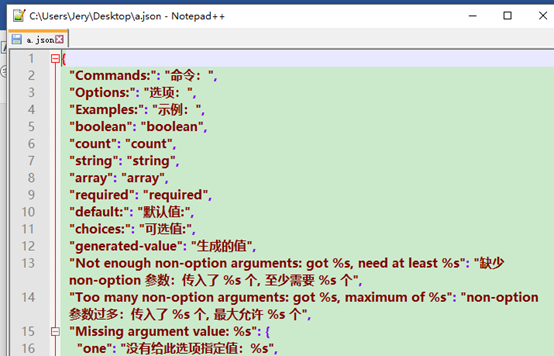
Json文档结构:
对象:名称:值 对集合——对应python字典
数组:一连串元素集合——对应python列表/元组
解码:
loads()将JSON字符串进行解码,返回python数据
load()读取文件或流,对JSON数据进行解码,返回python数据
eg:
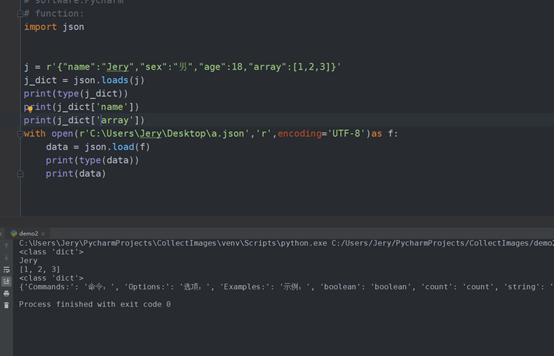
import json j = r'{"name":"Jery","sex":"男","age":18,"array":[1,2,3]}' j_dict = json.loads(j) print(type(j_dict)) print(j_dict['name']) print(j_dict['array']) with open(r'C:UsersJeryDesktopa.json','r',encoding='UTF-8')as f: data = json.load(f) print(type(data)) print(data)
配置文件ini
Windows系统配置文件ini:
结构:
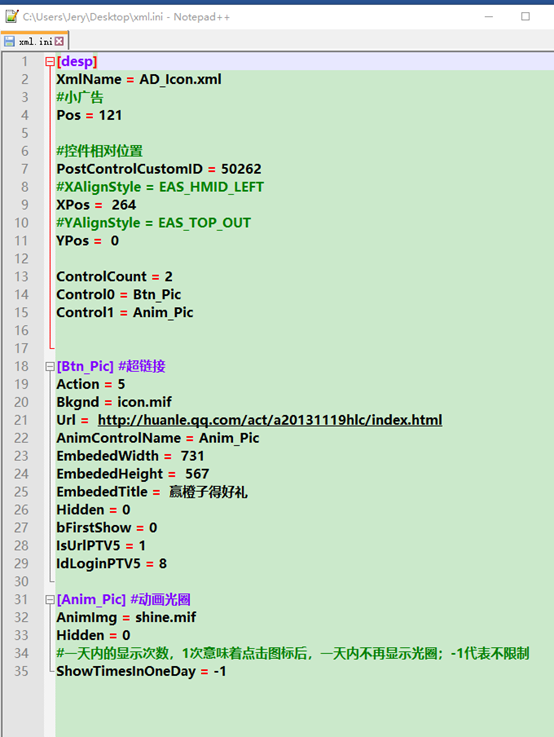
节:包括若干个配置项。如:[Startup]
配置项:由键值对构成,默认等号隔开。如:RequireOS = Windows10
注释:单独占一行,默认用分号隔开。如:;Startup节
配置文件的读取:eg
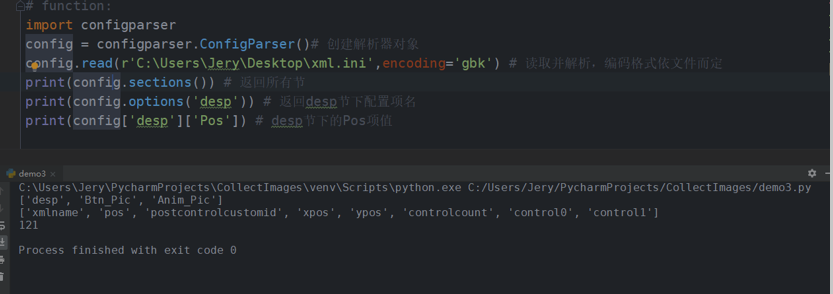
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser() # 创建解析器对象 config.read(r'C:UsersJeryDesktopxml.ini', encoding='gbk') # 读取并解析,编码格式依文件而定 print(config.sections()) # 返回所有节 print(config.options('desp')) # 返回desp节下配置项名 print(config['desp']['Pos']) # desp节下的Pos项值
配置文件的写入:
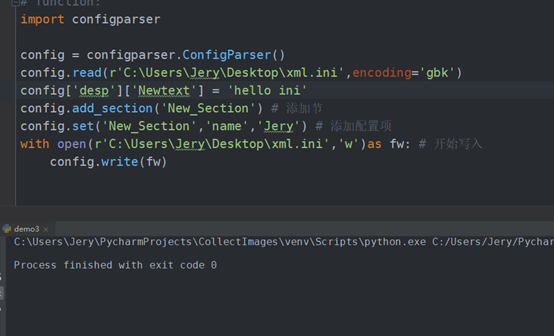

import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser() config.read(r'C:UsersJeryDesktopxml.ini',encoding='gbk') config['desp']['Newtext'] = 'hello ini' config.add_section('New_Section') # 添加节 config.set('New_Section','name','Jery') # 添加配置项 with open(r'C:UsersJeryDesktopxml.ini','w')as fw: # 开始写入 config.write(fw)