思维导图
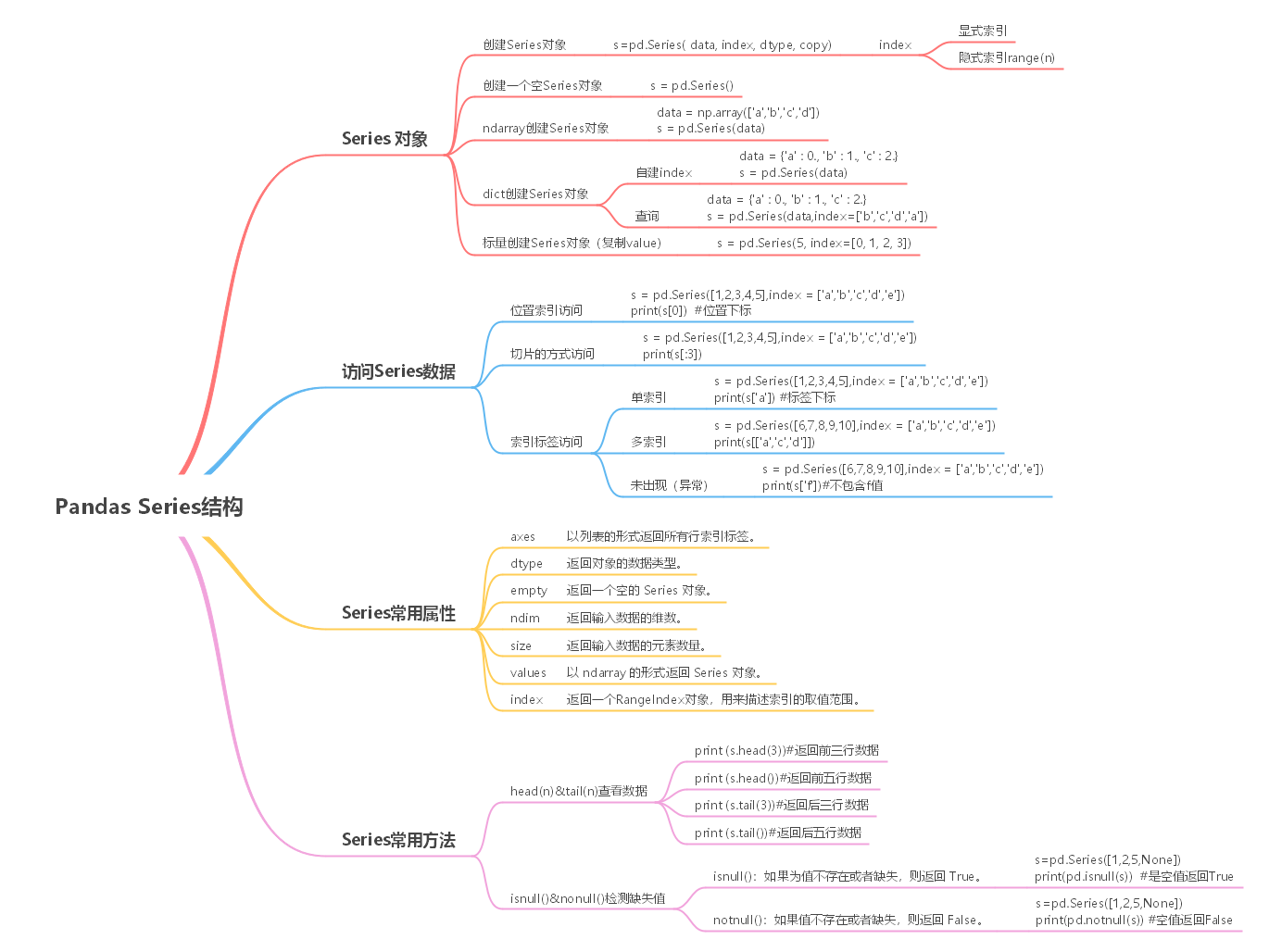
1 什么是Series结构?
