一:

示例代码:
package test;
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{
public Child()
{
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Child c = new Child();
}
}
§§测试截图:

§§如果在子类的构造方法在使用之前没有调用父类的构造方法会出现继承错误
把supper语句加进去后 测试截图:
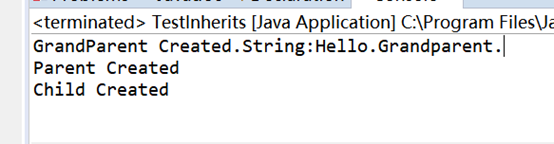
§§且supper语句必须放在前面,否则会报错。
二:

1. 子类拥有父的成员变量和成员方法,如果不调用,则从父类继承而来的成员变量和成员方法得不到正确的初始化,父类的属性不存在,子类的属性也不会存在
2. 不能反过来,子类继承于父类,父类不能继承子类。
三:

代码示例:
public class ExplorationJDKSource {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new A());
}
}
class A{}
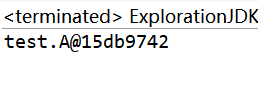
结果如上,分析:
main方法实际上调用的是:public void println(Object x),这一方法内部调用了String类的valueOf方法。valueOf方法内部又调用Object.toString方法:
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() +"@" +
Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
hashCode方法是本地方法,由JVM设计者实现:public native int hashCode();
四:

结果分析:
Fruit类覆盖了Object类的toString方法。f不再是字符串String的对象而是Fruit类的对象
五:
在子类中,若要调用父类中被覆盖的方法,可以使用super关键字调用父类的函数。
代码示例:
package test;
class FatherClass {
public int value;
public void f() {
value=100;
System.out.println("父类的value属性值="+value);
}
}
class ChildClass extends FatherClass {
public int value;
public void f() {
super.f();//使用super作为父类对象的引用对象来调用父类对象里面的f()方法
value=200;//这个value是子类自己定义的那个valu,不是从父类继承下来的那个value
System.out.println("子类的value属性值="+value);
System.out.println(value);//打印出来的是子类自定义的那个value的值,这个值是200
System.out.println(super.value);
}
}
public class tezt{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChildClass cc = new ChildClass();
cc.f();
}
}
子类中建立与父类相同的方法,supper实现子类中父类被覆盖的方法,supper可以引用方法,也可以引用变量
六

package test;
public class TestInstanceof
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//声明hello时使用Object类,则hello的编译类型是Object,Object是所有类的父类
//但hello变量的实际类型是String
Object hello = "Hello";
//String是Object类的子类,所以返回true。
System.out.println("字符串是否是Object类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Object));
//返回true。
System.out.println("字符串是否是String类的实例:" + (hello instanceof String));
//返回false。
System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (hello instanceof Math));
//String实现了Comparable接口,所以返回true。
System.out.println("字符串是否是Comparable接口的实例:" + (hello instanceof Comparable));
String a = "Hello";
//String类既不是Math类,也不是Math类的父类,所以下面代码编译无法通过
//System.out.println("字符串是否是Math类的实例:" + (a instanceof Math));
}
}
测试截图:
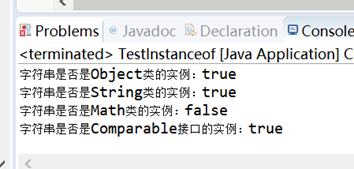
七:


package test;
class Mammal{}
class Dog extends Mammal {}
class Cat extends Mammal{}
public class TestCast
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Mammal m;
Dog d=new Dog();
Cat c=new Cat();
m=d;
//d=m;
d=(Dog)m;
//d=c;
//c=(Cat)m;
}
}
“//”去掉会报错,分析:1. 子类对象可以直接赋值给基类变量2. 基类对象要赋值给子类对象必须要进行类型转换 3. 子类对象变量=(子类名)基类对象名。
八:

代码示例:
package text;
public class ParentChildTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
parent.printValue();
}
}
class Parent{
public int myValue=100;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public int myValue=200;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
测试截图:
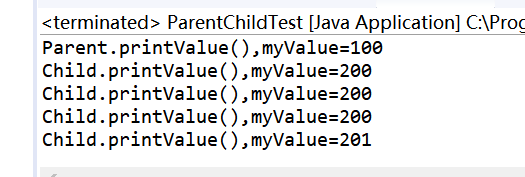
结果分析:
1. 子类对象赋值给基类对象,基类对象调用子类对象的方法
2. 对基类对象进行强制类型转换同样会使基类对象调用子类对象的方法,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。