基本数据类型的包装类
基本数据类型如int、float、double、boolean、char等是不具备对象的特征,比如:不能调用方法,功能比较简单。为了让基本数据类型具有对象的特征,Java为每个基本数据类型都提供了一个包装类,这样就具备了对象的特征。
将字符串转为基本类型的方法
通用格式:包装类.parseXxxx(String str)
int a=Integer.parseInt("123456");
System.out.println(a+1);

将基本类型转换为字符串
1、String a=基本数据类型+"";
2、调用String的valueOf(基本数据类型)方法
3、调用包装类中的toString(基本数据类型)方法
int a = 2; String b = a+""; System.out.println(b + 1); String c = String.valueOf(a); System.out.println(c + 1); String d = Integer.toString(a); System.out.println(d + 1);


基本数据类型和对应的包装类对象之间的转换
基本数值------->包装类的方式 装箱操作
1、构造方法(基本数据类型)

2、包装类.valueOf(基本数据类型)方法

Integer i = new Integer(3); //装箱操作 手动的
System.out.println(i + 1);
Integer ii = new Integer("3"); // 必须传入数字字符串,才能自动转为int类型的 装箱操作 手动的
System.out.println(ii + 1);
Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf(3); //装箱操作 手动的
Integer ii2 = Integer.valueOf("3"); //装箱操作 手动的
包装类------>基本数据类型 拆箱操作
包装类对象.xxValue(); 返回一个基本数据类型

int a = i.intValue(); //拆箱操作 手动的 System.out.println(a); Integer i = 4; // 自动装箱 基本数据--->包装类 int a = i + 5; // 自动拆箱 包装类---->基本数据 System.out.println(a);
自动装箱与拆箱
基本类型可以使用运算符直接进行计算,但是引用类型不可以。而基本类型包装类作为引用类型的一种却可以计算,
原因在于,Java”偷偷地”自动地进行了对象向基本数据类型的转换。
相对应的,引用数据类型变量的值必须是new出来的内存空间地址值,而我们可以将一个基本类型的值赋值给一个基本类型包装类的引用。
原因同样在于Java又”偷偷地”自动地进行了基本数据类型向对象的转换。
自动拆箱:对象转成基本数值
自动装箱:基本数值转成对象
自动装箱(byte常量池)细节的演示
当数值在byte范围之内时,进行自动装箱,不会新创建对象空间而是使用原来已有的空间。
Integer i1 = new Integer(100); //手动装箱
Integer i2 = new Integer(100);
System.out.println(i1 == i2); //false
System.out.println(i1.equals(i2)); //true
System.out.println("-------------------");
//再byte(-128-127)范围内,你创建新的引用的时候如果值相同会指向同一个地址。
Integer x = 124; //自动装箱
Integer y = 124;
System.out.println(x == y); //true
System.out.println(x.equals(y)); //true
System类
System类不能手动创建对象,因为构造方法被private修饰,阻止外界创建对象。System类中的都是static方法,类名访问即可
常用方法

Math类
Math类是一个工具类,使用的时候直接用类名.方法名就行
常用方法

Arrays类
Arrays类中包括操作数组的一些方法,例如排序、搜索
常用的方法

sort方法,用来对指定数组中的元素进行排序(元素值从小到大进行排序)
toString方法,用来返回指定数组元素内容的字符串形式
binarySearch方法,在指定数组中,查找给定元素值出现的位置。若没有查询到,返回位置为-1。要求该数组必须是个有序的数组。
定义一个方法,接收一个数组,数组中存储10个学生考试分数,该方法要求返回考试分数最低的后三名考试分数。
package com.oracle.demo1;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] score = { 64, 76, 98, 12, 23, 43, 34, 56, 78, 90 };
int[] b = print(score);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));
}
public static int[] print(int[] arr) {
Arrays.sort(arr); // 从小到大进行排序
int[] a = new int[3];
System.arraycopy(arr,0,a,0,3);// 将分数最低的前三位复制到新数组a中
return a;
}
}
大数据运算
BigInteger
在Java中把超过long型的整数不称为整数,它们被封装为BigInteger对象。在BigInteger类中,实现四则运算都是靠方法去实现的,而不是采用运算符。
BigInteger的构造方法

四则运算代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
//大数据封装为BigInteger对象
BigInteger big1 = new BigInteger("12345678909876543210");
BigInteger big2 = new BigInteger("98765432101234567890");
//add实现加法运算
BigInteger bigAdd = big1.add(big2);
//subtract实现减法运算
BigInteger bigSub = big1.subtract(big2);
//multiply实现乘法运算
BigInteger bigMul = big1.multiply(big2);
//divide实现除法运算
BigInteger bigDiv = big2.divide(big1);
}
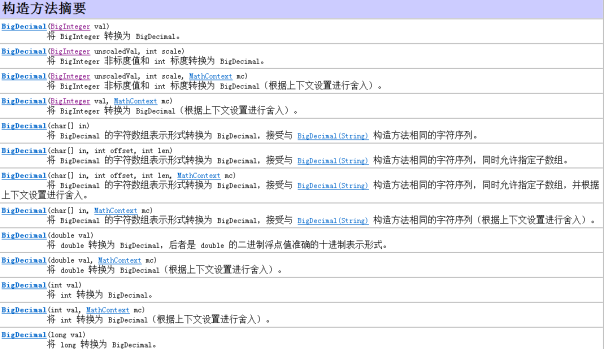
BigDecimal类
float和double类型做运算时,很容易造成精度的损失。此时就用到BigDecimal类来计算提高计算精度
构造方法

public static void main(String[] args) {
//大数据封装为BigDecimal对象
BigDecimal big1 = new BigDecimal("0.09");
BigDecimal big2 = new BigDecimal("0.01");
//add实现加法运算
BigDecimal bigAdd = big1.add(big2);
BigDecimal big3 = new BigDecimal("1.0");
BigDecimal big4 = new BigDecimal("0.32");
//subtract实现减法运算
BigDecimal bigSub = big3.subtract(big4);
BigDecimal big5 = new BigDecimal("1.105");
BigDecimal big6 = new BigDecimal("100");
//multiply实现乘法运算
BigDecimal bigMul = big5.multiply(big6);
对于浮点数据的除法运算,和整数不同,可能出现无限不循环小数,因此需要对所需要的位数进行保留和选择舍入模式