Series 结构,也称 Series 序列,是 Pandas 常用的数据结构之一,它是一种类似于一维数组的结构,由一组数据值(value)和一组标签组成,其中标签与数据值之间是一一对应的关系。
Series 可以保存任何数据类型,比如整数、字符串、浮点数、Python 对象等,它的标签默认为整数,从 0 开始依次递增。Series 的结构图,如下所示:

通过标签我们可以更加直观地查看数据所在的索引位置。
2 Series 对象
2.1 创建Series对象
Pandas 使用 Series() 函数来创建 Series 对象,通过这个对象可以调用相应的方法和属性,从而达到处理数据的目的:
import pandas as pd
s=pd.Series( data, index, dtype, copy)
参数说明如下所示:
| 参数名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| data | 输入的数据,可以是列表、常量、ndarray 数组等。 |
| index | 索引值必须是惟一的,如果没有传递索引,则默认为 np.arrange(n)。 |
| dtype | dtype表示数据类型,如果没有提供,则会自动判断得出。 |
| copy | 表示对 data 进行拷贝,默认为 False。 |
我们也可以使用数组、字典、标量值或者 Python 对象来创建 Series 对象。下面展示了创建 Series 对象的不同方法:
2.1.1 创建一个空Series对象
使用以下方法可以创建一个空的 Series 对象,如下所示:
import pandas as pd
#输出数据为空
s = pd.Series()
print(s)
输出结果如下:
Series([], dtype: float64)
2.1.2 ndarray创建Series对象
ndarray 是 NumPy 中的数组类型,当 data 是 ndarry 时,传递的索引必须具有与数组相同的长度。假如没有给 index 参数传参,在默认情况下,索引值将使用是 range(n) 生成,其中 n 代表数组长度,如下所示:
[0,1,2,3…. range(len(array))-1]
使用默认索引,创建 Series 序列对象:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = np.array(['a','b','c','d'])
s = pd.Series(data)
print (s)
输出结果如下:
0 a
1 b
2 c
3 d
dtype: object
上述示例中没有传递任何索引,所以索引默认从 0 开始分配 ,其索引范围为 0 到 len(data)-1,即 0 到 3。这种设置方式被称为“隐式索引”。
除了上述方法外,你也可以使用“显式索引”的方法定义索引标签,示例如下:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = np.array(['a','b','c','d'])
#自定义索引标签(即显示索引)
s = pd.Series(data,index=[100,101,102,103])
print(s)
输出结果:
100 a
101 b
102 c
103 d
dtype: object
2.1.3 dict创建Series对象
您可以把 dict 作为输入数据。如果没有传入索引时会按照字典的键来构造索引;反之,当传递了索引时需要将索引标签与字典中的值一一对应。
下面两组示例分别对上述两种情况做了演示。
示例1,没有传递索引时:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = {'a' : 0., 'b' : 1., 'c' : 2.}
s = pd.Series(data)
print(s)
输出结果:
a 0.0
b 1.0
c 2.0
dtype: float64
示例 2,为index参数传递索引时:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = {'a' : 0., 'b' : 1., 'c' : 2.}
s = pd.Series(data,index=['b','c','d','a'])
print(s)
输出结果:
b 1.0
c 2.0
d NaN
a 0.0
dtype: float64
当传递的索引值无法找到与其对应的值时,使用 NaN(非数字)填充。
2.1.4 标量创建Series对象
如果 data 是标量值,则必须提供索引,示例如下:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(5, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
print(s)
输出如下:
0 5
1 5
2 5
3 5
dtype: int64
标量值按照 index 的数量进行重复,并与其一一对应。
3 访问Series数据
3.1 位置索引访问
这种访问方式与 ndarray 和 list 相同,使用元素自身的下标进行访问。我们知道数组的索引计数从 0 开始,这表示第一个元素存储在第 0 个索引位置上,以此类推,就可以获得 Series 序列中的每个元素。下面看一组简单的示例:
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5],index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
print(s[0]) #位置下标
print(s['a']) #标签下标
输出结果:
1
1
通过切片的方式访问 Series 序列中的数据,示例如下:
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5],index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
print(s[:3])
输出结果:
a 1
b 2
c 3
dtype: int64
如果想要获取最后三个元素,也可以使用下面的方式:
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5],index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
print(s[-3:])
输出结果:
c 3
d 4
e 5
dtype: int64
3.2 索引标签访问
Series 类似于固定大小的 dict,把 index 中的索引标签当做 key,而把 Series 序列中的元素值当做 value,然后通过 index 索引标签来访问或者修改元素值。
示例1,使用索标签访问单个元素值:
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([6,7,8,9,10],index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
print(s['a'])
输出结果:
6
示例 2,使用索引标签访问多个元素值
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([6,7,8,9,10],index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
print(s[['a','c','d']])
输出结果:
a 6
c 8
d 9
dtype: int64
示例3,如果使用了 index 中不包含的标签,则会触发异常:
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([6,7,8,9,10],index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
#不包含f值
print(s['f'])
输出结果:
......
