CUDA并行算法系列之FFT快速卷积
卷积定义
在维基百科上,卷积定义为:
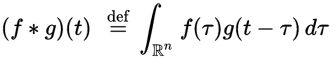
离散卷积定义为:
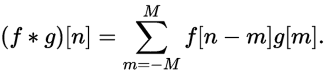
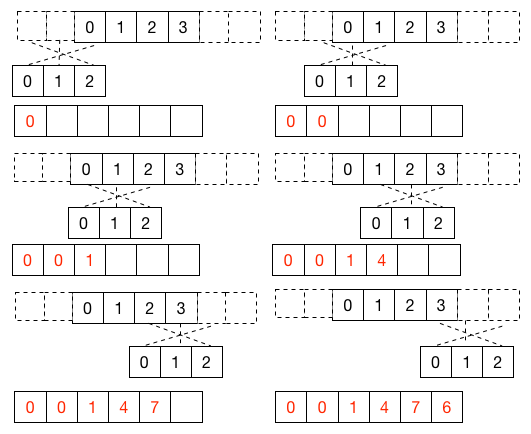
[ 0, 1, 2, 3]和[0, 1, 2]的卷积例子如下图所示:
Python实现(直接卷积)
根据离散卷积的定义,用Python实现:
def conv(a, b):
N = len(a)
M = len(b)
YN = N + M - 1
y = [0.0 for i in range(YN)]
for n in range(YN):
for m in range(M):
if 0 <= n - m and n - m < N:
y[n] += a[n - m] * b[m]
return y
把数组b逆序,则可以不交叉计算卷积(使用numpy的array[::-1]即可实现逆序):
import numpy as np
def conv2(a, b):
N = len(a)
M = len(b)
YN = N + M - 1
y = [0.0 for i in range(YN)]
b = np.array(b)[::-1] # 逆序
for n in range(YN):
for m in range(M):
k = n - M + m + 1;
if 0 <= k and k < N:
y[n] += a[k] * b[m]
return y
测试
可以利用numpy.convolve来检验计算结果的正确性:
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = [ 0, 1, 2, 3 ]
b = [ 0, 1, 2 ]
print(conv2(a, b))
print(np.convolve(a, b))
完整代码可以在Github上找到。
利用FFT快速卷积
时域的卷积和频域的乘法是等价的,同时时域的乘法和频域的卷积也是等价的。基于这个这个前提,可以把待卷积的数组进行FFT变换,在频域做乘法,然后再进行IFFT变换即可得到卷积结果。算法流程描述如下:
- 设
N=len(a),M = len(b), 其中a,b为待卷积的数组,将长度增加到L>= N+M-1, L=2^n, n 属于 Z,即 L=2(log_2(N + M - 1) +1)。 - 增加
a,b的长度到L,后面补零。 - 分别计算afft = fft(a),bfft=fft(b)。
- abfft = afft × bfft。
- 用IFFT计算
abaft的FFT逆变换,取前(N + M - 1)个值即为卷积结果。
FFT快速卷积Python代码如下:
def convfft(a, b):
N = len(a)
M = len(b)
YN = N + M - 1
FFT_N = 2 ** (int(np.log2(YN)) + 1)
afft = np.fft.fft(a, FFT_N)
bfft = np.fft.fft(b, FFT_N)
abfft = afft * bfft
y = np.fft.ifft(abfft).real[:YN]
return y
测试
对比直接卷积、FFT卷积、numpy的卷积结果:
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = [ 0, 1, 2, 3 ]
b = [ 0, 1, 2 ]
print(conv2(a, b))
print(convfft(a, b))
print(np.convolve(a, b))
可以看到,3个版本的计算结果是一致的。完整代码可以在Github上找到。
性能分析
复杂度分析
直接卷积的时间复杂度为o(MN),即o(n^2)。
FFT的时间复杂度为o(nlogn),FFT卷积复杂度为3次FFT+L次乘法,3o(nlogn)+o(n)=o(nlogn),及o(nlogn)。
在实际应用中,卷积核(b)被提前计算,则只需2次FFT变换。
运行测试
分别测试3个版本在数组长度为n * 1000 + 10, n=0,1,…,9的运行时间,并绘制运行时间曲线,编写如下测试代码:
def time_test():
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def run(func, a, b):
n = 1
start = time.clock()
for j in range(n):
func(a, b)
end = time.clock()
run_time = end - start
return run_time / n
n_list = []
t1_list = []
t2_list = []
t3_list = []
for i in range(10):
count = i * 1000 + 10
print(count)
a = np.ones(count)
b = np.ones(count)
t1 = run(conv, a, b) # 直接卷积
t2 = run(conv2, a, b)
t3 = run(convfft, a, b) # FFT卷积
n_list.append(count)
t1_list.append(t1)
t2_list.append(t2)
t3_list.append(t3)
# plot
plt.plot(n_list, t1_list, label='conv')
plt.plot(n_list, t2_list, label='conv2')
plt.plot(n_list, t3_list, label='convfft')
plt.legend()
plt.title(u"convolve times")
plt.ylabel(u"run times(ms/point)")
plt.xlabel(u"length")
plt.show()
运行得到的曲线图如下:
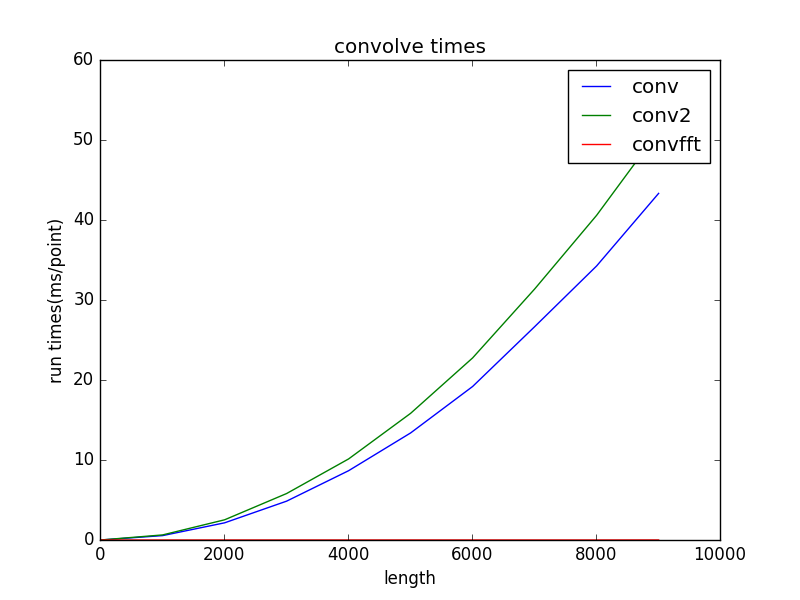
从图中可知,FFT卷积比直接卷积速度要快很多。完整代码可以在Github上找到。
CUDA实现
直接卷积