KeyError: 'f'
4 Series常用属性
下面我们介绍 Series 的常用属性和方法。在下表列出了 Series 对象的常用属性。
| 名称 | 属性 |
|---|---|
| axes | 以列表的形式返回所有行索引标签。 |
| dtype | 返回对象的数据类型。 |
| empty | 返回一个空的 Series 对象。 |
| ndim | 返回输入数据的维数。 |
| size | 返回输入数据的元素数量。 |
| values | 以 ndarray 的形式返回 Series 对象。 |
| index | 返回一个RangeIndex对象,用来描述索引的取值范围。 |
现在创建一个 Series 对象,并演示如何使用上述表格中的属性。如下所示:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5))
print(s)
输出结果:
0 0.898097
1 0.730210
2 2.307401
3 -1.723065
4 0.346728
dtype: float64
上述示例的行索引标签是 [0,1,2,3,4]。
4.1 axes
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5))
print ("The axes are:")
print(s.axes)
输出结果
The axes are:
[RangeIndex(start=0, stop=5, step=1)]
4.2 dtype
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5))
print ("The dtype is:")
print(s.dtype)
输出结果:
The dtype is:
float64
4.3 empty
返回一个布尔值,用于判断数据对象是否为空。示例如下:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5))
print("是否为空对象?")
print (s.empty)
输出结果:
是否为空对象?
False
4.4 ndim
查看序列的维数。根据定义,Series 是一维数据结构,因此它始终返回 1。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5))
print (s)
print (s.ndim)
输出结果:
0 0.311485
1 1.748860
2 -0.022721
3 -0.129223
4 -0.489824
dtype: float64
1
4.5 size
返回 Series 对象的大小(长度)。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(3))
print (s)
#series的长度大小
print(s.size)
输出结果:
0 -1.866261
1 -0.636726
2 0.586037
dtype: float64
3
4.6 values
以数组的形式返回 Series 对象中的数据。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(6))
print(s)
print("输出series中数据")
print(s.values)
输出结果:
0 -0.502100
1 0.696194
2 -0.982063
3 0.416430
4 -1.384514
5 0.444303
dtype: float64
输出series中数据
[-0.50210028 0.69619407 -0.98206327 0.41642976 -1.38451433 0.44430257]
4.7 index
该属性用来查看 Series 中索引的取值范围。示例如下:
#显示索引
import pandas as pd
s=pd.Series([1,2,5,8],index=['a','b','c','d'])
print(s.index)
#隐式索引
s1=pd.Series([1,2,5,8])
print(s1.index)
输出结果:
隐式索引:
Index(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], dtype='object')
显示索引:
RangeIndex(start=0, stop=4, step=1)
5 Series常用方法
5.1 head()&tail()查看数据
如果想要查看 Series 的某一部分数据,可以使用 head() 或者 tail() 方法。其中 head() 返回前 n 行数据,默认显示前 5 行数据。示例如下:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5))
print ("The original series is:")
print (s)
#返回前三行数据
print (s.head(3))
输出结果:
原系列输出结果:
0 1.249679
1 0.636487
2 -0.987621
3 0.999613
4 1.607751
head(3)输出:
dtype: float64
0 1.249679
1 0.636487
2 -0.987621
dtype: float64
tail() 返回的是后 n 行数据,默认为后 5 行。示例如下:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(4))
#原series
print(s)
#输出后两行数据
print (s.tail(2))
输出结果:
原Series输出:
0 0.053340
1 2.165836
2 -0.719175
3 -0.035178
输出后两行数据:
dtype: float64
2 -0.719175
3 -0.035178
dtype: float64
5.2 isnull()&nonull()检测缺失值
isnull() 和 nonull() 用于检测 Series 中的缺失值。所谓缺失值,顾名思义就是值不存在、丢失、缺少。
- isnull():如果为值不存在或者缺失,则返回 True。
- notnull():如果值不存在或者缺失,则返回 False。
其实不难理解,在实际的数据分析任物中,数据的收集往往要经历一个繁琐的过程。在这个过程中难免会因为一些不可抗力,或者人为因素导致数据丢失的现象。这时,我们可以使用相应的方法对缺失值进行处理,比如均值插值、数据补齐等方法。上述两个方法就是帮助我们检测是否存在缺失值。示例如下:
import pandas as pd
#None代表缺失数据
s=pd.Series([1,2,5,None])
print(pd.isnull(s)) #是空值返回True
print(pd.notnull(s)) #空值返回False
输出结果:
0 False
1 False
2 False
3 True
dtype: bool
notnull():
0 True
1 True
2 True
3 False
dtype: bool