只需要把外层循环并行化就可以在CUDA上实现卷积,代码如下:
// 直接计算卷积
__global__ void conv_kernel(const float *ina, const float *inb, float *out, size_t len_a, size_t len_b, size_t len_out)
{
const int tid = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (tid >= len_out)
{
return;
}
float sum = 0.0f;
for (int m = 0; m < len_b; ++m)
{
int k = tid - m;
if (0 <= k && k < len_a)
{
sum += ina[k] * inb[m];
}
}
out[tid] = sum;
}
当然,可以使用共享内存和常量内存(卷积核存入常量内存)进行优化,优化的代码请查看Github。
cuFFT卷积
使用CUDA的cuFFT可以方便的进行快速傅里叶变换,cuFFT的详细说明可以查看NVIDIA的官方文档。本文主要使用到一下两个函数:
- cufftExecR2C:实数到复数的快速傅里叶变换(FFT)
- cufftExecC2R:复数到实数的快速傅里叶逆变换(IFFT)
基于cuFFT的实数到复数的快速傅里叶变换代码如下:
void fft(float *in, Complex *out, size_t size)
{
cufftHandle plan;
cufftPlan1d(&plan, size, CUFFT_R2C, 1);
cufftExecR2C(plan, in, out);
cufftDestroy(plan);
}
基于cuFFT的复数到实数的快速傅里叶逆变换代码如下:
void ifft(Complex *in, float *out, size_t size)
{
cufftHandle plan;
cufftPlan1d(&plan, size, CUFFT_C2R, 1);
cufftExecC2R(plan, in, out);
cufftDestroy(plan);
}
其中Complex被定义为float2,typedef float2 Complex;
有了FFT,那么基于CUDA的卷积代码可如下编写:
void convfft( float *ina, float *inb, float *out, size_t len_out, size_t L, size_t numThreads)
{
thrust::device_vector<Complex> d_a_fft(L);
thrust::device_vector<Complex> d_b_fft(L);
thrust::device_vector<Complex> d_c_fft(L);
Complex *raw_point_a_fft = thrust::raw_pointer_cast(&d_a_fft[0]);
Complex *raw_point_b_fft = thrust::raw_pointer_cast(&d_b_fft[0]);
Complex *raw_point_c_fft = thrust::raw_pointer_cast(&d_c_fft[0]);
fft(ina, raw_point_a_fft, L);
fft(inb, raw_point_b_fft, L);
// 计算 d_c_fft = d_a_fft * d_b_fft;
ifft(raw_point_c_fft, out, L);
}
最后只剩下乘法运算了,可以自己编写一个复数乘法的内核,也可以使用thrush的transform。使用thrush实现复数乘法,首先定义一个复数乘法操作函数(可以参考Transformations):
struct complex_multiplies_functor
{
const int N;
complex_multiplies_functor(int _n) : N(_n) {}
__host__ __device__ Complex operator()(const Complex &a, const Complex &b) const
{
Complex c;
c.x = (a.x * b.x - a.y * b.y) / N;
c.y = (a.x * b.y + a.y * b.x) / N;
return c;
}
};
然后使用thrush::transform即可完成计算:
// 计算 d_c_fft = d_a_fft * d_b_fft;
thrust::transform(d_a_fft.begin(), d_a_fft.end(), d_b_fft.begin(), d_c_fft.begin(), complex_multiplies_functor(L));
结语
本文首先简要介绍了卷积运算,然后使用Python实现了卷积运行的代码,接着讨论了基于FFT的快速卷积算法,并使用Python实现了FFT卷积,接着对直接卷积和基于FFT的快速卷积算法的性能进行了分析,从实验结果可以看出,FFT卷积相比直接卷积具有更快的运行速度。最后,基于CUDA实现了直接卷积算法,并且使用cuFFT和thrush在CUDA平台实现了基于FFT的快速卷积算法。
本文完整代码可在Github上下载。
参考文献
- 维基百科.卷积.https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh/卷积
- 百度文库.利用FFT计算卷积.http://wenku.baidu.com/view/5606967101f69e3143329407.html
- 用Python做科学计算.FFT卷积的速度比较.http://old.sebug.net/paper/books/scipydoc/example_spectrum_fft_convolve_timeit.html
- NVIDIA.cuFFT.https://developer.nvidia.com/cufft
- thrust. https://github.com/thrust/thrust/tree/master/thrust